Abercrombie & Fitch 2013 Annual Report Download - page 72
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 72 of the 2013 Abercrombie & Fitch annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
72
quarterly. Any hedge ineffectiveness is reported in current period earnings and hedge accounting is discontinued if it is
determined that the derivative is not highly effective.
For derivatives that either do not qualify for hedge accounting or are not designated as hedges, all changes in the fair
value of the derivative are recognized in earnings. For qualifying cash flow hedges, the effective portion of the change in the
fair value of the derivative is recorded as a component of Other Comprehensive Income (“OCI”) and recognized in earnings
when the hedged cash flows affect earnings. The ineffective portion of the derivative gain or loss, as well as changes in the fair
value of the derivative’s time value are recognized in current period earnings. The effectiveness of the hedge is assessed based
on changes in the fair value attributable to changes in spot prices. The changes in the fair value of the derivative contract
related to the changes in the difference between the spot price and the forward price are excluded from the assessment of hedge
effectiveness and are also recognized in current period earnings. If the cash flow hedge relationship is terminated, the derivative
gains or losses that are deferred in OCI will be recognized in earnings when the hedged cash flows occur. However, for cash
flow hedges that are terminated because the forecasted transaction is not expected to occur in the original specified time period,
or a two-month period thereafter, the derivative gains or losses are immediately recognized in earnings.
The Company uses derivative instruments, primarily forward contracts designated as cash flow hedges, to hedge the
foreign currency exposure associated with forecasted foreign-currency-denominated intercompany inventory sales to foreign
subsidiaries and the related settlement of the foreign-currency-denominated inter-company accounts receivable. Fluctuations in
exchange rates will either increase or decrease the Company’s U.S. dollar equivalent cash flows and affect the Company’s U.S.
dollar earnings. Gains or losses on the foreign exchange forward contracts that are used to hedge these exposures are expected
to partially offset this variability. Foreign exchange forward contracts represent agreements to exchange the currency of one
country for the currency of another country at an agreed-upon settlement date. As of February 2, 2013, the maximum length of
time over which forecasted foreign-currency-denominated inter-company inventory sales were hedged was ten months. The
sale of the inventory to the Company’s customers will result in the reclassification of related derivative gains and losses that are
reported in Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss). Substantially all of the remaining unrealized gains or losses
related to foreign-currency-denominated inter-company inventory sales that have occurred as of February 2, 2013 will be
recognized in costs of goods sold over the following two months at the values at the date the inventory was sold to the
respective subsidiary.
The Company nets derivative assets and liabilities on the Consolidated Balance Sheets to the extent that master netting
arrangements meet the specific accounting requirements set forth by U.S. GAAP.
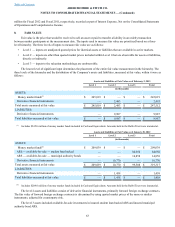
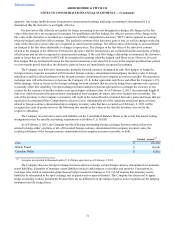
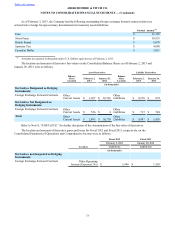
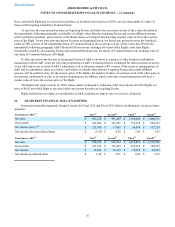
As of February 2, 2013, the Company had the following outstanding foreign exchange forward contracts that were
entered to hedge either a portion, or all, of forecasted foreign-currency-denominated inter-company inventory sales, the
resulting settlement of the foreign-currency-denominated inter-company accounts receivable, or both:
Notional Amount(1)
Euro $ 151,138
British Pound $ 98,600
Canadian Dollar $ 8,816
(1) Amounts are reported in thousands and in U.S. Dollars equivalent as of February 2, 2013.
The Company also uses foreign exchange forward contracts to hedge certain foreign currency denominated net monetary
assets/liabilities. Examples of monetary assets/liabilities include cash balances, receivables and payables. Fluctuations in
exchange rates result in transaction gains/(losses) being recorded in earnings as U.S. GAAP requires that monetary assets/
liabilities be remeasured at the spot exchange rate at quarter-end or upon settlement. The Company has chosen not to apply
hedge accounting to these instruments because there are no differences in the timing of gain or loss recognition on the hedging
instrument and the hedged item.
Table of Contents ABERCROMBIE & FITCH CO.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)