ICICI Bank 2015 Annual Report Download - page 107
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 107 of the 2015 ICICI Bank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
105Annual Report 2014-2015
Directed lending
RBI requires banks to lend to certain sectors of the economy. Such directed lending comprises priority sector lending and
export credit.
RBI guideline on priority sector lending requires the banks to lend 40.0% of their adjusted net bank credit (ANBC) to certain
activities carried out by the specified borrowers. The definition of ANBC includes certain investments and is computed
with reference to the respective amounts at March 31 of the previous year. Further, RBI allowed exclusion from ANBC for
loans extended in India against incremental FCNR (B)/NRE deposits from the date of July 26, 2013 and outstanding as on
March 7, 2014.
Priority sector includes lending to agricultural sector, food and agri-based industries, small enterprises/businesses and
housing finance up to certain limits. Out of the 40.0%, banks are required to lend a minimum of 18.0% of their ANBC to the
agriculture sector and the balance to certain specified sectors. The banks are also required to lend 10.0% of their ANBC to
certain borrowers under weaker sections category.
The Bank is required to comply with the priority sector lending requirements prescribed by RBI from time to time. The
shortfall in the amount required to be lent to the priority sectors and weaker sections may be required to be deposited with
government sponsored Indian development banks like the National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development/Small
Industries Development Bank of India/National Housing Bank/other Financial Institutions, as decided by RBI from time to
time, based on the allocations made by RBI. These deposits have a maturity of up to seven years and carry interest rates
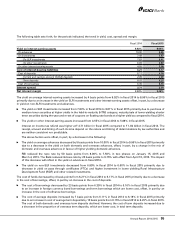
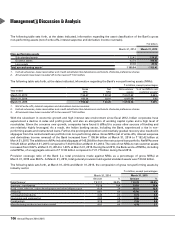
lower than market rates. At March 31, 2015, the Bank’s total investment in such bonds was ` 284.51 billion, of which the
amount eligible for consideration in overall priority sector achievement was ` 243.23 billion.
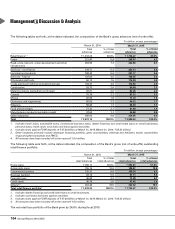
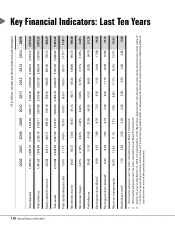
The Bank’s priority sector lending increased from ` 1,010.30 billion at March 31, 2014 to ` 1,130.07 billion at
March 31, 2015, constituting 41.0% (March 31, 2014: 43.4%) of ANBC against the requirement of 40.0% of ANBC. The
qualifying total agriculture loans increased from ` 250.61 billion at March 31, 2014 to ` 332.67 billion at March 31, 2015,
constituting 12.1% (March 31, 2014: 10.8%) of ANBC against the requirement of 18.0%. The advances to direct agriculture
increased from ` 145.85 billion at March 31, 2014 to ` 208.73 billion at March 31, 2015, constituting about 56.1%
(March 31, 2014: 46.4%) of the requirement. The advances to weaker sections increased from ` 62.78 billion at
March 31, 2014 to ` 94.89 billion at March 31, 2015 constituting about 34.5% (March 31, 2014: 27.0%) of the requirement.
In April 2015, RBI issued revised guidelines on priority sector lending, based on the report of the internal working group set
up to revisit priority sector lending. As per the guidelines, the overall target for priority sector lending would continue to be
40% of adjusted net bank credit; sub-targets for direct and indirect lending to agriculture were combined; and sub-targets
of 8.0% for lending to small & marginal farmers and 7.5% lending target to micro-enterprises were introduced. These
sub-targets are to be achieved in a phased manner by March 2017. Sectors qualifying for priority sector lending have been
broadened to include medium enterprises, social infrastructure and renewable energy. Priority sector lending achievement
would be evaluated on a quarterly average basis from fiscal 2017.
Classification of loans
The Bank classifies its assets as performing and non-performing in accordance with RBI guidelines. Under RBI guidelines,
an asset is classified as non-performing if any amount of interest or principal remains overdue for more than 90 days, in
respect of term loans. In respect of overdraft or cash credit, an asset is classified as non-performing if the account remains
out of order for a period of 90 days and in respect of bills, if the account remains overdue for more than 90 days. Loans and
advances held at the overseas branches that are identified as impaired as per host country regulations for reasons other
than record of recovery, but which are standard as per the RBI guidelines, are classified as non-performing to the extent of
amount outstanding in the host country.
RBI has separate guidelines for restructured loans. A fully secured standard asset can be restructured by re-schedulement of
principal repayments and/or the interest element, but must be separately disclosed as a restructured asset. The diminution
in the fair value of the loan, if any, measured in present value terms, is either written off or a provision is made to the extent
of the diminution involved. Similar guidelines apply to sub-standard loans.