Nissan 2004 Annual Report Download - page 71
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 71 of the 2004 Nissan annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Nissan Annual Report 2003 69
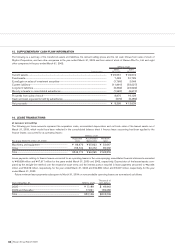
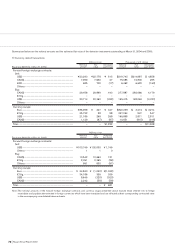
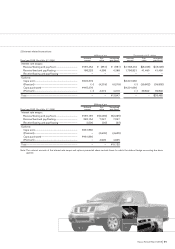
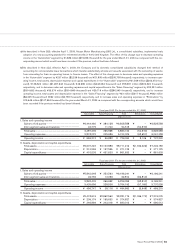
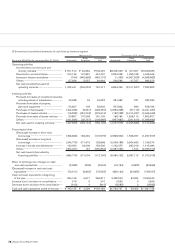
20. DERIVATIVE TRANSACTIONS
Hedging Policies
The Company and its consolidated subsidiaries (collectively, the
“Group”) utilize derivative transactions for the purpose of hedging
their exposure to fluctuation in foreign exchange rates, interest rates
and market prices. However, based on an internal management rule
on financial market risk (the “Rule”) approved by the Company’s
Board of Directors, they do not enter into transactions involving
derivatives for speculative purposes. The Rule prescribes that (i) the
Group’s financial market risk is to be controlled by the Company in a
centralized manner, and that (ii) no individual subsidiary can initiate a
hedge position without the prior approval of, and regular reporting
back to the Company.
Risk to be hedged by derivative transactions
(1) Market risk
The financial market risk to which the Group is generally exposed in its
operations and the relevant derivative transactions primarily used for
hedging are summarized as follows:
·Foreign exchange risk associated with assets and liabilities denomi-
nated in foreign currencies; forward foreign exchange contracts,
foreign currency options, and currency swaps;
·Interest rate risk associated with sourcing funds and investing:
interest-rate swaps;
·Risk of fluctuation in stock prices: options on stocks;
·Risk of fluctuation in commodity prices (mainly for precious metals):
commodity futures contracts
(2) Credit risk
The Group is exposed to the risk that a counterparty to its financial
transactions could default and jeopardize future profits. We believe
that this risk is insignificant as the Group enters into derivative trans-
actions only with financial institutions which have a sound credit pro-
file. The Group enters into these transactions also with Renault
Finance S.A. (“RF”), a specialized financial subsidiary of the Renault
Group which, we believe, is not subject to any such material risk.
This is because RF enters into derivative transactions to cover such
derivative transactions with us only with financial institutions of the
highest caliber carefully selected by RF based on its own rating sys-
tem which takes into account each counterparty’s long-term credit
rating and shareholders’ equity.
(3) Legal risk
The Group is exposed to the risk of entering into a financial agree-
ment which may contain inappropriate terms and conditions as well
as the risk that an existing contract may be affected by revisions to
the relevant laws and regulations. The Company’s Legal Department
and Finance Department make every effort to minimize legal risk by
reviewing any new agreements of significance and by reviewing the
related documents in a centralized way.
Risk Management
All strategies to manage financial market risk and risk hedge opera-
tions of the Group are carried out pursuant to the Rule which stipulates
the Group’s basic policies for derivative transactions, management
policies, management items, procedures, criteria for the selection of
counterparties, and the reporting system, and so forth. The Rule pre-
scribes that (i) the Group’s financial market risk is to be controlled by
the Company in a centralized manner, and that (ii) no individual sub-
sidiary is permitted to initiate a hedging operation without the prior
approval of, and regular reporting back to the Company.
The basic hedge policy is subject to the approval of the Monthly
Hedge Policy Meeting attended by the corporate officer in charge of
Treasury Department. Execution and management of all deals are to
be conducted pursuant to the Rule. Derivative transactions are con-
ducted by a special section of the Treasury Department and monitoring
of contracts for such transactions and confirming the balance of all
open positions are the responsibility of back office and risk manage-
ment section. Commodity futures contracts are to be handled also
by Treasury Department under guidelines which are to be drawn up
by the MRMC (Materials Risk Management Committee). The MRMC
is chaired by the corporate officer in charge of the Purchasing
Department and the corporate officer in charge of Treasury
Department and it will meet approximately once every six months.
The status of derivative transactions is reported on a daily basis to
the chief officer in charge of Treasury Department and on an annual
basis to the Board of Directors. Credit risk is monitored quantitatively
with reference to Renault’s rating system based principally on the
counterparties’ long-term credit ratings and on their shareholders’
equity. The Finance Department sets a maximum upper limit on posi-
tions with each of the counterparties for the Group and monitors the
balances of open positions every day.