Konica Minolta 2010 Annual Report Download - page 40
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 40 of the 2010 Konica Minolta annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
deemed other than temporary. In these instances, securities are written
down to the fair market value and the resulting losses are charged to
income during the period.
Hedge Accounting
Gains or losses arising from changes in fair market value of derivatives
designated as “hedging instruments” are deferred as an asset or a
liability and charged or credited to income in the same period that the
gains and losses on the hedged items or transactions are recognized.
Derivatives designated as hedging instruments by the Companies are
primarily interest rate swaps and forward foreign currency exchange
contracts. The related hedged items are trade accounts receivable,
trade accounts payable and long-term bank loans.
The Companies have a policy to utilize the above hedging instru-
ments in order to reduce the Companies’ exposure to the risks of
interest rate and exchange rate fluctuations. As such, the Companies’
purchases of the hedging instruments are limited to, at maximum, the
amounts of the hedged items.
The Companies evaluate the effectiveness of their hedging activities by
reference to the accumulated gains or losses on the hedging instruments
and the related hedged items from the commencement of the hedges.
(l) Retirement Benefit Plans
Retirement Benefits for Employees
The Company, domestic consolidated subsidiaries and certain overseas
consolidated subsidiaries have obligations to make defined benefit
retirement payments to their employees and, therefore, provide accrued
retirement benefits based on the estimated amount of projected benefit
obligations and the fair value of plan assets.
For the Company and its domestic consolidated subsidiaries, unrec-
ognized prior service cost is amortized using the straight-line method
over a 10-year period, which is shorter than the average remaining
years of service of the eligible employees. Unrecognized net actuarial
gain or loss is primarily amortized in the following year using the
straight-line method over a 10-year period, which is shorter than the
average remaining years of service of the eligible employees.
Changes in Accounting Standards
Effective from the year ended March 31, 2010, the Company and its
domestic consolidated subsidiaries adopted Accounting Standards
Board of Japan (ASBJ) Statement No. 19, “Partial Amendments to
Accounting Standard for Retirement Benefits (Part 3)”, issued by the
ASBJ on July 31, 2008.
The new accounting standard requires domestic companies to use
the rate of return on long-term government or gilt-edged bonds as of
the end of the fiscal year for calculating the projected benefit obligation
of a defined-benefit plan. Previously, domestic companies were allowed
to use a discount rate determined by taking into consideration fluctua-
tions in the yield of long-term government or gilt-edged bonds over a
certain period.
This adoption had no impact on the consolidated statements of income
and retirement benefit obligations for the year ended March 31, 2010.
Accrued Retirement Benefits for Directors
and Statutory Auditors
Domestic consolidated subsidiaries record a reserve for retirement
benefits for directors and statutory auditors based on the amount
payable accumulated at the end of the period in accordance with their
internal regulations.
(m) Per Share Data
Net income per share of common stock has been computed based on
the weighted-average number of shares outstanding during the year.
Cash dividends per share shown for each year in the accompanying
consolidated statements are dividends declared as applicable to the
respective year.
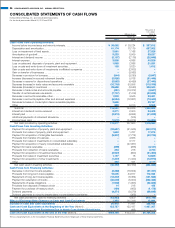
(n) Cash Flows from Operating Activities
“Decrease/increase in consumption taxes receivable/payable” which
were included within “Other” in the “Cash flows from operating activi-
ties” section of the consolidated statements of cash flows in the previ-
ous fiscal year, are now separately disclosed from the year ended
March 31, 2010.
The amount for the year ended March 31, 2009 was ¥952 million.
(o) Practical Solution on Unification of Accounting Policies
Applied to Foreign Subsidiaries for Consolidated Financial
Statements
Effective from the year ended March 31, 2009, the Company applied
the “Practical Solution on Unification of Accounting Policies Applied to
Foreign Subsidiaries for Consolidated Financial Statements” (ASBJ
Practical Issues Task Force (PITF) No. 18, issued by the ASBJ on May
17, 2006).
The Company makes necessary adjustments upon consolidation to
unify accounting standards for foreign subsidiaries in principle.
3. U.S. DOLLAR AMOUNTS
The translation of Japanese yen amounts into U.S. dollars is included
solely for the convenience of the reader, using the prevailing exchange
rate at March 31, 2010, of ¥93.04 to U.S.$1.00. The translations
should not be construed as representations that the Japanese yen
amounts have been, could have been, or could in the future be, con-
verted into U.S. dollars at this or any other exchange rate.
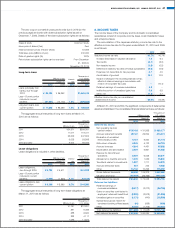
4. CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS
Cash and cash equivalents as of March 31, 2010 and 2009, consist of:
Millions of yen
Thousands of
U.S. dollars
March 31 March 31
2010 2009 2010
Cash on hand and in banks ¥ 85,533 ¥ 85,753 $ 919,314
Time deposits (over 3 months) (387) (26) (4,160)
Short-term investments 79,000 48,000 849,097
Cash and cash equivalents ¥164,146 ¥133,727 $1,764,252
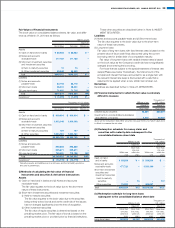
5. FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS
Additional Information
Effective from the year ended March 31, 2010, the Companies adopted
ASBJ Statement No. 10, “Accounting Standards for Financial Instru-
ments”, issued by the ASBJ on March 10, 2008 and ASBJ Guidance
No. 19, “Implementation Guidance on Disclosures about the Fair Value
of Financial Instruments”, issued by the ASBJ on March 10, 2008.
Conditions of Financial Instruments
The Companies raise short-term working capital mainly with bank
borrowings and invest temporary surplus funds in financial instruments
deemed to have lower risk. The Companies enter into derivative trans-
actions based on the need for these transactions in accordance with its
internal regulations.
In principle, the risk of currency fluctuations relating to receivables
and payables, denominated in foreign currencies, are hedged using the
forward exchange contract. With respect to the interest volatility risk
relating to certain long-term loans payable, the Companies use interest-
rate swap to fix interest expenses.
Investment securities consist mainly of stocks, and the market values
of listed stocks are determined on a quarterly basis.
The Companies control credit risk of customers relating to notes
and accounts receivable-trade through a comprehensive monitoring of
reviewing aging schedules and balances.
38 KONICA MINOLTA HOLDINGS, INC. ANNUAL REPORT 2010