Aflac 2007 Annual Report Download - page 68
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 68 of the 2007 Aflac annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
64 There’s Only One Aflac
The incurred claims development related to prior years reflects
favorable development in the unpaid policy claims liability
previously provided for. There are no additional or return of
premium considerations associated with that development.
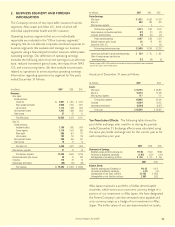
7. NOTES PAYABLE
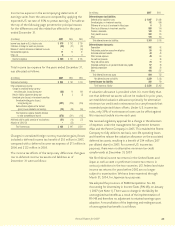
A summary of notes payable as of December 31 follows:
(In millions) 2007 2006
6.50% senior notes due April 2009 $ 450 $ 450
Yen-denominated Uridashi notes:
1.52% notes due September 2011 (principal amount ¥15 billion) 131 126
2.26% notes due September 2016 (principal amount ¥10 billion) 88 84
Variable interest rate notes due September 2011 (1.32% at December 2007,
principal amount ¥20 billion) 175 168
Yen-denominated Samurai notes:
.96% notes paid June 2007 (principal amount ¥30 billion) –252
.71% notes due July 2010 (principal amount ¥40 billion) 350 336
1.87% notes due June 2012 (principal amount ¥30 billion) 263 –
Capitalized lease obligations payable through 2013 810
Total notes payable $1,465 $1,426
In February 2006, the Parent Company filed a Shelf
Registration Statement (SRS) with Japanese regulatory
authorities to issue up to ¥100 billion of yen-denominated
Samurai notes in Japan. In June 2007, the Parent Company
issued yen-denominated Samurai notes totaling ¥30 billion.
We used the net proceeds of these Samurai notes to pay in
full the .96% Samurai notes that were issued in 2002 and
matured in June 2007. These Samurai notes issued by the
Parent Company in 2007 and those issued in 2005 each have
five year maturities. Each series of Samurai notes pays interest
semiannually, may only be redeemed prior to maturity upon
the occurrence of a tax event as specified in the respective
bond agreement and is not available to U.S. persons.
In August 2006, the Parent Company filed an SRS with
Japanese regulatory authorities to issue up to ¥100 billion of
yen-denominated Uridashi notes in Japan. In September 2006,
the Parent Company issued three tranches of Uridashi notes
totaling ¥45 billion. The first tranche totaled ¥15 billion and
has a five-year maturity. The second tranche totaled ¥10
billion and has a 10-year maturity. The third tranche totaled
¥20 billion and has a five-year maturity and a variable interest
coupon of six-month yen LIBOR plus a spread. We have
entered into interest rate swaps related to the ¥20 billion
variable interest rate notes (see Note 4). Each tranche of
Uridashi notes pays interest semiannually, may only be
redeemed prior to maturity upon the occurrence of a tax
event as specified in the respective bond agreement and is not
available to U.S. persons. If issued, the ¥55 billion of Uridashi
notes remaining under the August 2006 SRS will not be
available to U.S. persons.
For our yen-denominated loans, the principal amount as stated
in dollar terms will fluctuate from period to period due to
changes in the yen/dollar exchange rate. We have designated
all of our yen-denominated notes payable as a hedge of the
foreign currency exposure of our investment in Aflac Japan.
We have also designated the interest rate swaps on our variable
interest rate Uridashi notes as a hedge of the variability in our
interest cash flows associated with these notes.
In 1999, we issued $450 million of senior notes. These notes
pay interest semiannually and are redeemable at our option at
any time with a redemption price equal to the principal
amount of the notes redeemed plus a make-whole premium.
We have entered into cross-currency swaps related to these
notes (see Note 4).
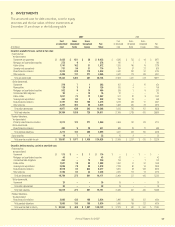
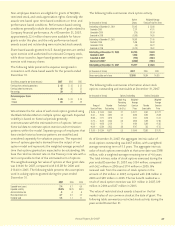
The aggregate contractual maturities of notes payable during
each of the years after December 31, 2007, are as follows:
Capitalized Total
Long-term Lease Notes
(In millions) Debt Obligations Payable
2008 $ – $ 3 $ 3
2009 450 2 452
2010 350 2 352
2011 306 1 307
2012 263 – 263
Thereafter 88 – 88
Total $ 1,457 $ 8 $ 1,465
We were in compliance with all of the covenants of our notes
payable at December 31, 2007. No events of default or
defaults occurred during 2007 and 2006.
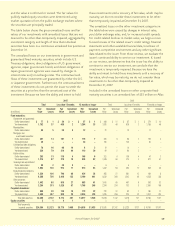
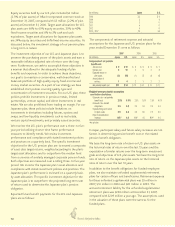
8. INCOME TAXES
The components of income tax expense (benefit) applicable
to pretax earnings for the years ended December 31 were as
follows:
(In millions) Japan U.S. Total
2007:
Current $ 450 $ 98 $ 548
Deferred 222 95 317
Total income tax expense $ 672 $ 193 $ 865
2006:
Current $ 398 $ 21 $ 419
Deferred 229 133 362
Total income tax expense $ 627 $ 154 $ 781
2005:
Current $ 485 $ 14 $ 499
Deferred 159 119 278
Release of valuation allowance on
deferred tax assets – (34) (34)
Total income tax expense $ 644 $ 99 $ 743