Harley Davidson 2013 Annual Report Download - page 39
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 39 of the 2013 Harley Davidson annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
39
Income Taxes – The Company accounts for income taxes in accordance with ASC Topic 740, “Income Taxes.” Deferred
tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the future tax consequences attributable to differences between financial statement
carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases and operating loss and other loss carry-
forwards. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the
years in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled.
The Company is subject to income taxes in the United States and numerous foreign jurisdictions. Significant judgment is
required in determining the Company’s worldwide provision for income taxes and recording the related deferred tax assets and
liabilities. In the ordinary course of the Company’s business, there are transactions and calculations where the ultimate tax
determination is uncertain. Accruals for unrecognized tax benefits are provided for in accordance with the requirements of ASC
Topic 740. An unrecognized tax benefit represents the difference between the recognition of benefits related to items for
income tax reporting purposes and financial reporting purposes. The unrecognized tax benefit is included within other long-
term liabilities in the Consolidated Balance Sheets. The Company has a reserve for interest and penalties on exposure items, if
applicable, which is recorded as a component of the overall income tax provision. The Company is regularly under audit by tax
authorities. Although the outcome of tax audits is always uncertain, management believes that it has appropriate support for the
positions taken on its tax returns and that its annual tax provision includes amounts sufficient to pay any assessments.
Nonetheless, the amounts ultimately paid, if any, upon resolution of the issues raised by the taxing authorities may differ
materially from the amounts accrued for each year.
Contractual Obligations
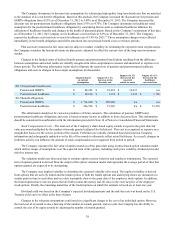
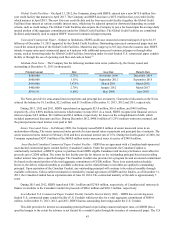
A summary of the Company’s expected payments for significant contractual obligations as of December 31, 2013 is as
follows (in thousands):
2014 2015 - 2016 2017 - 2018 Thereafter Total
Principal payments on debt $ 1,834,591 $ 1,761,324 $ 1,663,255 $ — $ 5,259,170
Interest payments on debt 146,815 189,948 95,711 — 432,474
Operating lease payments 10,866 17,421 10,477 19,790 58,554
$ 1,992,272 $ 1,968,693 $ 1,769,443 $ 19,790 $ 5,750,198
Interest for floating rate instruments assumes December 31, 2013 rates remain constant.
As of December 31, 2013, the Company generally had no significant purchase obligations, other than those created in the
ordinary course of business, which largely have terms of less than 90 days.
The Company has long-term obligations related to its pension, SERPA and postretirement healthcare plans at
December 31, 2013. During 2013, the Company contributed $204.8 million to its pension, SERPA and postretirement
healthcare plans, which included a $175.0 million voluntary contribution to its pension plan. No additional contributions were
required during 2013 beyond current benefit payments for SERPA and postretirement healthcare plans. The Company does not
expect to make any additional qualified pension plan contributions in 2014.(1) Also, the Company expects it will continue to
make on-going contributions related to current benefit payments for SERPA and postretirement healthcare plans.(1) The
Company’s expected future contributions to these plans are provided in Note 14 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
As described in Note 13 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, the Company has unrecognized tax benefits of
$63.1 million and accrued interest and penalties of $24.4 million as of December 31, 2013. However, the Company cannot
make a reasonably reliable estimate for the period of cash settlement for either the liability for unrecognized tax benefits or
accrued interest and penalties.
Commitments and Contingencies
The Company is subject to lawsuits and other claims related to environmental, product and other matters. In determining
required reserves related to these items, the Company carefully analyzes cases and considers the likelihood of adverse
judgments or outcomes, as well as the potential range of possible loss. The required reserves are monitored on an ongoing basis
and are updated based on new developments or new information in each matter.