Entergy 2005 Annual Report Download - page 92
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 92 of the 2005 Entergy annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
ENTERGY CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES 2005
*
88
NOTES to CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS continuedNOTES to CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS continued
OTHER POSTRETIREMENT BENEFITS
Entergy also currently provides health care and life insurance bene-
fits for retired employees. Substantially all domestic employees may
become eligible for these benefits if they reach retirement age while
still working for Entergy. Entergy uses a December 31 measurement
date for its postretirement benefit plans.
Effective January 1, 1993, Entergy adopted SFAS 106, which
required a change from a cash method to an accrual method of
accounting for postretirement benefits other than pensions. At
January 1, 1993, the actuarially determined accumulated postretire-
ment benefit obligation (APBO) earned by retirees and active
employees was estimated to be approximately $241.4 million for
Entergy (other than Entergy Gulf States) and $128 million for
Entergy Gulf States. Such obligations are being amortized over a
20-year period that began in 1993. For the most part, the domestic
utility companies and System Energy recover SFAS 106 costs
from customers and are required to fund postretirement benefits
collected in rates to an external trust.
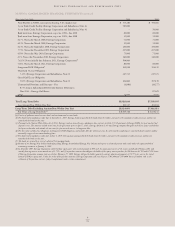
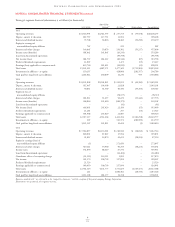
COMPONENTS OF NET OTHER POSTRETIREMENT
BENEFIT COST
Total 2005, 2004, and 2003 other postretirement benefit costs of
Entergy Corporation and its subsidiaries, including amounts capitalized
and deferred, included the following components (in thousands):
2005 2004 2003
Service cost – benefits earned
during the period $ 37,310 $ 30,947 $ 37,799
Interest cost on APBO 51,883 53,801 52,746
Expected return on assets (17,402) (18,825) (15,810)
Amortization of
transition obligation 3,368 9,429 15,193
Amortization of
prior service cost (13,738) (5,222) (925)
Recognized net (gain)/loss 22,295 15,546 12,369
Curtailment loss – – 57,958
Special termination benefits – – 5,444
Net other postretirement
benefit cost $ 83,716 $ 85,676 $164,774
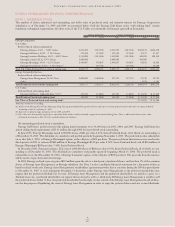
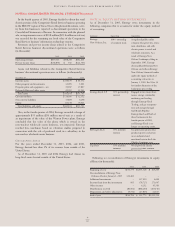
OTHER POSTRETIREMENT BENEFIT OBLIGATIONS,
PLAN ASSETS, FUNDED STATUS, AND AMOUNTS
NOT YET RECOGNIZED AND RECOGNIZED IN THE
BALANCE SHEET AS OF DECEMBER 31, 2005 AND 2004
(IN THOUSANDS):
2005 2004
Change in APBO
Balance at beginning of year $ 928,217 $ 941,803
Service cost 37,310 30,947
Interest cost 51,883 53,801
Actuarial loss 98,041 73,890
Benefits paid (60,031) (66,456)
Plan amendments (64,200) (60,231)
Plan participant contributions 6,749 9,312
Balance at end of year $ 997,969 $ 983,066
Change in Plan Assets
Fair value of assets at
beginning of year $ 214,005 $ 227,446
Actual return on plan assets 15,003 15,550
Employer contributions 58,790 63,399
Plan participant contributions 6,749 9,312
Benefits paid (60,031) (66,455)
Fair value of assets
at end of year $ 234,516 $ 249,252
Funded status $(763,453) $ (733,814)
Amounts not yet recognized
in the balance sheet
Unrecognized transition obligation 15,176 5,594
Unrecognized prior service cost (66,105) (39,560)
Unrecognized net loss 403,252 391,940
Accrued other postretirement benefit
cost recognized in the balance sheet $(411,130) $ (375,840)
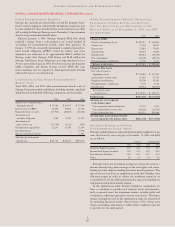
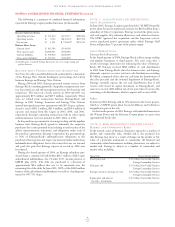
QUALIFIED PENSION AND OTHER
POSTRETIREMENT PLANS’ ASSETS
Entergy’s qualified pension and postretirement plans weighted-average
asset allocations by asset category at December 31, 2005 and 2004
are as follows:
Pension Postretirement
2005 2004 2005 2004
Domestic Equity Securities 45% 46% 37% 38%
International Equity Securities 21% 21% 15% 14%
Fixed–Income Securities 32% 31% 47% 47%
Other 2% 2% 1% 1%
Entergy’s trust asset investment strategy is to invest the assets in a
manner whereby long-term earnings on the assets (plus cash contri-
butions) provide adequate funding for retiree benefit payments. The
mix of assets is based on an optimization study that identifies asset
allocation targets in order to achieve the maximum return for an
acceptable level of risk, while minimizing the expected contributions
and pension and postretirement expense.
In the optimization study, Entergy formulates assumptions (or
hires a consultant to provide such analysis) about characteristics,
such as expected asset class investment returns, volatility (risk), and
correlation coefficients among the various asset classes. The future
market assumptions used in the optimization study are determined
by examining historical market characteristics of the various asset
classes, and making adjustments to reflect future conditions expected
to prevail over the study period.