Motorola 2013 Annual Report Download - page 72
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 72 of the 2013 Motorola annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
70
uses forward contracts and options to hedge these currency exposures. In addition, the Company enters into derivative
contracts for some forecasted transactions, which are designated as part of a hedging relationship if it is determined that the
transaction qualifies for hedge accounting under the provisions of the authoritative accounting guidance for derivative
instruments and hedging activities. A portion of the Company’s exposure is from currencies that are not traded in liquid
markets and these are addressed, to the extent reasonably possible, by managing net asset positions, product pricing and
component sourcing.
At December 31, 2013, the Company had outstanding foreign exchange contracts totaling $837 million, compared to
$523 million outstanding at December 31, 2012. Management believes that these financial instruments should not subject the
Company to undue risk due to foreign exchange movements because gains and losses on these contracts should generally offset
losses and gains on the underlying assets, liabilities and transactions, except for the ineffective portion of the instruments,
which is charged to Other within Other income (expense) in the Company’s consolidated statements of operations.
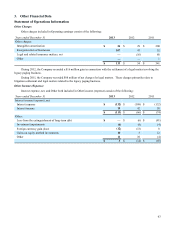
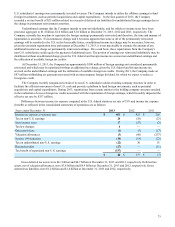
The following table shows the five largest net notional amounts of the positions to buy or sell foreign currency as of
December 31, 2013 and the corresponding positions as of December 31, 2012:
Notional Amount
Net Buy (Sell) by Currency 2013 2012
British Pound $ 257 $ 225
Chinese Renminbi (181)(99)
Euro (132)(9)
Norwegian Krone (95)(48)
Brazilian Real (44)3
At December 31, 2013, the maximum term of derivative instruments that hedge forecasted transactions was seven
months. The weighted average duration of the Company’s derivative instruments that hedge forecasted transactions was three
months.
Interest Rate Risk
As part of its liability management program, one of the Company's European subsidiaries has outstanding interest rate
agreements (“Interest Agreements”) relating to Euro-denominated loans. The interest on the Euro-denominated loans is
variable. The Interest Agreements change the characteristics of interest rate payments from variable to maximum fixed-rate
payments. The Interest Agreements are not accounted for as a part of a hedging relationship and, accordingly, the changes in
the fair value of the Interest Agreements are included in Other income (expense) in the Company's consolidated statements of
operations. The weighted average fixed rate payment on the Interest Agreements for the year ended December 31, 2013 was
4.44%. The fair value of the Interest Agreements resulted in a liability position of $3 million at December 31, 2013, compared
to a liability position of $4 million at December 31, 2012.
Counterparty Risk
The use of derivative financial instruments exposes the Company to counterparty credit risk in the event of
nonperformance by counterparties. However, the Company’s risk is limited to the fair value of the instruments when the
derivative is in an asset position. The Company actively monitors its exposure to credit risk. At present time, all of the
counterparties have investment grade credit ratings. The Company is not exposed to material credit risk with any single
counterparty. As of December 31, 2013, the Company was exposed to an aggregate credit risk of approximately $4 million with
all counterparties.