Aflac 2007 Annual Report Download - page 66
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 66 of the 2007 Aflac annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
62 There’s Only One Aflac
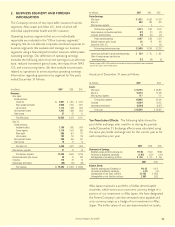
4. FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS
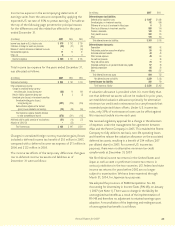
The carrying values and estimated fair values of the Company’s
financial instruments as of December 31 were as follows:
2007 2006
Carrying Fair Carrying Fair
(In millions) Value Value Value Value
Assets:
Fixed-maturity securities $ 47,330 $ 46,702 $ 42,288 $ 42,174
Perpetual debentures 8,080 8,029 8,398 8,432
Equity securities 22 22 25 25
Liabilities:
Notes payable (excl. capitalized leases) 1,457 1,452 1,416 1,421
Cross-currency and interest rate swaps 35 35 77
Obligation to Japanese policyholder
protection corporation 151 151 175 175
The methods of determining the fair values of our investments
in debt and equity securities are described in Note 3. The fair
values of notes payable with fixed interest rates were obtained
from an independent financial information service. The fair
values of our cross-currency swaps are the expected amounts
that we would receive or pay to terminate the swaps, taking
into account current interest rates, foreign currency rates and
the current creditworthiness of the swap counterparties. The
fair value of the obligation to the Japanese policyholder
protection corporation is our estimated share of the industry’s
obligation calculated on a pro rata basis by projecting our
percentage of the industry’s premiums and reserves and
applying that percentage to the total industry obligation
payable in future years.
The carrying amounts for cash and cash equivalents,
receivables, accrued investment income, accounts payable, cash
collateral and payables for security transactions approximated
their fair values due to the short-term nature of these
instruments. Consequently, such instruments are not included
in the above table. The preceding table also excludes liabilities
for future policy benefits and unpaid policy claims as these
liabilities are not financial instruments as defined by GAAP.
We have outstanding cross-currency swap agreements related
to the $450 million senior notes (see Note 7). We have
designated the foreign currency component of these cross-
currency swaps as a hedge of the foreign currency exposure of
our investment in Aflac Japan. The notional amounts and
terms of the swaps match the principal amount and terms of
the senior notes.
We entered into cross-currency swaps to minimize the impact
of foreign currency translation on shareholders’ equity and to
reduce interest expense by converting the dollar-denominated
principal and interest on the senior notes we issued into yen-
denominated obligations. By entering into these cross-currency
swaps, we have been able to reduce our interest rate from
6.5% in dollars to 1.67% in yen. See Note 1 for information on
the accounting policy for cross-currency swaps.
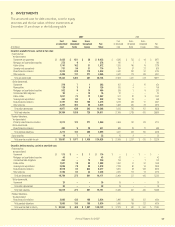
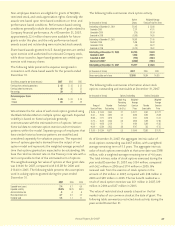
The components of the fair value of the cross-currency and
interest rate swaps were reflected as an asset or (liability) in the
balance sheet as of December 31 as follows:
(In millions) 2007 2006
Interest rate component $7 $6
Foreign currency component (47) (17)
Accrued interest component 54
Total fair value of cross-currency swaps and interest rate swaps $ (35) $ (7)
The following is a reconciliation of the foreign currency
component of the cross-currency swaps included in
accumulated other comprehensive income for the years
ended December 31.
(In millions) 2007 2006 2005
Balance, beginning of year $ (17) $ (22) $ (91)
Increase (decrease) in fair value of cross-currency swaps (26) 554
Interest rate component not qualifying for hedge accounting
reclassified to net earnings (4) –15
Balance, end of year $ (47) $ (17) $ (22)
We have entered into interest rate swap agreements related to
the ¥20 billion variable interest rate Uridashi notes (see Note
7). By entering into these contracts, we have been able to lock
in the interest rate at 1.52% in yen. We have designated these
interest rate swaps as a hedge of the variability in our interest
cash flows associated with the variable interest rate Uridashi
notes. The notional amounts and terms of the swaps match
the principal amount and terms of the variable interest rate
Uridashi notes. The swaps had no value at inception. Changes
in the fair value of the swap contracts are recorded in other
comprehensive income. The fair value of these swaps and
related changes in fair value were immaterial during the years
ended December 31, 2007 and 2006.
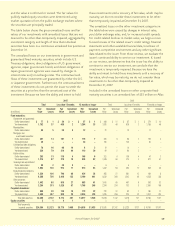
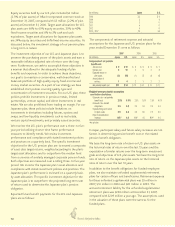
We are exposed to credit risk in the event of nonperformance
by counterparties to our cross-currency and interest rate
swaps. The counterparties to our swap agreements are U.S.
and Japanese financial institutions with the following credit
ratings as of December 31.
(In millions) 2007 2006
Counterparty Fair Value Notional Amount Fair Value Notional Amount
Credit Rating of Swaps of Swaps of Swaps of Swaps
AA $ (24) $ 387 $ (7) $ 459
A(11) 238 – 159
Total $ (35) $ 625 $ (7) $ 618