Kia 2004 Annual Report Download - page 63
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 63 of the 2004 Kia annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
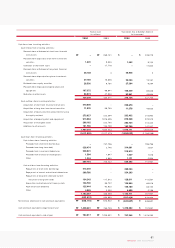
63
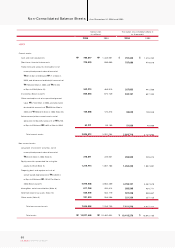
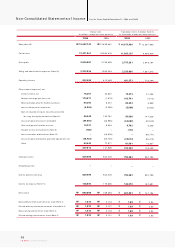
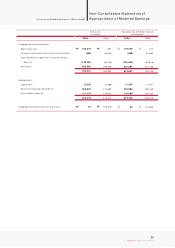
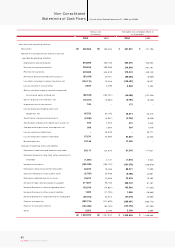
KIA Motors_2004 Annual Report
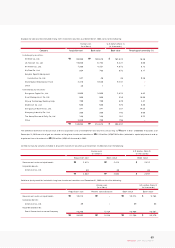
In addition, this change in accounting methods has been accounted for retrospectively and the comparative statements for 2003 have been restated.
The significant accounting policies followed by the Company in the preparation of its non-consolidated financial statements are summarized below.
REVENUE RECOGNITION
Sales, including long-term instalment sales, are recognized at the time of shipment of motor vehicles and parts, which is when the significant risks and rewards of
ownership of the goods have been transferred to the buyer. The interest income arising from long-term instalment sales contracts is recognized using the level
yielding method.
ACCRUED WARRANTIES
The Company generally provides a warranty to the ultimate consumer for each product sold and accrues warranty expense at the time of sale based on actual
claims history. Also, the Company accrues potential expenses, which may occur due to product liabilities suits and voluntary recall campaign pending as of the
balance sheet date. Additionally, the Company recognizes accrued liabilities of the provision for the projected costs for dismantling and recycling vehicles that the
Com pany sold in European Union region to comply with a European Parliament directive regarding End-of-Life Vehicles (ELV), in which manufacturers are
financially responsible for a portion of the cost of the dismantling and recycling of vehicles placed in service (See Note 12).
ALLOWANCE FOR DOUBTFUL ACCOUNTS
The Company provides an allowance for doubtful accounts based on management s estimate of the collectibility of the receivables.
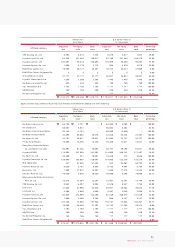
INVENTORIES
Inventories are stated at the low er of cost or net realizable value, cost being determined by the moving average method except for materials in transit for which
cost is determined using the specific identification method. Valuation loss incurred when the market value of an inventory falls below its carrying amount is added
to the cost of goods sold.
INVESTMENTS IN SECURITIES OTHER THAN THOSE ACCOUNTED FOR USING THE EQUITY METHOD
CLASSIFICATION OF SECURITIES
At acquisition, the Com pany classifies securities into one of the three categories: trading, held-to-maturity securities or available-for-sale. Trading securities are those
that were acquired principally to generate profit from short-term fluctuations in prices. Held-to-maturity securities are those with fixed or determinable payments
and fixed maturity that an enterprise has the positive intent and ability to hold to maturity. Available-for-sale securities are those not classified either as held-to-
maturity or trading securities. Trading securities are classified as short term investment securities, whereas available-for-sale securities and held-to-maturity securities
are classified as long-term investment securities, except for those whose m aturity dates or whose likelihood of being disposed of are within one year from the
balance sheet date, which are classified as short-term investment securities.
VALUATION OF SECURITIES
Investments in securities are initially measured at cost, which consists of the market price of the consideration given to acquire them and incidental expenses. If the
market price of the consideration given is not available, the market prices of the securities purchased are used as the basis for measurem ent. If neither the market
price of the consideration given nor those of the acquired securities are available, the acquisition cost is measured at the best estimates of its fair value.
After initial recognition, held-to-maturity securities are valued at am ortized cost. The difference between their acquisition costs and face values is amortized over the
remaining term of the securities by applying the effective interest method and added to or subtracted from the acquisition costs and interest incom e of the