PG&E 2015 Annual Report Download - page 39
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 39 of the 2015 PG&E annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
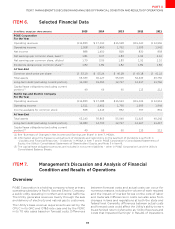
31
PART I
ITEM 1A.RISK FACTORS
Other Risk Factors
The Utility may be required to incur substantial costs
in order to obtain or renew licenses and permits
needed to operate the Utility’s business and the Utility
may be subject to fines and penalties for failure to
comply or obtain license renewal.
The Utility must comply with the terms of various
governmental permits, authorizations, and licenses, including
those issued by the FERC for the continued operation of the
Utility’s hydroelectric generation facilities, and those issued by
environmental and other federal, state and local governmental
agencies. Many of the Utility’s capital investment projects,
and some maintenance activities, often require the Utility
to obtain land use, construction, environmental, or other
governmental permits. These permits, authorizations,
and licenses may be dicult to obtain on a timely basis,
causing work delays. Further, existing permits and licenses
could be revoked or modified by the agencies that granted
them if facts develop that dier significantly from the facts
assumed when they were issued. In addition, the Utility
often seeks periodic renewal of a license or permit, such as
a waste discharge permit or a FERC operating license for a
hydroelectric generation facility. If a license or permit is not
renewed for a particular facility and the Utility is required
to cease operations at that facility, the Utility could incur
an impairment charge or other costs. Before renewing a
permit or license, the issuing agency may impose additional
requirements that may increase the Utility’s compliance costs.
In particular, in connection with a license renewal for one
or more of the Utility’s hydroelectric generation facilities or
assets, the FERC may impose new license conditions that
could, among other things, require increased expenditures
or result in reduced electricity output and/or capacity at
the facility. In addition, local governments may attempt to
assert jurisdiction over various utility operations by requiring
permits or other approvals that the Utility has not been
previously required to obtain.
The Utility may incur penalties and sanctions for failure to
comply with the terms and conditions of licenses and permits
which could have a material eect on PG&E Corporation’s
and the Utility’s financial condition, results of operations,
and cash flows. If the Utility cannot obtain, renew, or comply
with necessary governmental permits, authorizations,
licenses, ordinances, or other requirements, or if the Utility
cannot recover the increase in associated compliance and
other costs in a timely manner, PG&E Corporation’s and
the Utility’s financial results could be materially aected.
Poor investment performance or other factors could
require PG&E Corporation and the Utility to make
significant unplanned contributions to its pension
plan, other postretirement benefits plans, and nuclear
decommissioning trusts.
PG&E Corporation and the Utility provide defined benefit
pension plans and other postretirement benefits for eligible
employees and retirees. The Utility also maintains three trusts
for the purposes of providing funds to decommission its
nuclear facilities. The performance of the debt and equity
markets aects the value of plan assets and trust assets.
A decline in the market value may increase the funding
requirements for these plans and trusts. The cost of providing
pension and other postretirement benefits is also aected
by other factors, including interest rates used to measure
the required minimum funding levels, the rate of return on
plan assets, employee demographics, discount rates used in
determining future benefit obligations, rates of increase in
health care costs, future government regulation, and prior
contributions to the plans. Similarly, funding requirements for
the nuclear decommissioning trusts are aected by the rates
of return on trust assets, changes in the laws or regulations
regarding nuclear decommissioning or decommissioning
funding requirements as well as changes in assumptions
or forecasts related to decommissioning dates, technology
and the cost of labor, materials and equipment. (See Note
2: Summary of Significant Accounting Policies of the
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements in Item
8.) If the Utility is required to make significant unplanned
contributions to fund the pension and postretirement plans
or if actual nuclear decommissioning costs exceed the
amount of nuclear decommissioning trust funds and the
Utility is unable to recover the contributions or additional
costs in rates, PG&E Corporation’s and the Utility’s financial
results could be materially aected.
The Utility’s success depends on the availability
of the services of a qualified workforce and its
ability to maintain satisfactory collective bargaining
agreements which cover a substantial number of
employees. PG&E Corporation’s and the Utility’s
results may suer if the Utility is unable to attract and
retain qualified personnel and senior management
talent, or if prolonged labor disruptions occur.
The Utility’s workforce is aging and many employees are
or will become eligible to retire within the next few years.
Although the Utility has undertaken eorts to recruit and
train new field service personnel, the Utility may be faced
with a shortage of experienced and qualified personnel. The
majority of the Utility’s employees are covered by collective
bargaining agreements with three unions. Labor disruptions
could occur depending on the outcome of negotiations to
renew the terms of these agreements with the unions or if
tentative new agreements are not ratified by their members.
In addition, some of the remaining non-represented Utility
employees could join one of these unions in the future.
PG&E Corporation and the Utility also may face challenges
in attracting and retaining senior management talent
especially if they are unable to restore the reputational
harm generated by the negative publicity stemming
from the ongoing enforcement proceedings. Any such
occurrences could negatively impact PG&E Corporation’s
and the Utility’s financial condition and results of operations.