Samsung 2012 Annual Report Download - page 32
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 32 of the 2012 Samsung annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.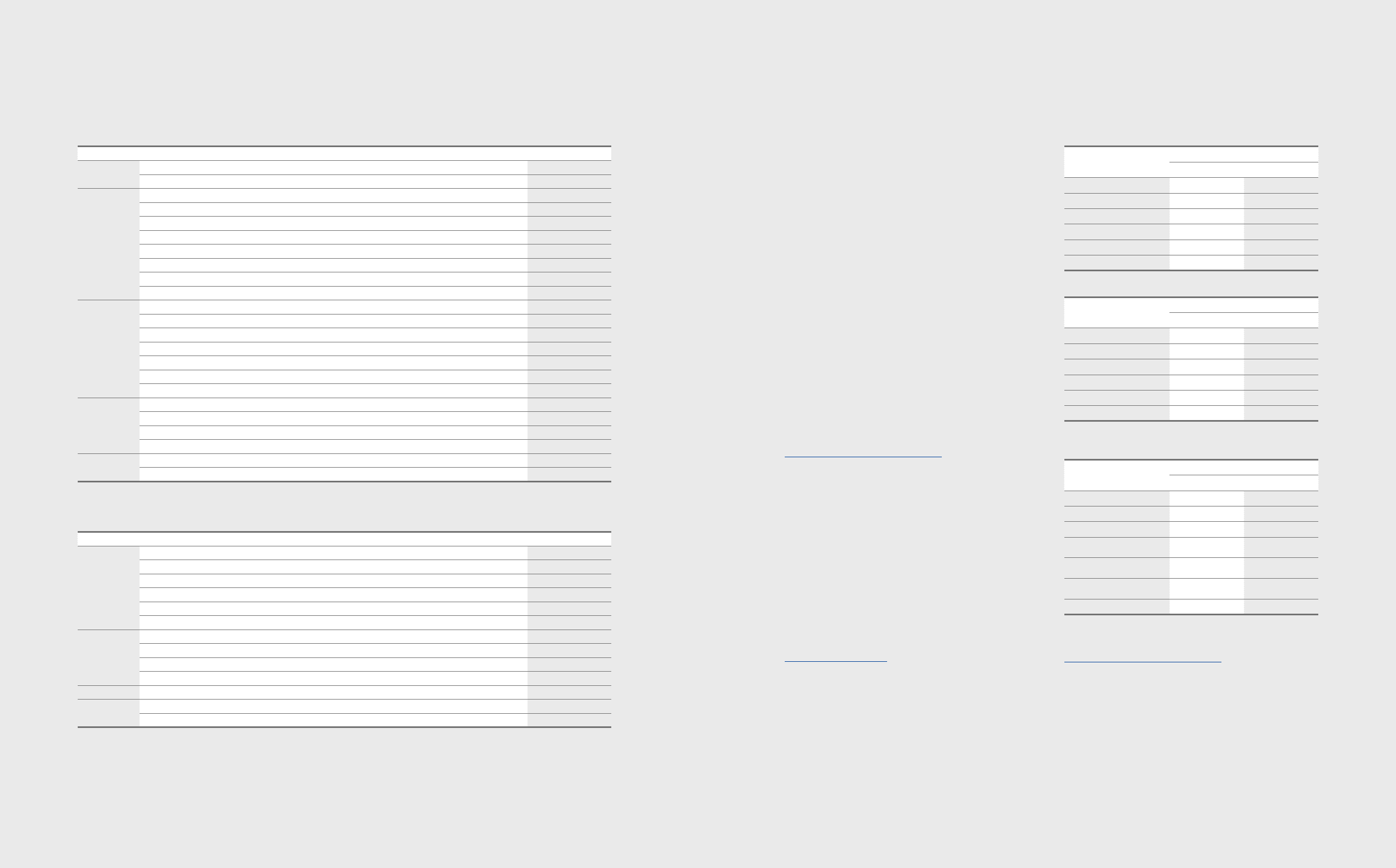
2. Summary of Signicant Accounting
Policies
2.1 Basis of Presentation
The Company first adopted International Financial Reporting Standards
as adopted by the Republic of Korea ("Korean IFRS") from January 1, 2010.
International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) have been adopted by the
Korean Accounting Standards Board as Korean IFRS based on standards and
interpretations published by the International Accounting Standards Board.
The Company has prepared the consolidated nancial statements in accordance
with Korean IFRS (“K-IFRS”). KIFRS permits the use of critical accounting estimates
in the preparation of the financial statements and requires management
judgments in applying accounting policies. Footnote 3 explains where more
complex and higher standards of judgment or critical assumptions and estimates
are required.
The principal accounting policies applied in the preparation of these consolidated
financial statements are set out below. These policies have been consistently
applied to all the years presented, unless otherwise stated. Changes in accounting
policies applied in the current scal year are presented in footnote 2.2.
2.2 Changes in Accounting Standards
(A) Amendments Adopted
K-IFRS 1001, ‘Presentation of nancial statements’
The amendment requires entities to present operating income after deducting
cost of sales, selling, and general and administrative expenses from revenue. The
amendment has been retroactively applied in the preparation of the consolidated
statement of income. Dividend income, profit on business transfer, gains and
losses on disposal of property, plant and equipment, donations, and impairment
losses on intangible assets which were previously classied as operating income
are now excluded from operating income. As a result, operating income has
increased by ₩23,036 million for the current financial year and decreased by
₩638,329 million for the prior financial years, relative to the figures under the
standard prior to the amendment. The amendment does not have an impact on
net income or earnings per share in the current or prior nancial years.
(B) Standards Early Adopted
New standards issued and effective for the financial year beginning January 1,
2013 and early adopted are set out below:
K-IFRS 1019, ‘Employee benets’
The main impacts on the Company will be that the corridor approach will no
longer be applied and instead all actuarial gains and losses will be recognized
in other comprehensive income as they occur; all past service costs will be
immediately recognized, and expected return on plan assets will be replaced with
a net interest amount calculated by applying the discount rate to the net dened
benet liability. The impacts of the amendment on the nancialstatements are as
follows:
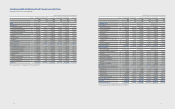
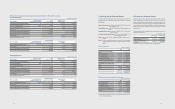
(1) Impacts on Financial Position
(In millions of Korean won)
December 31, 2011
Pre-amendment Post-amendment
Deferred income tax assets 1,614,077 1,783,086
Dened benet liability 418,486 1,119,188
Deferred income tax liability 2,333,442 2,333,442
Other components of equity (5,244,167) (5,833,896)
Retained earnings 97,542,525 97,622,872
Non-controlling interests 4,245,558 4,223,247
(In millions of Korean won)
January 1, 2011
Pre-amendment Post-amendment
Deferred income tax assets 1,124,009 1,144,068
Dened benet liability 597,829 823,486
Deferred income tax liability 1,652,667 1,618,523
Other components of equity (4,726,398) (4,931,290)
Retained earnings 85,014,550 85,071,444
Non-controlling interests 3,759,532 3,736,075
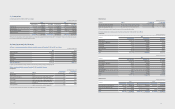
(2) Impacts on Business Performance
(In millions of Korean won)
2011
Pre-amendment Post-amendment
Operating income (*) 15,611,388 15,644,291
Income tax expense 3,424,948 3,432,875
Net income 13,734,067 13,759,043
Net income attributable to non-
controlling interests 374,875 376,398
Basic earnings per share
(in Korean won) 89,073 89,229
Diluted earnings per share
(in Korean won) 88,990 89,146
Other comprehensive income (502,271) (887,485)
(*) Operating income is calculated by retroactively applying the changes in the
calculation method of operating income and expenses.
K-IFRS 1001, ‘Presentation of nancial statements’
The amendment requires entities to group items presented in other
comprehensive income based on whether they are potentially reclassifiable
to profit or loss subsequently. The Company early adopted and applied the
amendment retroactively in the preparation of the nancial statements.
(C) Standards Not Eective or Early Adopted
New standards, amendments and interpretations issued but not eective for the
nancial year beginning January 1, 2012 and not early adopted are set out below:
6160
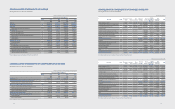
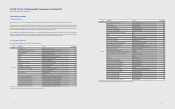
(C) Changes in scope of consolidation
(In millions of Korean won)
Area Subsidiaries Description
Domestic Samsung Display (SDC) Spin-o
Samsung Venture Capital Union #23 Acquisition of shares
America
mSpot Acquisition of shares
Nanoradio Acquisition of shares
Samsung LED America (SLA) Acquisition of shares
Samsung Electronics Panama (SEPA) Incorporation
Samsung Electronics Corporativo (SEC) Acquisition of shares
Samsung Electronics Digital appliance (SEDAM) Acquisition of shares
Nvelo Acquisition of shares
Newton Sub Incorporation
Europe
Samsung Nanoradio Design Center (SNDC) Acquisition of shares
Nanoradio Hellas Acquisition of shares
General RF Modules Acquisition of shares
Samsung LED Europe GmbH (SLEG) Acquisition of shares
Samsung Cambridge Solution Centre (SCSC) Incorporation
Samsung Denmark Research Center (SDRC) Incorporation
Samsung France Research Center (SFRC) Acquisition of shares
Middle East and
Africa
Samsung Electronics Egypt (SEEG) Incorporation
Samsung Electronics Tunisia (SETN) Incorporation
Samsung Electronics Israel (SEIL) Incorporation
Samsung Electronics Pakistan (SEPAK) Incorporation
China Tianjin Samsung LED (TSLED) Acquisition of shares
Samsung (China) Semiconductor (SCS) Incorporation
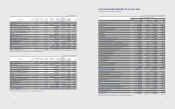
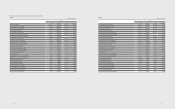
(D) Details of subsidiaries deconsolidated for the year ended December 31, 2012, are as follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
Area Subsidiaries Description
Domestic
Medison Healthcare Merger
Prosonic Merger
Samsung Mobile Display Merger
SLCD Merger
Samsung Venture Capital Union #7 Liquidation
SEHF Korea Merger
America
Samsung LED America (SLA) Liquidation
HX Diagnostics (HX) Liquidation
HX Reagents (HX Reagent) Liquidation
Nanoradio Liquidation
Europe Samsung LED Europe GmbH (SLEG) Merger
Asia Samsung Asia Private (SAPL) (*) Merger
Samsung Medison Japan (SMJP) Liquidation
(*) Samsung Asia Private merged with Samsung Electronics Asia Holding, and the resulting subsidiary is named Samsung Asia Private (Note 37).