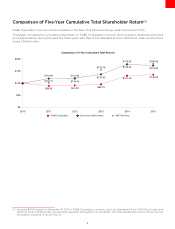
PG&E 2015 Annual Report Download - page 17
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 17 of the 2015 PG&E annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
9
PART I
ITEM1.BUSINESS
Regulatory Environment
The Utility’s business is subject to the regulatory jurisdiction
of various agencies at the federal, state, and local levels.
At the state level, the Utility is regulated primarily by
the CPUC. At the federal level, the Utility is subject to
the jurisdiction of the FERC and the NRC. The Utility is
also subject to the requirements of other federal, state
and local regulatory agencies with respect to safety, the
environment and health. This section and the “Ratemaking
Mechanisms” section below summarize some of the more
significant laws, regulations, and regulatory proceedings
aecting the Utility.
PG&E Corporation is a “public utility holding company” as
defined under the Public Utility Holding Company Act of
2005 and is subject to regulatory oversight by the FERC.
PG&E Corporation and its subsidiaries are exempt from
all requirements of the Public Utility Holding Company
Act of 2005 other than the obligation to provide access
to their books and records to the FERC and the CPUC
for ratemaking purposes.
The California Public Utilities Commission
The CPUC consists of five members appointed by the
Governor of California and confirmed by the California
State Senate for staggered six-year terms. The CPUC
has jurisdiction over the rates and terms and conditions
of service for the Utility’s electricity and natural gas
distribution operations, electricity generation, and natural
gas transmission and storage services. The CPUC also
has jurisdiction over the Utility’s issuances of securities,
dispositions of utility assets and facilities, energy purchases
on behalf of the Utility’s electricity and natural gas retail
customers, rates of return, rates of depreciation, oversight
of nuclear decommissioning, and aspects of the siting
offacilities used in providing electric and natural gas
utility service.
The CPUC enforces state laws and regulations that set forth
safety requirements pertaining to the design, construction,
testing, operation, and maintenance of utility gas and
electric facilities. The CPUC can impose penalties of
up to $50,000 per day, per violation, for violations that
occurred after January 1, 2012. (The statutory maximum
penalty for violations that occurred before January 1, 2012
is $20,000 per violation.) The CPUC has wide discretion to
determine the amount of penalties based on the totality of
the circumstances, including such factors as the gravity of
the violations; the type of harm caused by the violations
and the number of persons aected; and the good faith of
the entity charged in attempting to achieve compliance,
after notification of a violation. The CPUC also is required
to consider the appropriateness of the amount of the
penalty to the size of the entity charged.
As discussed above, in April 2015, the CPUC concluded
its three investigative enforcement actions against the
Utility by imposing penalties totaling $1.6 billion. (For
more information about the Penalty Decision, see Item 1.A.
Risk Factors and Note 13 of the Notes to the Consolidated
Financial Statements in Item 8. below.) The CPUC is also
conducting investigative enforcement proceedings relating
to the Utility’s natural gas distribution facilities record-
keeping practices and the Utility’s potential violations of the
CPUC’s ex parte communication rules. (See “Enforcement
and Litigation Matters” in MD&A for more information.)
Further, in August 2015, the CPUC began an investigation
into whether the organizational culture and governance
of PG&E Corporation and the Utility prioritize safety and
adequately direct resources to promote accountability and
achieve safety goals and standards. (For more information,
see “Regulatory Matters” in MD&A.)
The CPUC has adopted separate gas and electric safety
enforcement programs that authorize the SED to issue
citations and impose fines for violations of certain
regulations. Under both the gas and electric programs,
the SED is required to impose the maximum statutory
penalty of $50,000 for each separate violation and
has the discretion to impose daily fines for continuing
violations. During 2016, the CPUC is expected to develop
and implement improvements and refinements to the
electric and gas safety citation programs, including steps
to reconcile the dierences between the two programs.
The California State Legislature also directs the CPUC
to implement state laws and policies, such as the laws
relating to increasing renewable energy resources, the
development and widespread deployment of distributed
generation and self-generation resources, the reduction
of GHG emissions, the development of energy storage
technologies and facilities, and the development of a state-
wide electric vehicle charging infrastructure. The CPUC is
responsible for approving funding and administration of
state-mandated public purpose programs such as energy
eciency and other customer programs. The CPUC also
conducts audits and reviews of the Utility’s accounting,
performance and compliance with regulatory guidelines.
The CPUC has imposed various conditions that govern the
relationship between the Utility and PG&E Corporation and
other aliates, including financial conditions that require
PG&E Corporation’s Board of Directors to give first priority
to the capital requirements of the Utility, as determined to
be necessary and prudent to meet the Utility’s obligation
to serve or to operate the Utility in a prudent and ecient
manner. (For more information, see “Liquidity and Financial
Resources” in MD&A and Item 1A. Risk Factors.)
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission and the
California Independent System Operator
The FERC has jurisdiction over the Utility’s electricity
transmission revenue requirements and rates, the licensing
of substantially all of the Utility’s hydroelectric generation
facilities, and the interstate sale and transportation of
natural gas. The FERC regulates the interconnections
of the Utility’s transmission systems with other electric
systems and generation facilities, the taris and conditions
of service of regional transmission organizations and the
terms and rates of wholesale electricity sales. The FERC
also is charged with adopting and enforcing mandatory