Kraft 2001 Annual Report Download - page 41
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 41 of the 2001 Kraft annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Kraft Foods Inc.
35
Commodities: The Company is exposed to price risk related to
forecasted purchases of certain commodities used as raw
materials by the Company’s businesses. Accordingly, the Company
uses commodity forward contracts, as cash flow hedges, primarily
for coffee, cocoa, milk, cheese and wheat. Commodity futures and
options are also used to hedge the price of certain commodities,
including milk, coffee, cocoa, wheat, corn, sugar and soybean.
At December 31, 2001 and 2000, the Company had net long
commodity positions of $589 million and $617 million, respectively.
Interest Rates: The Company uses interest rate swaps to hedge
the fair value of an insignificant portion of its long-term debt. The
differential to be paid or received is accrued and recognized as
interest expense. If an interest rate swap agreement is terminated
prior to maturity, the realized gain or loss is recognized over the
remaining life of the agreement if the hedged amount remains
outstanding, or immediately if the underlying hedged exposure does
not remain outstanding. If the underlying exposure is terminated
prior to the maturity of the interest rate swap, the unrealized gain or
loss on the related interest rate swap is recognized in earnings
currently. At December 31, 2001, the aggregate notional principal
amount of those agreements, which converted fixed-rate debt to
variable-rate debt, was $102 million. Aggregate maturities at
December 31, 2001 were $29 million in 2003 and $73 million in
2004. During the year ended December 31, 2001, there was no
ineffectiveness relating to these fair value hedges.
Value at Risk: The Company uses a value at risk (“VAR”)
computation to estimate the potential one-day loss in the fair value
of its interest rate-sensitive financial instruments and to estimate
the potential one-day loss in pre-tax earnings of its foreign currency
and commodity price-sensitive derivative financial instruments.
The VAR computation includes the Company’s debt; short-term
investments; foreign currency forwards, swaps and options; and
commodity futures, forwards and options. Anticipated transactions,
foreign currency trade payables and receivables, and net
investments in foreign subsidiaries, which the foregoing instruments
are intended to hedge, were excluded from the computation.
The VAR estimates were made assuming normal market
conditions, using a 95% confidence interval. The Company used
a “variance/co-variance” model to determine the observed
interrelationships between movements in interest rates and various
currencies. These interrelationships were determined by observing
interest rate and forward currency rate movements over the
preceding quarter for the calculation of VAR amounts at December
31, 2001 and 2000, and over each of the four preceding quarters
for the calculation of average VAR amounts during each year. The
values of foreign currency and commodity options do not change
on a one-to-one basis with the underlying currency or commodity,
and were valued accordingly in the VAR computation.
The estimated potential one-day loss in fair value of the Company’s
interest rate-sensitive instruments, primarily debt, under normal
market conditions and the estimated potential one-day loss in pre-
tax earnings from foreign currency and commodity instruments
under normal market conditions, as calculated in the VAR model,
were as follows:
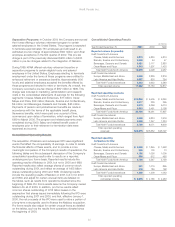
Pre-Tax Earnings Impact
(in millions) At 12/31/01 Average High Low
Instruments sensitive to:
Foreign currency rates $ 2 $6 $13 $2
Commodity prices 57115
Fair Value Impact
(in millions) At 12/31/01 Average High Low
Instruments sensitive to:
Interest rates $122 $79 $122 $56
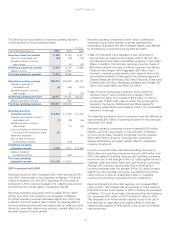
Pre-Tax Earnings Impact
(in millions) At 12/31/00 Average High Low
Instruments sensitive to:
Foreign currency rates $ 20 $20 $ 24 $15
Commodity prices 98 97
Fair Value Impact
(in millions) At 12/31/00 Average High Low
Instruments sensitive to:
Interest rates $166 $83 $166 $39