Aflac 2007 Annual Report Download - page 65
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 65 of the 2007 Aflac annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
61
Annual Report for 2007
issuer, but rank higher than equity securities. Although these
securities have no contractual maturity, the interest coupons
that were fixed at issuance subsequently change to a floating
short-term interest rate of 125 to more than 300 basis points
above an appropriate market index, generally by the 25th year
after issuance, thereby creating an economic maturity date.
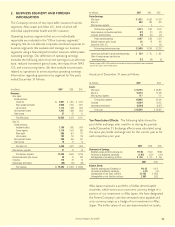
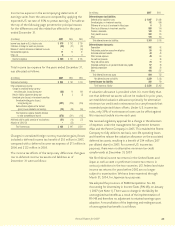
The economic maturities of our investments in perpetual
debentures at December 31, 2007, were as follows:
Aflac Japan Aflac U.S.
Amortized Fair Amortized Fair
(In millions) Cost Value Cost Value
Available for sale:
Due in one year or less $ 291 $ 298 $ – $ –
Due after one year through five years 61 111 15 16
Due after five years through 10 years 263 307 35 34
Due after 10 years through 15 years 268 250 – –
Due after 15 years 3,031 2,799 308 280
Total perpetual debentures
available for sale $ 3,914 $ 3,765 $ 358 $ 330
Held to maturity:
Due in one year or less $ 133 $ 134 $ – $ –
Due after one year through five years 788 816 – –
Due after five years through 10 years 1,567 1,628 – –
Due after 10 years through 15 years – – – –
Due after 15 years 1,497 1,356 – –
Total perpetual debentures
held to maturity $ 3,985 $ 3,934 $ – $ –
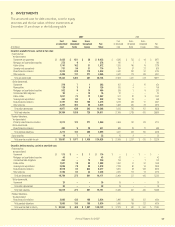
As part of our investment activities, we own investments in
qualified special purpose entities (QSPEs). At December 31,
2007, available-for-sale QSPEs totaled $3.2 billion at fair value
($3.3 billion at amortized cost, or 6.0% of total debt
securities), compared with $2.3 billion at fair value ($2.3 billion
at amortized cost, or 4.7% of total debt securities) at
December 31, 2006. We have no equity interests in any of the
QSPEs, nor do we have control over these entities. Therefore,
our loss exposure is limited to the cost of our investment.
We also own investments in variable interest entities (VIEs)
totaling $2.1 billion at fair value ($2.4 billion at amortized cost,
or 4.5% of total debt securities) at December 31, 2007. We
are the primary beneficiary of VIEs totaling $1.3 billion at fair
value ($1.6 billion at amortized cost) and have consolidated
our interests in these VIEs in accordance with FASB
Interpretation No. 46 (revised December 2003),
Consolidation of Variable Interest Entities. The activities of the
VIEs that we consolidate are limited to holding debt securities
and utilizing the cash flows from the debt securities to service
our investments therein. The terms of these debt securities
mirror the terms of the notes held by Aflac.
We have interests in VIEs in which we are not the primary
beneficiary and therefore are not required to consolidate
totaling $760 million at fair value ($853 million at amortized
cost) as of December 31, 2007. These interests primarily
consist of corporate collateralized debt obligations (CDOs).
The activities of these VIEs are limited to holding underlying
collateral, comprising investment-grade debt securities at the
time of issuance and credit default swap (CDS) contracts on
specific corporate entities and utilizing the cash flows from
the collateral and CDS contracts to service our investments
therein. All corporate entities covered by the CDS contracts
were investment grade at the time of issuance. Our remaining
VIEs that we are not required to consolidate consist of loans
to financing vehicles that are irrevocably and unconditionally
guaranteed by their corporate parents. These VIEs are used to
raise financing for their respective parent companies in the
international capital markets. The guarantors of these VIEs
were investment grade at the time of issuance.
The loss on any of our VIE investments would be limited to
its cost.
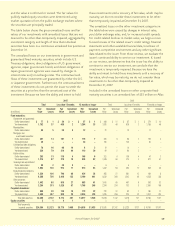
We lend fixed-maturity securities to financial institutions in
short-term security lending transactions. These short-term
security lending arrangements increase investment income
with minimal risk. Our security lending policy requires that the
fair value of the securities and/or cash received as collateral
be 102% or more of the fair value of the loaned securities. At
December 31, 2007, we had security loans outstanding with a
fair value of $790 million, and we held cash in the amount of
$808 million as collateral for these loaned securities. At
December 31, 2006, we had security loans outstanding with a
fair value of $780 million, and we held cash in the amount of
$807 million as collateral for these loaned securities.
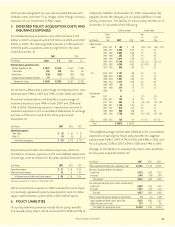
During 2007, we reclassified an investment from held to
maturity to available for sale as a result of a deterioration in
the issuer’s creditworthiness. At the date of transfer, this
debt security had an amortized cost of $169 million. The
investment was subsequently sold at a realized gain of
$12 million.
During 2006, we reclassified an investment from held to
maturity to available for sale as a result of the issuer’s credit
rating downgrade. At the date of transfer, this debt security
had an amortized cost of $118 million and an unrealized loss
of $15 million.
During 2005, we reclassified an investment from held to
maturity to available for sale as a result of the issuer’s credit
rating downgrade. This debt security had an amortized cost of
$254 million and an unrealized loss of $46 million at the date
of transfer.