Rosetta Stone 2010 Annual Report Download - page 89
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 89 of the 2010 Rosetta Stone annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Table of Contents
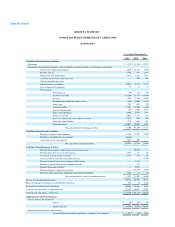
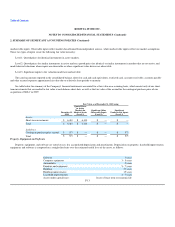
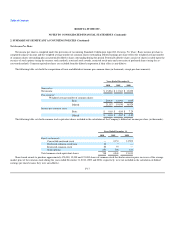
ROSETTA STONE INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
2. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (Continued)
interpretation of this standard. In accordance with this standard, derivative instruments are recognized as either assets or liabilities in the balance sheet and are
measured at fair values with gains or losses recognized in earnings. Embedded derivatives that are not clearly and closely related to the host contract are
bifurcated and are recognized at fair value with changes in fair value recognized as either a gain or loss in earnings. The Company determines the fair value of
derivative instruments and hybrid instruments based on available market data using appropriate valuation models, giving consideration to all of the rights and
obligations of each instrument.
Stock Split
On March 23, 2009, in connection with the Company's initial public offering of common stock, the Board of Directors approved a 1.3-to-1 split of
common stock to stockholders of record as of such date. All references to the number of common shares and per share amounts have been restated as
appropriate to reflect the effect of the split for all periods presented.
Guarantees
Indemnifications are provided of varying scope and size to certain institutional customers against claims of intellectual property infringement made by
third parties arising from the use of its products. The Company has not incurred any costs or accrued any liabilities as a result of such obligations.
Cost of Revenue
Cost of product revenue consists of the direct and indirect materials and labor costs to produce and distribute our products. Such costs include packaging
materials, computer headsets, freight, inventory receiving, personnel costs associated with product assembly, third-party royalty fees and inventory storage,
obsolescence and shrinkage. Cost of subscription and service revenue primarily represents costs associated with supporting our online language learning
service, which includes hosting costs and depreciation. We also include the cost of credit card processing and customer technical support in both cost of
product revenue and cost of subscription and service revenue.
Research and Development
Research and development expenses include employee compensation costs, professional services fees and overhead costs associated with product
development. Software products are developed for sale to external customers. The Company considers technological feasibility to be established when all
planning, designing, coding, and testing has been completed according to design specifications. The Company has determined that technological feasibility for
its software products is reached shortly before the products are released to manufacturing. Costs incurred after technological feasibility is established have not
been material, and accordingly, the Company has expensed all research and development costs when incurred.
Software Developed for Internal Use
Product development also includes certain software products for internal use. Development costs for internal use software are expensed as incurred until
the project reaches the application development stage, in accordance with Accounting Standards Codification topic 350, Accounting for the Costs of
Computer Software Developed or Obtained for Internal Use ("ASC 350"). Internal-use software is defined
F-15