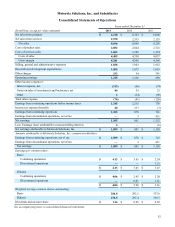
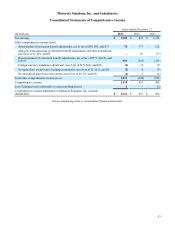
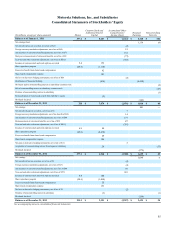
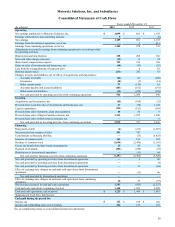
Motorola 2013 Annual Report Download - page 63
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 63 of the 2013 Motorola annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.61
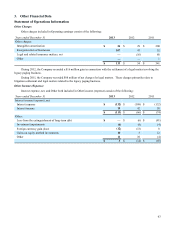
Derivative Instruments: Gains and losses on hedges of existing assets or liabilities are marked-to-market and the
result is included in Other within Other income (expense) within the Company’s consolidated statements of operations. Certain
financial instruments are used to hedge firm future commitments or forecasted transactions. Gains and losses pertaining to
those instruments that qualify for hedge accounting are deferred until such time as the underlying transactions are recognized
and subsequently recognized in the same line within the consolidated statements of operations as the hedged item. Gains and
losses pertaining to those instruments that do not qualify for hedge accounting are recorded immediately in Other income
(expense) within the consolidated statements of operations.
Earnings Per Share: The Company calculates its basic earnings per share based on the weighted-average effect of all
common shares issued and outstanding. Net earnings attributable to Motorola Solutions, Inc. is divided by the weighted
average common shares outstanding during the period to arrive at the basic earnings per share. Diluted earnings per share is
calculated by dividing net earnings attributable to Motorola Solutions, Inc. by the sum of the weighted average number of
common shares used in the basic earnings per share calculation and the weighted average number of common shares that would
be issued assuming exercise or conversion of all potentially dilutive securities, excluding those securities that would be anti-
dilutive to the earnings per share calculation. Both basic and diluted earnings per share amounts are calculated for earnings
from continuing operations and net earnings attributable to Motorola Solutions, Inc. for all periods presented. All earnings per
share information presented gives effect to the distribution of Motorola Mobility and a reverse stock split, which occurred on
January 4, 2011 (see further discussion in Note 3).
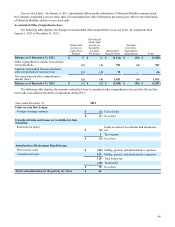
Share-Based Compensation Costs: The Company has incentive plans that reward employees with stock options, stock
appreciation rights, restricted stock and restricted stock units, as well as an employee stock purchase plan. The amount of
compensation cost for these share-based awards is generally measured based on the fair value of the awards as of the date that
the share-based awards are issued and adjusted to the estimated number of awards that are expected to vest. The fair values of
stock options and stock appreciation rights are generally determined using a Black-Scholes option pricing model which
incorporates assumptions about expected volatility, risk free rate, dividend yield, and expected life. Compensation cost for
share-based awards is recognized on a straight-line basis over the vesting period.
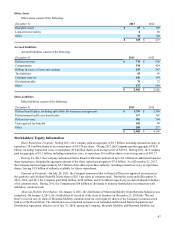
Retirement Benefits: The Company records annual expenses relating to its pension benefit and postretirement plans
based on calculations which include various actuarial assumptions, including discount rates, assumed asset rates of return,
compensation increases, turnover rates and health care cost trend rates. The Company reviews its actuarial assumptions on an
annual basis and makes modifications to the assumptions based on current rates and trends. The effects of the gains, losses, and
prior service costs and credits are amortized either over the average service life or over the average remaining lifetime of the
participants, depending on the number of active employees in the plan. The funded status, or projected benefit obligation less
plan assets, for each plan, is reflected in the Company’s consolidated balance sheets using a December 31 measurement date.
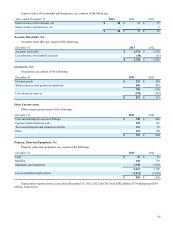
Advertising Expense: Advertising expenses, which are the external costs of marketing the Company’s products, are
expensed as incurred. Advertising expenses were $95 million, $95 million and $98 million for the years ended December 31,
2013, 2012 and 2011, respectively.
Use of Estimates: The preparation of the accompanying consolidated financial statements in conformity with
accounting principles generally accepted in the U.S. requires management to make estimates and assumptions about future
events. These estimates and the underlying assumptions affect the amounts of assets and liabilities reported, disclosures about
contingent assets and liabilities, and reported amounts of revenues and expenses. Such estimates include the valuation of
accounts receivable and long term receivables, inventories, investments, goodwill, intangible and other long-lived assets, legal
contingencies, guarantee obligations, indemnifications, and assumptions used in the calculation of income taxes, retirement and
other post-employment benefits and allowances for discounts, price protection, product returns, and customer incentives,
among others. These estimates and assumptions are based on management’s best estimates and judgment. Management
evaluates its estimates and assumptions on an ongoing basis using historical experience and other factors, including the current
economic environment, which management believes to be reasonable under the circumstances. The Company adjusts such
estimates and assumptions when facts and circumstances dictate. Illiquid credit markets, volatile equity, foreign currency, and
energy markets together with declines in consumer spending have increased the uncertainty inherent in such estimates and
assumptions. As future events and their effects cannot be determined with precision, actual results could differ significantly
from these estimates. Changes in those estimates resulting from continuing changes in the economic environment will be
reflected in the financial statements in future periods.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements:
In February 2013, the Financing Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”)
No. 2013-04, “Obligations Resulting from Joint and Several Liability Arrangements for which the Total Amount of the
Obligation Is Fixed at the Reporting Date.” The standard addresses the recognition, measurement, and disclosure of certain
obligations resulting from joint and several liability arrangements for which the total amount of the obligation is fixed at the
reporting date, including debt arrangements, other contractual obligations, and settled litigation and judicial rulings. U.S.
GAAP does not currently include specific guidance on accounting for such obligations with joint and several liability which has