Cisco 2004 Annual Report Download - page 41
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 41 of the 2004 Cisco annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
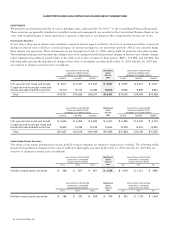
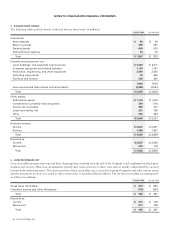
Goodwill and Purchased Intangible Assets Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 142, “Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets”
(“SFAS 142”), requires goodwill to be tested for impairment on an annual basis and between annual tests in certain circumstances,
and written down when impaired. Based on the impairment tests performed, there was no impairment of goodwill in fiscal 2004,
2003, and 2002. Furthermore, SFAS 142 requires purchased intangible assets other than goodwill to be amortized over their useful
lives unless these lives are determined to be indefinite. Purchased intangible assets are carried at cost less accumulated amortization.
Amortization is computed over the estimated useful lives of the respective assets, generally two to five years.
Income Taxes Income tax expense is based on pretax financial accounting income. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for
the expected tax consequences of temporary differences between the tax bases of assets and liabilities and their reported amounts.
Computation of Net Income per Share Basic net income per share is computed using the weighted-average number of common shares
outstanding during the period. Diluted net income per share is computed using the weighted-average number of common shares and
dilutive potential common shares outstanding during the period. Diluted net loss per share is computed using the weighted-average number
of common shares and excludes dilutive potential common shares outstanding, as their effect is antidilutive. Dilutive potential common
shares primarily consist of employee stock options and restricted common stock.
Foreign Currency Translation Assets and liabilities of non-U.S. subsidiaries that operate in a local currency environment are translated to
U.S. dollars at exchange rates in effect at the balance sheet date, with the resulting translation adjustments directly recorded to a separate
component of accumulated other comprehensive income. Income and expense accounts are translated at average exchange rates during
the year. Where the U.S. dollar is the functional currency, translation adjustments are recorded in other income (loss), net.
Derivative Instruments The Company recognizes derivative instruments as either assets or liabilities in the Consolidated Balance Sheets
and measures those instruments at fair value. The accounting for changes in the fair value of a derivative depends on the intended use
of the derivative and the resulting designation.
For a derivative instrument designated as a fair value hedge, the gain or loss is recognized in earnings in the period of change together
with the offsetting loss or gain on the hedged item attributed to the risk being hedged. For a derivative instrument designated as a cash
flow hedge, the effective portion of the derivative’s gain or loss is initially reported as a component of accumulated other comprehensive
income and subsequently reclassified into earnings when the hedged exposure affects earnings. The ineffective portion of the gain or
loss is reported in earnings immediately.
Certain forecasted transactions and foreign currency assets and liabilities expose the Company to foreign currency risk. The Company
purchases currency options and designates these currency options as cash flow hedges of foreign currency forecasted transactions related
to certain operating expenses. The Company enters into foreign exchange forward contracts to minimize the short-term impact of
currency fluctuations on certain foreign currency receivables, investments, and payables. The foreign exchange forward contracts are
not designated as accounting hedges, and all changes in fair value are recognized in earnings in the period of change.
The fair value of derivative instruments as of July 31, 2004 and changes in fair value during fiscal 2004 were not material. During
fiscal 2004, there were no significant gains or losses recognized in earnings for hedge ineffectiveness. The Company did not discontinue
any hedges because it was probable that the original forecasted transactions would not occur.
Consolidation of Variable Interest Entities Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) Interpretation No. 46, “Consolidation of Variable
Interest Entities” (“FIN 46”), was issued in January 2003. FIN 46 requires that if an entity is the primary beneficiary of a variable
interest entity, the assets, liabilities, and results of operations of the variable interest entity should be included in the consolidated
financial statements of the entity. FASB Interpretation No. 46(R), “Consolidation of Variable Interest Entities” (“FIN 46(R)”), was
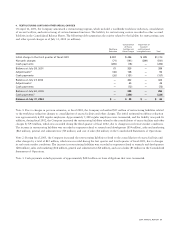
issued in December 2003. The Company adopted FIN 46(R) effective January 24, 2004, and recorded a noncash cumulative stock
compensation charge of $567 million, net of tax, relating to the consolidation of Andiamo Systems, Inc. (“Andiamo”). For additional
information regarding Andiamo, see Note 3 to these Consolidated Financial Statements. For additional information regarding variable
interest entities, see Note 8 to these Consolidated Financial Statements.
44 CISCO SYSTEMS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS