CarMax 2007 Annual Report Download - page 44
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 44 of the 2007 CarMax annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
34
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk.
Automobile Installment Loan Receivables
At February 28, 2007, and February 28, 2006, all loans in our portfolio of automobile loan receivables were fixed-
rate installment loans. Financing for these automobile loan receivables is achieved through asset securitization
programs that, in turn, issue both fixed- and floating-rate securities. We manage the interest rate exposure relating
to floating-rate securitizations through the use of interest rate swaps. Receivables held for investment or sale are
financed with working capital. Generally, changes in interest rates associated with underlying swaps will not have a
material impact on earnings. However, changes in interest rates associated with underlying swaps may have a
material impact on cash and cash flows.
Credit risk is the exposure to nonperformance of another party to an agreement. We mitigate credit risk by dealing
with highly rated bank counterparties. The market and credit risks associated with financial derivatives are similar
to those relating to other types of financial instruments. Refer to Note 5 for a description of these items.
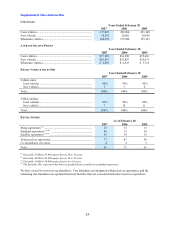
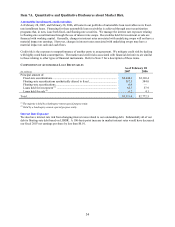
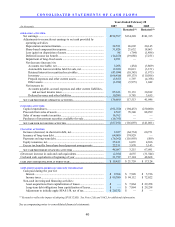
COMPOSITION OF AUTOMOBILE LOAN RECEIVABLES
As of February 28
(In millions) 2007 2006
Principal amount of:
Fixed-rate securitizations ......................................................................................... $2,644.1 $2,126.4
Floating-rate securitizations synthetically altered to fixed....................................... 597.5 584.0
Floating-rate securitizations..................................................................................... 0.6 —
Loans held for investment (1) ................................................................................... 62.7 57.9
Loans held for sale (2) ............................................................................................... 6.2 4.1
Total............................................................................................................................. $3,311.0 $2,772.5
(1) The majority is held by a bankruptcy-remote special purpose entity.
(2) Held by a bankruptcy-remote special purpose entity.
Interest Rate Exposure
We also have interest rate risk from changing interest rates related to our outstanding debt. Substantially all of our
debt is floating-rate debt based on LIBOR. A 100-basis point increase in market interest rates would have decreased
our fiscal 2007 net earnings per share by less than $0.01.