Samsung 2012 Annual Report Download - page 36
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 36 of the 2012 Samsung annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Deferred income tax assets and liabilities are offset when there is a legally
enforceable right to oset current tax assets against current tax liabilities and when
the deferred income taxes assets and liabilities relate to income taxes levied by the
same taxation authority on either the taxable entity or different taxable entities
where there is an intention to settle the balances on a net basis.
2.21 Derivative Instruments
All derivative instruments are accounted for at fair value with the resulting valuation
gain or loss recorded as an asset or liability. If the derivative instrument is not
designated as a hedging instrument, the gain or loss is recognized in the statement
of income in the period of change.
Fair value hedge accounting is applied to a derivative instrument with the purpose
of hedging the exposure to changes in the fair value of an asset or a liability or
a firm commitment (hedged item) that is attributable to a particular risk. Hedge
accounting is applied when the derivative instrument is designated as a hedging
instrument and the hedge accounting criteria have been met. The gain or loss, both
on the hedging derivative instrument and on the hedged item attributable to the
hedged risk, is reected in the statement of income.
2.22 Dividend Distribution
Dividend distribution to SEC’s shareholders is recognized as a liability in the
Company’s nancial statements in the period in which the dividends are approved.
2.23 Share Capital and Premium
Common shares and preferred shares with no repayment obligations are classied
as equity. When the Company purchases its common shares, the acquisition costs
including direct transaction costs are deducted from equity until the redemption
or reissuance of treasury shares. Consideration received on the subsequent sale or
issue of treasury shares is credited to equity.
2.24 Revenue Recognition
Revenue mainly comprises the fair value of the consideration received or receivable
for the sale of goods in the ordinary course of the Company’s activities. Revenue
is shown net of value-added tax, returns, sales incentives and discounts and after
eliminating intercompany transactions.
The Company recognizes revenue when specic recognition criteria have been met
for each of the Company’s activities as described below. The Company bases its
estimates on historical results, taking into consideration the type of customer, the
type of transaction and the specics of each arrangement.
(A) Sales of goods
Sales of products and merchandise are recognized upon delivery when the
signicant risks and rewards of ownership of goods have transferred to the buyer,
continuing managerial involvement usually associated with ownership and eective
control have ceased, the amount of revenue can be measured reliably, it is probable
that the economic benets associated with the transaction will ow to the Company
and the costs incurred or to be incurred in respect of the transaction can be
to US $1, the exchange rate in eect on December 31, 2012. Such presentation is
not in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and should not be
construed as a representation that the Won amounts shown could be readily
converted, realized or settled in U.S. dollars at this or at any other rate.
2.29 Approval of Financial Statements
These consolidated nancial statements were approved by the Board of Directors
on January 25, 2013.
3. Critical Estimates and Judgments
The Company makes estimates and assumptions concerning the future. The
estimates and assumptions are continuously assessed, considering historical
experience and other factors, including expectations of future events that are
believed to be reasonable under the circumstances. The resulting accounting
estimates will, by denition, seldom equal the related actual results. The estimates
and assumptions that have a signicant risk of causing a material adjustment to the
carrying amounts of assets and liabilities within the next nancial year are addressed
below.
(A) Revenue recognition
The Company uses the percentage-of-completion method in accounting for its
fixed-price contracts to deliver installation services. Use of the percentage-of-
completion method requires the Company to estimate the services performed to
date as a proportion of the total services to be performed. Revenues and earnings
are subject to significant change, effected by early steps in a long-term projects,
change in scope of a project, cost, period, and plans of the customers.
(B) Provision for warranty
The Company recognizes provision for warranty on products sold. The Company
accrues provision for warranty based on the best estimate of amounts necessary
to settle future and existing claims. The amounts are estimated based on historical
data.
(C) Fair value of derivatives and other nancial instruments
The fair value of financial instruments that are not traded in an active market is
determined by using a variety of methods and assumptions that are mainly based
on market conditions existing at the end of each reporting period.
(D) Pension benets
The pension obligations depend on a number of factors that are determined
on an actuarial basis using a number of assumptions. Any changes in these
assumptions will impact the carrying amount of pension obligations. The Company,
in consideration of the interest rates of high-quality corporate bonds, determines
the appropriate discount rate at the end of each year. This is the interest rate that is
used to determine the present value of estimated future cash
outows expected to be required to settle the pension obligations.
The principal actuarial assumptions associated with the dened benet liability are
based on the current market expectations.
(E) Estimated impairment of goodwill
The Company tests at the end of each reporting period whether goodwill has
suffered any impairment in accordance with the accounting policy described
in Note 2.12. The recoverable amounts of cash generating units have been
determined based on value-in-use calculations. These calculations are based on
estimates.
(F) Income taxes
The operating activities of SEC span across various countries in the world; likewise,
income taxes on the taxable income from operating activities are subject to
various tax laws and determinations of each tax authority. There is uncertainty
in determining the eventual tax effects on the taxable income from operating
activities. The Company has recognized current tax and deferred tax at the end
of the scal year based on the best estimation of future taxes payable as a result
of operating activities. However, the resulting deferred income tax assets and
liabilities may not equal the actual future taxes payable and such dierence may
impact on the current tax and deferred income tax assets and liabilities upon the
determination of eventual tax eects.
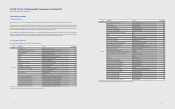
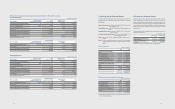
4. Cash and Cash Equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents include cash on hand, deposits held at call with banks,
and other short-term highly liquid investments that are readily convertible to a
known amount of cash and are subject to an insignicant risk of change in value.
Cash and cash equivalents as of December 31, 2012 and 2011, consist of the
following:
(In millions of Korean won)
2012 2011
Cash on hand ₩12,900 ₩16,042
Bank deposits, etc. 18,778,560 14,675,719
Total ₩18,791,460 ₩14,691,761
5. Financial Assets Subject to Withdrawal
Restrictions
Financial instruments subject to withdrawal restrictions as of December 31, 2012
and 2011, consist of the following:
(In millions of Korean won)
2012 2011
Short-term nancial instruments
Other non-current assets ₩46,489 ₩39,770
- Long-term nancial instruments 29 21
6968
measured reliably. The Company records reductions to revenue for special pricing
arrangements, price protection and other volume based discounts. If product sales
are subject to customer acceptance, revenue is not recognized until customer
acceptance occurs.
(B) Sales of services
Revenues from rendering services are generally recognized using the percentage-
of-completion method, based on the percentage of costs to date compared to the
total estimated costs, contractual milestones or performance.
(C) Other sources of revenue
Interest income is recognized using the eective interest method. When a loan and
receivable is impaired, the Company reduces the carrying amount to its recoverable
amount, being the estimated future cash ow discounted at the original eective
interest rate of the instrument, and continues unwinding the discount as interest
income. Royalty income is recognized on an accruals basis in accordance with the
substance of the relevant agreements. Dividend income is recognized when the
right to receive payment is established.
2.25 Government Grants
Grants from the government are recognized at their fair value where there is a
reasonable assurance that the grant will be received and the Company will comply
with the conditions attached. Government grants relating to income are deferred
and recognized in the statement of income over the period necessary to match
them with the income that they are intended to compensate. Government grants
relating to property, plant and equipment are included in non-current liabilities
as deferred government grants and are credited to the statement of income on a
straight-line basis over the expected lives of the related assets.
2.26 Earnings per Share
Basic earnings per share is calculated by dividing net prot for the period available
to common shareholders by the weighted-average number of common shares
outstanding during the year. Diluted earnings per share is calculated using the
weighted-average number of common shares outstanding adjusted to include the
potentially dilutive eect of common equivalent shares outstanding.
2.27 Operating Segments
Operating segments are disclosed in the manner reported to the chief operating
decision-maker (please see footnote 33). The chief operating decision-maker is
responsible for making strategic decisions on resource allocation and performance
assessment of the operating segments. The management committee which makes
strategic decisions is regarded as the chief operating decision-maker.
2.28 Convenience Translation into United States Dollar
Amounts
The Company operates primarily in Korean won and its ocial accounting records
are maintained in Korean won. The U.S. dollar amounts provided in the financial
statements represent supplementary information solely for the convenience of
the reader. All Won amounts are expressed in U.S. dollars at the rate of ₩1,171.10