Motorola 2013 Annual Report Download - page 71
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 71 of the 2013 Motorola annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
69
4. Debt and Credit Facilities
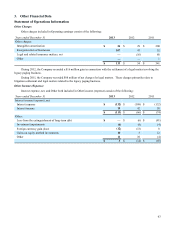
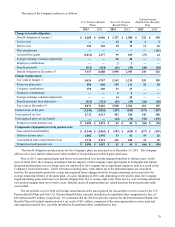
Long-Term Debt
December 31 2013 2012
6.0% senior notes due 2017 399 399
3.75% senior notes due 2022 747 747
3.5% senior notes due 2023 593 —
6.5% debentures due 2025 118 118
7.5% debentures due 2025 346 346
6.5% debentures due 2028 36 36
6.625% senior notes due 2037 54 54
5.22% debentures due 2097 89 89
Other long-term debt 58 45
2,440 1,834
Adjustments, primarily unamortized gains on interest rate swap terminations 21 29
Less: current portion (4)(4)
Long-term debt $ 2,457 $ 1,859
During the year ended December 31, 2013, the Company issued an aggregate face principal amount of $600 million of
3.50% Senior Notes due March 1, 2023, recognizing net proceeds of $588 million, after debt issuance costs and debt discounts.
During the year ended December 31, 2012, the Company issued an aggregate face principal amount of $750 million of
3.75% Senior Notes due 2022 (the “2022 Senior Notes”). The Company also redeemed $400 million aggregate principal
amount outstanding of its 5.375% Senior Notes due November 2012 for an aggregate purchase price of approximately $408
million. After accelerating the amortization of debt issuance costs and debt discounts, the Company recognized a loss of
approximately $6 million related to this redemption within Other income (expense) in the consolidated statements of
operations. This debt was repurchased with a portion of the proceeds from the issuance of the 2022 Senior Notes.
Aggregate requirements for long-term debt maturities during the next five years are as follows: 2014—$20 million; 2015
—$5 million; 2016—$6 million; 2017—$406 million; and 2018—$6 million.
Credit Facilities
As of December 31, 2013, the Company had a $1.5 billion unsecured syndicated revolving credit facility (the “2011
Motorola Solutions Credit Agreement”) that is scheduled to expire on June 30, 2014. The Company must comply with certain
customary covenants, including maintaining maximum leverage and minimum interest coverage ratios as defined in the 2011
Motorola Solutions Credit Agreement. The Company was in compliance with its financial covenants as of December 31, 2013.
The Company has never borrowed under the 2011 Motorola Solutions Credit Agreement. At December 31, 2013, the
commitment fee assessed against the daily average unused amount was 25 basis points.
5. Risk Management
Derivative Financial Instruments
Foreign Currency Risk
The Company uses financial instruments to reduce its overall exposure to the effects of currency fluctuations on cash
flows. The Company’s policy prohibits speculation in financial instruments for profit on exchange rate price fluctuations,
trading in currencies for which there are no underlying exposures, or entering into transactions for any currency to intentionally
increase the underlying exposure. Instruments that are designated as part of a hedging relationship must be effective at
reducing the risk associated with the exposure being hedged and are designated as part of a hedging relationship at the
inception of the contract. Accordingly, changes in the market values of hedge instruments must be highly correlated with
changes in market values of the underlying hedged items both at the inception of the hedge and over the life of the hedge
contract.
The Company’s strategy related to foreign exchange exposure management is to offset the gains or losses on the financial
instruments against losses or gains on the underlying operational cash flows or investments based on the Company's
assessment of risk. The Company enters into derivative contracts for some of its non-functional currency cash, receivables, and
payables, which are primarily denominated in major currencies that can be traded on open markets. The Company typically