Albertsons 2005 Annual Report Download - page 28
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 28 of the 2005 Albertsons annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
as well as the assumptions to be used in such models. The company plans to adopt the revised statement in its
first quarter of its fiscal year 2007, which begins on February 26, 2006.
QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK
The company is exposed to market pricing risk consisting of interest rate risk related to debt obligations
outstanding, its investment in notes receivable and, from time to time, derivatives employed to hedge interest rate
changes on variable and fixed rate debt. The company does not use financial instruments or derivatives for any
trading or other speculative purposes.
The company manages interest rate risk through the strategic use of fixed and variable rate debt and, to a
limited extent, derivative financial instruments. Variable interest rate debt (commercial paper, bank loans,
industrial revenue bonds and other variable interest rate debt) is utilized to help maintain liquidity and finance
business operations. Long-term debt with fixed interest rates is used to assist in managing debt maturities and to
diversify sources of debt capital.
The company makes long-term loans to certain retail customers (see Notes Receivable in the accompanying
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for further information) and as such, carries notes receivable in the
normal course of business. The notes generally bear fixed interest rates negotiated with each retail customer. The
market value of the fixed rate notes is subject to change due to fluctuations in market interest rates.
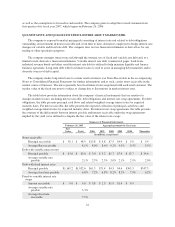
The table below provides information about the company’s financial instruments that are sensitive to
changes in interest rates, including notes receivable, debt obligations and interest rate swap agreements. For debt
obligations, the table presents principal cash flows and related weighted average interest rates by expected
maturity dates. For notes receivable, the table presents the expected collection of principal cash flows and
weighted average interest rates by expected maturity dates. For interest rate swap agreements, the table presents
the estimate of the differentials between interest payable and interest receivable under the swap agreements
implied by the yield curve utilized to compute the fair value of the interest rate swaps.
Summary of Financial Instruments
February 26, 2005 Aggregate payments by fiscal year
Fair
Value Total 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 Thereafter
(in millions, except rates)
Notes receivable
Principal receivable $ 50.1 $ 48.9 $13.8 $ 9.8 $7.5 $4.9 $ 3.0 $ 9.9
Average Rate receivable 8.1% 8.0% 8.6% 9.2% 9.9% 9.5% 5.5%
Debt with variable interest rates
Principal payable $ 63.6 $ 63.6 $ 3.0 $ 3.2 $1.7 $7.4 $ 13.7 $ 34.6
Average variable rate
payable 2.1% 2.5% 2.5% 3.0% 2.1% 2.1% 2.0%
Debt with fixed interest rates
Principal payable $1,169.2 $1,052.6 $61.3 $71.4 $4.5 $4.6 $363.3 $547.5
Average fixed rate payable 6.8% 7.2% 6.8% 8.2% 8.2% 7.9% 6.2%
Fixed-to-variable interest rate
swaps
Amount receivable $ 9.6 $ 9.6 $ 3.8 $ 2.3 $1.9 $1.4 $ 0.3
Average variable rate
payable 5.3%
Average fixed rate
receivable 7.9%
22