Cisco 2004 Annual Report Download - page 42
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 42 of the 2004 Cisco annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Minority Interest The Company consolidated its investment in a venture fund managed by SOFTBANK Corp. and its affiliates
(“SOFTBANK”). As of July 31, 2004, minority interest of $84 million represents SOFTBANK’s share of the venture fund. The remaining
minority interest of $6 million represents the preferred stockholders’ proportionate share of the equity of Cisco Systems, K.K. (Japan).
At July 31, 2004, the Company owned all issued and outstanding common stock, amounting to 97.6% of the aggregate voting rights
of Cisco Systems, K.K. (Japan). Each share of preferred stock is convertible into one share of common stock of Cisco Systems, K.K. (Japan)
at any time at the option of the holder.
Use of Estimates The preparation of financial statements and related disclosures in conformity with accounting principles generally
accepted in the U.S. requires management to make estimates and judgments that affect the amounts reported in the Consolidated
Financial Statements and accompanying notes. Estimates are used for revenue recognition, allowance for doubtful accounts and sales
returns, allowance for inventory, warranty costs, investment impairments, goodwill impairments, income taxes, and loss contingencies,
among others. The actual results experienced by the Company may differ materially from management’s estimates.
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets Long-lived assets and certain identifiable intangible assets to be held and used are reviewed for impairment
whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of such assets may not be recoverable. Determination of
recoverability of long-lived assets is based on an estimate of undiscounted future cash flows resulting from the use of the asset and its
eventual disposition. Measurement of an impairment loss for long-lived assets and certain identifiable intangible assets that manage-
ment expects to hold and use is based on the fair value of the asset. Long-lived assets and certain identifiable intangible assets to be dis-
posed of are reported at the lower of carrying amount or fair value less costs to sell.
Employee Stock Benefit Plans The Company accounts for stock-based awards to employees and directors using the intrinsic value method
of accounting in accordance with Accounting Principles Board Opinion No. 25, “Accounting for Stock Issued to Employees” (“APB 25”).
Under the intrinsic value method, because the exercise price of the Company’s employee stock options equals the market price of the
underlying stock on the date of grant, no compensation expense is recognized in the Company’s Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Pro forma information regarding option grants made to the Company’s employees and directors and common stock issued pursuant
to the Employee Stock Purchase Plan is based on specified valuation techniques that produce estimated compensation charges. The
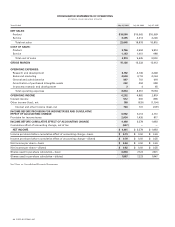
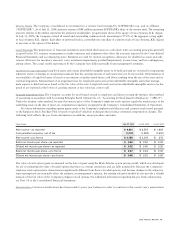
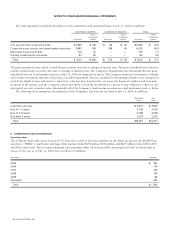
following table reflects the pro forma information (in millions, except per-share amounts):
Years Ended July 31, 2004 July 26, 2003 July 27, 2002
Net income—as reported $ 4,401 $ 3,578 $ 1,893
Compensation expense, net of tax (1,215) (1,259) (1,520)
Net income—pro forma $ 3,186 $ 2,319 $ 373
Basic net income per share—as reported $ 0.64 $ 0.50 $ 0.26
Diluted net income per share—as reported $ 0.62 $ 0.50 $ 0.25
Basic net income per share—pro forma $ 0.47 $ 0.33 $ 0.05
Diluted net income per share—pro forma $0.45 $0.32 $ 0.05
The value of each option grant is estimated on the date of grant using the Black-Scholes option pricing model, which was developed
for use in estimating the value of traded options that have no vesting restrictions and are fully transferable. Because the Company’s
employee stock options have characteristics significantly different from those of traded options, and because changes in the subjective
input assumptions can materially affect the estimate, in management’s opinion, the existing valuation models do not provide a reliable
measure of the fair value of the Company’s employee stock options. For additional information regarding this pro forma information,
see Note 10 to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
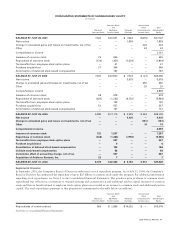
Reclassifications Certain reclassifications have been made to prior year balances in order to conform to the current year’s presentation.
2004 ANNUAL REPORT 45