Tyson Foods 1999 Annual Report Download - page 45
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 45 of the 1999 Tyson Foods annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Notes to consolidated financial statements
TYSON FOODS, INC. 1999 ANNUAL REPORT
43
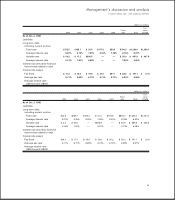
Capital Stock: Holders of Class B common stock (Class B stock) may convert such stock into Class A common stock (Class
A stock) on a share-for-share basis. Holders of Class B stock are entitled to 10 votes per share while holders of Class A
stock are entitled to one vote per share on matters submitted to shareholders for approval. Cash dividends cannot be paid
to holders of Class B stock unless they are simultaneously paid to holders of Class A stock, and the per share amount of
the cash dividend paid to holders of Class B stock cannot exceed 90% of the cash dividend simultaneously paid to hold-
ers of Class A stock. The Company pays quarterly cash dividends to Class A and Class B shareholders. The Company
paid Class A dividends per share of $0.115, $0.10 and $0.095 and Class B dividends per share of $0.104, $0.09 and $0.086
in 1999, 1998 and 1997, respectively.
On Jan. 10, 1997, the Company’s Board of Directors authorized a three-for-two stock split in the form of a stock divi-
dend, effective Feb. 15, 1997, for shareholders of record on Feb.1, 1997.
Stock-Based Compensation: Stock-based compensation is recognized using the intrinsic value method. For disclosure
purposes, pro forma net income and earnings per share impacts are provided as if the fair value method had been applied.
Financial Instruments: Periodically, the Company uses derivative financial instruments to reduce its exposure to various
market risks. The Company does not regularly engage in speculative transactions, nor does the Company regularly hold
or issue financial instruments for trading purposes. Contracts that effectively meet risk reduction and correlation criteria
are recorded using hedge accounting. Financial instruments which do not meet the criteria for hedge accounting are
marked-to-market with gains or losses reported currently in earnings. Interest rate swaps are used to hedge exposure to
changes in interest rates under various leveraged equipment loans. Settlements of interest rate swaps are accounted for
as an adjustment to interest expense. Commodity futures and options are used to hedge a portion of the Company’s pur-
chases of certain commodities for future processing requirements. Such contracts are accounted for as hedges, with
gains and losses recognized as part of cost of goods sold, and generally have terms of less than 15 months. Foreign cur-
rency forwards and option contracts are used to hedge sale and debt transactions denominated in foreign currencies to
reduce the currency risk associated with fluctuating exchange rates. Such contracts generally have terms of less than one
year. Unrealized gains and losses are deferred as part of the basis of the underlying transaction.
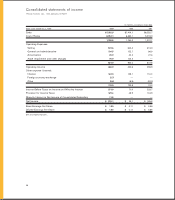
Advertising and Promotion Expenses: Advertising and promotion expenses are charged to operations in the period
incurred. Advertising and promotion expenses for 1999, 1998 and 1997 were $300.6 million, $294.2 million and $233.2 mil-
lion, respectively.
Use of Estimates: The consolidated financial statements are prepared in conformity with generally accepted accounting
principles which require management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the amounts reported in the con-
solidated financial statements and accompanying notes. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
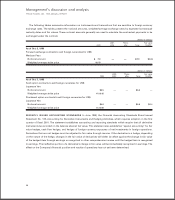
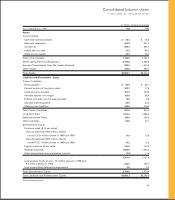
NOTE 2: DISPOSITIONS AND ASSETS HELD FOR SALE
Effective Sept. 28, 1999, the Company signed a letter of intent to sell its wholly-owned subsidiary, The Pork Group, Inc.
(The Pork Group) to Smithfield Foods, Inc. (Smithfield). The Company will receive approximately three million shares of
Smithfield common stock, subject to certain restrictions. Certain assets of The Pork Group with a fair value of approxi-
mately $70 million are classified as assets held for sale at Oct. 2, 1999. Additionally, the Company has accrued expenses
related to the closure of certain assets not purchased by Smithfield. The Company’s operating results for the fiscal year
ended Oct. 2, 1999 include a pretax charge of $35.2 million related to the anticipated loss on the sale and closure of these
assets. The transaction is subject to the successful negotiation of a definitive agreement and is expected to close by the
second quarter of fiscal 2000.