Bank of the West 2014 Annual Report Download - page 39
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 39 of the 2014 Bank of the West annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
affect our results of operations for a particular period, based upon consultation with counsel, management does not
expect that the aggregate liability, if any, resulting from these proceedings would have a material effect on the Bank’s
consolidated balance sheets, consolidated statements of income or liquidity.
14. Derivative Financial Instruments
The Bank enters into derivative contracts primarily to manage its interest rate risk, as well as for customer
accommodation purposes. The derivatives are recognized on the consolidated balance sheets either as assets or liabilities
at fair value. Derivatives can be measured in terms of their notional amounts, but this amount is not recorded in the
consolidated balance sheets and is not, when viewed in isolation, a meaningful measure of the risk profile of the
instruments. The notional amount is generally not exchanged, but is used only as the basis on which interest and other
payments are determined.
Credit and market risks are inherent in derivative instruments. Credit risk is defined as the possibility that a loss
may occur from the failure of another party to perform in accordance with the terms of the contract, which exceeds the
value of the existing collateral, if any. Market risk is defined as the risk of loss arising from an adverse change in the
market value of the derivative instrument caused by fluctuations in market prices or rates.
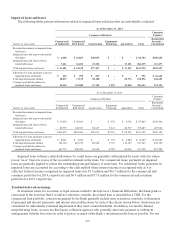
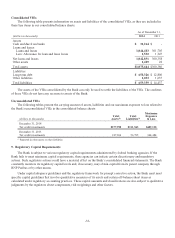
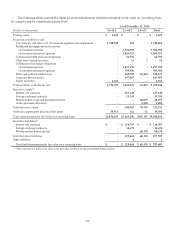
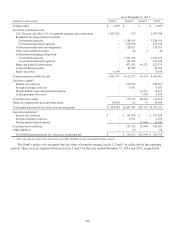
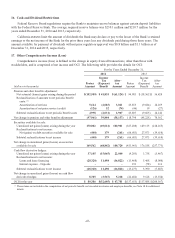
The following table summarizes information on derivative notional or contract amounts, receivables (asset
derivatives) and payables (liability derivatives) by accounting designation and contract types:
As of December 31,
2014 2013
Fair Value(1) Fair Value(1)
(dollars in thousands)
Notional or
Contract
Amount
Asset
Derivatives
Liability
Derivatives
Notional or
Contract
Amount
Asset
Derivatives
Liability
Derivatives
Derivatives designated as hedging instruments:
Fair value hedges:
Interest rate contracts $ 350,000 $ 291 $ 1,092 $ 1,200,000 $ 3,979 $ 3,662
Cash flow hedges:
Interest rate contracts 5,000,775 14,250 7,458 2,150,000 9,723 13,660
Subtotal 5,350,775 14,541 8,550 3,350,000 13,702 17,322
Derivatives not designated as hedging instruments:
Free-standing derivatives:
Interest rate contracts(2) 9,470,853 212,607 206,237 9,716,302 257,110 247,878
Market-linked swaps and options(3) 1,994,906 68,079 68,138 1,716,184 36,833 36,944
Foreign exchange contracts 725,637 13,354 14,674 600,912 4,303 4,552
Credit guarantee derivative 61,945 2,650 - 130,960 3,570 -
Subtotal 12,253,341 296,690 289,049 12,164,358 301,816 289,374
Total derivatives $17,604,116 $311,231 $297,599 $15,514,358 $315,518 $306,696
(1) Asset derivatives and liability derivatives are recorded in other assets and other liabilities, respectively, on the consolidated balance sheets.
(2) Includes derivatives related to mortgage sale activity with notional amount of $144 million and $46.8 million as of December 31, 2014 and 2013,
respectively. The fair value of asset derivatives was $1.2 million and $0.4 million and fair value of liability derivative was $0.5 million and nil as of
December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
(3) Includes bifurcated derivatives embedded in market-linked instruments. The asset derivatives represent market-linked swaps and purchased options
and the liability derivatives represent written market-linked options.
Fair value hedges
The Bank uses interest rate swap contracts to hedge changes in fair value from interest rate changes of underlying
fixed-rate debt instruments, including fixed-rate certificates of deposit and certain fixed-rate FHLB advances. As of
December 31, 2014, the weighted-average remaining life of the currently active fair value hedges was approximately 4.2
years.
-37-