Food Lion 2013 Annual Report Download - page 66
Download and view the complete annual report
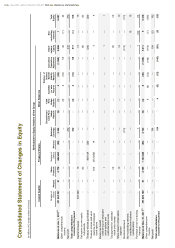
Please find page 66 of the 2013 Food Lion annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
In order to manage its identified and quantified market risks, Delhaize
Group uses derivative financial instruments such as foreign exchange
forward contracts, interest rate swaps, currency swaps and other
derivative instruments. These financial instruments are not used for
speculative purposes.
Funding and Liquidity Risk
Funding and liquidity risk is the risk that the Group will encounter
difficulty in meeting payment obligations when they come due. Del-
haize Group manages this exposure by closely monitoring its liquidity
resources, consisting of a combination of retained cash flows, bank
facilities, long-term debt and leases, which are essential to fulfil working
capital, capital expenditures and debt servicing requirements.
Delhaize Group operates an international cash-pooling structure in
order to centralize cash on a daily basis wherever possible. At year-end
2013 the Group’s cash and cash equivalents amounted to €1 149 million.
Delhaize Group also monitors the amount of short-term funding, the
mix of short-term funding to total debt and the availability of committed
credit facilities in relation to the level of outstanding short-term debt (see
Note 18.2 “Short-term Borrowings” in the Financial Statements). At year-
end 2013, the Group had committed and undrawn credit lines totalling
€725 million. These credit lines consisted of a syndicated multicurrency
credit facility of €600 million for the Company and certain of its subsidi-
aries including Delhaize America, LLC and €125 million of bilateral credit
facilities for the European entities. In addition, the Group had €25 million
of committed credit facilities for letters of credit and guarantees of
which €9 million was used. At December 31, 2013, the maturities of the
committed credit facilities were as follows: €25 million maturing in 2014,
€75 million maturing in 2015 and €650 million maturing in 2016.
Delhaize Group pro-actively monitors the maturities of its outstanding debt
in order to reduce refinancing risk. At December 31, 2013, the expected
redemption values of the long-term debt through 2018 were €210 million
in 2014, €1 million in 2015, €7 million in 2016, €325 million in 2017 and
€400 million in 2018 after the effect of interest rate swaps and cross-cur-
rency interest rate swaps. As described in Note 18.1 ”Long-term Debt” in the
Financial Statements the debt maturing in 2014 has been largely refinanced
and no significant principal payment of financial debt is due until 2017.
Delhaize Group’s long-term issuer ratings from Standard & Poor’s and
Moody’s are BBB- (stable) and Baa3 (stable) respectively. These credit
ratings are supported by cross-guarantee arrangements among
Delhaize Group and substantially all of Delhaize Group’s U.S. subsidi-
aries, whereby the entities are guaranteeing each other’s financial debt
obligations. Delhaize Group leverages its investment grade credit rating
to optimally refinance maturing debt.
As also described in Notes 18.1 ”Long-term Debt” and 18.2 “Short-term
Borrowings” in the Financial Statements, the Group is subject to certain
financial and non-financial covenants related to its long- and short-term
debt instruments, which contain certain accelerated repayment terms
that are detailed in these Notes.
Interest Rate Risk
Interest rate risk arises on interest-bearing financial instruments and
represents the risk that the fair value or the associated interest cash
flows of the underlying financial instrument will fluctuate because of
future changes in market interest rates.
Delhaize Group’s interest rate risk management objectives are to
reduce earnings volatility, to minimize interest expense over the long
term, and to protect future cash flows from the impact of material
adverse movements in interest rates.
Delhaize Group reviews its interest rate risk exposure on a quarterly
basis and at the inception of any new financing operation. As part of its
interest rate risk management activities, the Group may enter into inter-
est rate swap agreements (see Note 19 ”Derivative Financial Instruments
and Hedging” in the Financial Statements). At the end of 2013, 74.3% of
the financial debt after swaps of the Group carried a fixed interest rate
(2012: 75.8%; 2011: 75.1%).
The sensitivity analysis presented in the table on the page 66 estimates
the impact on the net financial expenses (with all other variables held
constant) and equity of a parallel shift in the interest rate curve. The shift
in that curve is based on the standard deviation of daily volatilities of the
“Reference Interest Rates” (Euribor 3 months and Libor 3 months) during
the year, within a 95% confidence interval.
Currency Risk
Delhaize Group’s foreign currency risk management objectives are to
minimize the impact of currency fluctuations on the Group’s income
statement, cash flows and balance sheet, using foreign exchange con-
tracts, including derivative financial instruments such as currency swaps
and forward instruments (see Note 19 ”Derivative Financial Instruments
and Hedging” in the Financial Statements).
Translation exposure
The results of operations and the financial position of each of Delhaize
Group’s entities outside the euro zone are accounted for in the relevant
local currency and then translated into euros at the applicable foreign
currency exchange rate for inclusion in the Group’s consolidated
financial statements, which are presented in euros (see also Note 2.3
”Summary of Significant Accounting Policies” in the Financial Statements
with respect to translation of foreign currencies).
Delhaize Group does not hedge this “translation exposure”. However,
the Group aims to minimize this exposure by funding the operations of
Delhaize Group’s entities in their local currency, wherever feasible.
If the average U.S. dollar exchange rate had been 1 cent higher/lower
and all other variables were held constant, the Group’s net profit would
have increased/decreased by €1 million in 2013 (€2 million in 2012 and
2011), solely due to the translation of the financial statements denom-
inated in U.S. dollars. The effect from the translation of the functional
currency to the reporting currency of the Group does not affect the cash
flows in local currencies.
In 2013, 64% of the Group’s EBITDA was generated in U.S. dollars (63%
and 69% in 2012 and 2011, respectively). At December 31, 2013, 69% of
64
DELHAIZE GROUP ANNUAL REPORT 2013
RISK FACTORS