Qantas 2015 Annual Report Download - page 86
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 86 of the 2015 Qantas annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
85
QANTAS ANNUAL REPORT 2015
Forward foreign exchange contracts and currency options are used to hedge a portion of remaining net foreign currency revenue or
expenditure in accordance with Qantas Group policy. Net foreign currency revenue and expenditure out to two years may be hedged
within specific parameters, with any hedging outside these parameters requiring approval by the Board. Purchases and disposals
of property, plant and equipment denominated in a foreign currency may be hedged out to two years using a combination of forward
foreign exchange contracts and currency options.
For the year ended 30 June 2015, other financial assets and liabilities included derivative financial instruments used to hedge foreign
currency, including hedging of future capital and operating expenditure payments, totalling $54 million (net asset) (2014: $2 million
(net liability)). These are recognised at fair value in accordance with AASB 9.
iii. Future AUD Fuel Costs
The Qantas Group uses options and swaps on jet kerosene, gasoil and crude oil to hedge exposure to movements in the USD price of
aviation fuel. Qantas considers the crude component to be a separately identifiable and measureable component of aviation fuel.
The foreign exchange risk in the total fuel cost is separately hedged using foreign exchange contracts and currency options. Hedging
is conducted in accordance with Qantas Group policy. Fuel consumption out to two years may be hedged within specific parameters,
with any hedging outside these parameters requiring approval by the Board.
For the year ended 30 June 2015, other financial assets and liabilities include fuel and foreign exchange derivatives totalling
$120million (net asset) (2014: $24 million (net asset)). These are recognised at fair value in accordance with AASB 9.
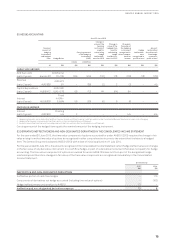
iv. Sensitivity on Interest Rate, Foreign Exchange and Fuel Price Risk
The table below summarises the gain/(loss) impact of reasonably possible changes in market risk, relating to existing financial
instruments, on net profit and equity before tax. For the purpose of this disclosure, the following assumptions were used:
–100 basis points (2014: 100 basis points) increase and decrease in all relevant interest rates
–20 per cent (2014: 20 per cent) USD depreciation and USD appreciation
–20 per cent (2014: 20 per cent) increase and decrease in all relevant fuel indices
–Sensitivity analysis assumes hedge designations as at 30 June 2015 remain unchanged and that all designations are effective
–Sensitivity analysis on foreign currency pairs and fuel indices of 20 per cent represent recent volatile market conditions
–Sensitivity analysis assumes an offset between USD and fuel price indices based on observed market movements
Profit Before Tax Equity (Before Tax)
Qantas Group
$M 2015 2014 2015 2014
100bps increase in interest rates
Variable rate interest-bearing instruments (net of cash) (10) (18) – –
Derivatives designated in a cash flow hedge relationship – – 21 25
Derivatives and fixed rate debt in a fair value hedge relationship ––––
100bps decrease in interest rates
Variable rate interest-bearing instruments (net of cash) 10 18 – –
Derivatives designated in a cash flow hedge relationship – – (22) (26)
Derivatives and fixed rate debt in a fair value hedge relationship – – – –
20% movement in AUD fuel costs
20% (2014: 20%) USD depreciation, 20% (2014: 20%) increase
perbarrel in fuel indices –(77) (26) 14
20% (2014: 20%) USD appreciation, 20% (2014: 20%) decrease
perbarrel in fuel indices –(61) 519 723
(C) CREDIT RISK
Credit risk is the potential loss from a transaction in the event of default by the counterparty during the term of the transaction or on
settlement of the transaction. Credit exposure is measured as the cost to replace existing transactions should a counterparty default.
The Qantas Group conducts transactions with the following major types of counterparties:
–Trade debtor counterparties: the credit risk is the recognised amount, net of any impairment losses. As at 30 June 2015, trade
debtors amounted to $710 million (2014: $721 million). The Qantas Group has credit risk associated with travel agents, industry
settlement organisations and credit provided to direct customers. The Qantas Group minimises this credit risk through the
application of stringent credit policies and accreditation of travel agents through industry programs.
–Other financial asset counterparties: the Qantas Group restricts its dealings to counterparties that have acceptable credit ratings.
Should the rating of a counterparty fall below certain levels, internal policy dictates that approval by the Board is required to
maintain the level of the counterparty exposure.