JCPenney 2003 Annual Report Download - page 20
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 20 of the 2003 JCPenney annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
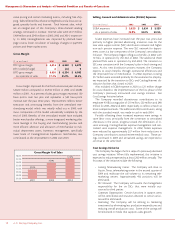
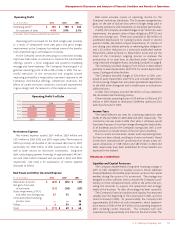
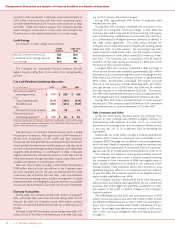
J. C. Penney Company, Inc.18
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
controls and documentation to provide the assurance and
required reporting in fiscal 2004, when Section 404 becomes
effective.
Independent Support Functions — Internal Audit, Legal,
Controller’s/Finance and Treasurer’s support the Company’s risk
management function. They operate independently of the oper-
ating divisions of the Company. As an important component of
the Company’s control structure, the Internal Audit department
reports functionally to the Audit Committee of the Board of
Directors, and administratively to the Company’s General
Counsel. Internal Audit performs reviews and test work to ensure
that: (a) risks are appropriately identified and managed; (b) inter-
action with various internal governance groups, such as the legal
compliance team, occurs as needed; (c) significant financial, man-
agerial and operating information is reliable and timely; (d) asso-
ciates’ actions are in compliance with policies, standards,
procedures, and applicable laws and regulations; (e) resources are
acquired economically, used efficiently and adequately protected;
(f) quality and continuous improvement are fostered in the orga-
nization’s control process; and (g) significant legislative or regulato-
ry issues impacting the organization are recognized and addressed
appropriately. The legal compliance team is responsible for ensur-
ing that all areas of the Company have effective procedures in
place to comply with various laws and regulations and any changes
thereto.
Categories of Risk
Management defines risk as the potential deviation from
planned operating results that may have a negative impact on
investor enterprise value in the short or long term. The deviation
can arise from inadequate or ineffective internal processes or sys-
tems, external events or Company personnel. The Company’s key
risks and related risk mitigation/management practices are dis-
cussed below:
Business
•Strategic — The Company’s key business risk is the successful
execution of the five-year turnaround plan for Department
Stores and Catalog/Internet to achieve competitive levels of
profitability.
The Company has strategies and processes in place to
ensure that the turnaround is successful and progresses on tar-
get. The overriding goal is to re-establish and solidify the cus-
tomer franchise and strengthen customer confidence that
JCPenney consistently offers fashion-right, quality merchandise
at value prices. The primary initiatives for Department Stores
and Catalog/Internet are to improve the merchandise assort-
ments through more fashionable items with good quality and
value, support the offerings with compelling marketing pro-
grams, improve the visual appeal of the store environment and
catalogs, reduce the expense structure to more competitive
levels and focus on having the right people in the right jobs.
While results have been positive for the most recent three
years and indicate that the Company is on track in achieving
its financial targets, the turnaround is complex and the
Company will face continued challenges in the execution of
its strategic initiatives.
An important factor in the Company’s turnaround is the
ability of Department Stores to operate under a centralized
merchandising model. Certain information technology sys-
tems have been purchased (and others are in various stages of
development) to plan merchandise assortments, allocate
inventory and stock stores, better track sales trends to enable
prompt replenishment and manage pricing. To efficiently
handle inventory flow, the Company has completed the roll-
out of centralized logistics store support centers. The effec-
tiveness of these systems and processes is an important com-
ponent of the Company’s ability to have the right inventory
in the right place, at the right time and at the right price.
•Management — The Human Resources Committee ensures
that processes are in place to provide competitive compen-
sation packages, human resource development and training,
and management succession plans. As part of the strategy
to return the Company to competitive levels of profitability,
management has hired seasoned individuals, including
executive level and others with a breadth of experience in
merchandising, marketing, buying and allocation under a
centralized model, as well as to manage Catalog and Internet
operations.
Financial
•Financial Position and Liquidity — The Company’s strong
financial position and liquidity substantially mitigates the
strategic business risk inherent during the turnaround peri-
od. To support the Company’s previously stated turn-
around initiatives, in 2001 management developed a long-
term financing strategy to strengthen the Company’s liquid-
ity position. The primary goal of the Company’s strategy is
to ensure financial flexibility and access to capital over the
turnaround timeframe. This will allow adequate time to
restore the profitability of the Company to competitive
levels and to increase capital spending to fund
planned department store renewals, new freestanding
stores and relocations, and to make additional investments
in technology.
Achieving a competitive level of profitability will enable the
Company to generate a competitive level of capital resources
for investment in its businesses on a sustainable basis.
Competitive operating profit margins are necessary to restore
the Company’s return on invested capital and return on
stockholders’ equity to retail industry standards, and thereby
improve the Company’s access to the capital markets. In
addition, management believes that it is important to restore
the Company’s credit ratings to investment-grade levels and
thereby enhance shareholder value.
The Company’s financing strategy has been effectively exe-
cuted over the 2000-2003 period. As a result, the Company’s
financial position has strengthened significantly over this peri-