Dollar General 2003 Annual Report Download - page 31
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 31 of the 2003 Dollar General annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Impairment of long-lived assets
When indicators of impairment are present, the Company evaluates the carrying value of long-lived assets, other than goodwill, in
relation to the operating performance and future undiscounted cash flows or the appraised values of the underlying assets. The
Company adjusts the net book value of the underlying assets if the sum of expected future cash flows or the appraised value is less
than the book value. Assets to be disposed of are adjusted to the fair value less the cost to sell if less than the book value. The
Company recorded impairment charges of approximately $0.6 million and $1.1 million in 2003 and 2001, respectively, to reduce the
carrying value of the Homerville, Georgia DC (which was closed in fiscal 2000). The Company also recorded an impairment charge
of approximately $0.2 million in 2003 to reduce the carrying value of 14 of its stores based upon negative sales trends and cash
flows at these locations. These charges are included in Selling, general and administrative ("SG&A") expense.
Investments in securities
The Company accounts for investments in debt and equity securities in accordance with Statement of Financial Accounting
Standards ("SFAS") No. 115, "Accounting for Certain Investments in Debt and Equity Securities."
Other assets
Other assets consist primarily of debt issuance costs which are amortized over the life of the related obligations, utility and security
deposits, life insurance policies and goodwill.
Vendor rebates
The Company records vendor rebates, primarily consisting of new store allowances and volume purchase rebates, when realized.
The rebates are recorded as a reduction to inventory purchases, at cost, which has the effect of reducing cost of goods sold, as pre-
scribed by Emerging Issues Task Force ("EITF") Issue No. 02-16, "Accounting by a Customer (including a Reseller) for Certain
Consideration Received from a Vendor" ("EITF 02-16").
Operating leases
Contingent rentals. The Company recognizes contingent rental expense when the achievement of specified sales targets are con-
sidered probable, in accordance with EITF Issue No. 98-9, "Accounting for Contingent Rent." The amount expensed but not paid
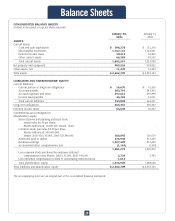
as of January 30, 2004 and January 31, 2003 was approximately $8.9 million and $9.0 million, respectively, and is included in
Accrued expenses and other in the consolidated balance sheets. (See Notes 3 and 7).
Deferred rent. The Company records rental expense on a straight-line basis over the base, non-cancelable lease term. Any differ-
ence between the calculated expense and the amounts actually paid are reflected as a liability in Accrued expenses and other in
the consolidated balance sheets and totaled approximately $8.4 million and $6.7 million at January 30, 2004 and January 31, 2003,
respectively.
Insurance claims provisions
The Company retains a significant portion of risk for its workers' compensation, employee health, general liability, property and
automobile claim exposures. Accordingly, provisions are made for the Company's estimates of such risks. Actuaries are utilized
to determine the undiscounted future claim costs for the workers' compensation, general liability, and health claim risks. To the
extent that subsequent claim costs vary from those estimates, future results of operations will be affected. The Greater Cumberland
Insurance Company ("GCIC"), a Vermont-based wholly-owned captive insurance subsidiary of the Company, charges the operating
subsidiary companies premiums to insure the retained workers' compensation and non-property general liability exposures. GCIC
currently insures no unrelated third-party risk.
Fair value of financial instruments
The carrying amounts reflected in the consolidated balance sheets for cash, cash equivalents, receivables and payables approxi-
mate their respective fair values. At January 30, 2004 and January 31, 2003, the fair value of the Company’s debt, excluding capi-
tal lease obligations, was approximately $265.4 million (net of the fair value of a note receivable on the South Boston, Virginia DC
of $48.9 million, as discussed in Note 7) and $287.0 million, respectively, based upon the estimated market value of the debt at those
dates. Such fair value exceeds the carrying value of the debt at January 30, 2004 by approximately $21.7 million and is less than
the carrying value of the debt at January 31, 2003 by approximately $7.4 million. Fair values are based primarily on quoted prices
for those or similar instruments. A discussion of the carrying value and fair value of the Company’s derivative financial instruments
is included in the section entitled "Derivative financial instruments" below.
Notes
29