Oracle 2009 Annual Report Download - page 111
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 111 of the 2009 Oracle annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Table of Contents
ORACLE CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
May 31, 2010
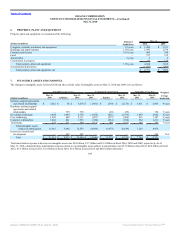
were insignificant for fiscal 2010, 2009 and 2008. The following table summarizes the components of our cash equivalents and marketable securities held,
substantially all of which were classified as available-for-sale:
May 31,
(in millions) 2010 2009
Money market funds $ 2,423 $ 467
U.S. Treasury, U.S. government and U.S. government agency debt securities 3,010 4,078
Commercial paper, corporate debt securities and other 5,634 2,700
Total investments $ 11,067 $ 7,245
Investments classified as cash equivalents $ 2,512 $ 3,616
Investments classified as marketable securities $ 8,555 $ 3,629
Substantially all of our marketable security investments held as of May 31, 2010 mature within one year. Our investment portfolio is subject to market risk due to
changes in interest rates. We place our investments with high credit quality issuers as described above and, by policy, limit the amount of credit exposure to any
one issuer. As stated in our investment policy, we are averse to principal loss and seek to preserve our invested funds by limiting default risk, market risk and
reinvestment risk.
4. FAIR VALUE MEASUREMENTS
We perform fair value measurements in accordance with the guidance provided by ASC 820, Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures. ASC 820 defines fair
value as the price that would be received from selling an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the
measurement date. When determining the fair value measurements for assets and liabilities required to be recorded at fair value, we consider the principal or
most advantageous market in which we would transact and consider assumptions that market participants would use when pricing the asset or liability, such as
inherent risk, transfer restrictions, and risk of nonperformance.
ASC 820 establishes a fair value hierarchy that requires an entity to maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs when
measuring fair value. An asset’s or liability’s categorization within the fair value hierarchy is based upon the lowest level of input that is significant to the fair
value measurement. ASC 820 establishes three levels of inputs that may be used to measure fair value:
• Level 1: quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities;
• Level 2: inputs other than Level 1 that are observable, either directly or indirectly, such as quoted prices in active markets for similar assets or
liabilities, quoted prices for identical or similar assets or liabilities in markets that are not active, or other inputs that are observable or can be
corroborated by observable market data for substantially the full term of the assets or liabilities; or
• Level 3: unobservable inputs that are supported by little or no market activity and that are significant to the fair values of the assets or liabilities.
107
Source: ORACLE CORP, 10-K, July 01, 2010 Powered by Morningstar® Document Research℠