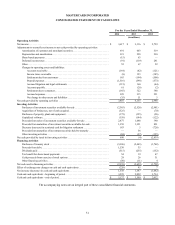
MasterCard 2014 Annual Report Download - page 57
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 57 of the 2014 MasterCard annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.MASTERCARD INCORPORATED
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS – (Continued)
55
The Valuation Hierarchy is based upon the transparency of inputs to the valuation of an asset or liability as of the measurement
date. A financial instrument’s categorization within the Valuation Hierarchy is based upon the lowest level of input that is significant
to the fair value measurement. The three levels of the Valuation Hierarchy are as follows:
• Level 1 - inputs to the valuation methodology are quoted prices (unadjusted) for identical assets or liabilities in active
markets.
• Level 2 - inputs to the valuation methodology include quoted prices for similar assets and liabilities in active markets,
quoted prices for identical assets and liabilities in inactive markets and inputs that are observable for the asset or liability,
either directly or indirectly, for substantially the full term of the financial instrument.
• Level 3 - inputs to the valuation methodology are unobservable and cannot be directly corroborated by observable market
data.
Certain assets are measured at fair value on a nonrecurring basis. The Company’s assets measured at fair value on a nonrecurring
basis include property, plant and equipment, nonmarketable equity investments, goodwill and other intangible assets. These assets
are subject to fair value adjustments in certain circumstances, such as when there is evidence of impairment.
The valuation methods for goodwill and other intangible assets involve assumptions concerning comparable company multiples,
discount rates, growth projections and other assumptions of future business conditions. The Company uses an income approach
for estimating the fair value of its intangible assets and a market approach for estimating the fair value of its reporting unit, when
necessary. As the assumptions employed to measure these assets and liabilities on a nonrecurring basis are based on management’s
judgment using internal and external data, these fair value determinations are classified in Level 3 of the Valuation Hierarchy.
Investment securities - The Company classifies investments in debt and equity securities as available-for-sale. Available-for-sale
securities that are available to meet the Company’s current operational needs are classified as current assets. Available-for-sale
securities that are not available to meet the Company’s current operational needs are classified as non-current assets.
The investments in debt and equity securities are carried at fair value, with unrealized gains and losses, net of applicable taxes,
recorded as a separate component of other comprehensive income on the consolidated statement of comprehensive income. Net
realized gains and losses on debt and equity securities are recognized in investment income on the consolidated statement of
operations. The specific identification method is used to determine realized gains and losses.
Derivative financial instruments - The Company records all derivatives at fair value. The Company’s foreign exchange forward
contracts are included in Level 2 of the Valuation Hierarchy as the fair value of these contracts are based on broker quotes for the
same or similar instruments. Changes in the fair value of derivative instruments are reported in current-period earnings. These
derivative contracts hedge foreign exchange risk and were not entered into for trading or speculative purposes. The Company did
not have any derivative contracts accounted for under hedge accounting as of December 31, 2014 and 2013.
Settlement due from/due to customers - The Company operates systems for clearing and settling payment transactions among
MasterCard customers. Net settlements are generally cleared daily among customers through settlement cash accounts by wire
transfer or other bank clearing means. However, some transactions may not settle until subsequent business days, resulting in
amounts due from and due to MasterCard customers.
Restricted security deposits held for MasterCard customers - MasterCard requires collateral from certain customers for settlement
of their transactions. The majority of collateral for settlement is in the form of standby letters of credit and bank guarantees which
are not recorded on the balance sheet. Additionally, MasterCard holds cash deposits and certificates of deposit from certain
customers of MasterCard as collateral for settlement of their transactions. These assets are fully offset by corresponding liabilities
included on the consolidated balance sheet.
Property, plant and equipment - Property, plant and equipment are stated at cost less accumulated depreciation and amortization.
Depreciation and amortization is computed using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the assets. Depreciation
of leasehold improvements and amortization of capital leases is included in depreciation and amortization expense.