Capital One 2000 Annual Report Download - page 38
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 38 of the 2000 Capital One annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
36 md&a
CAPITAL ADEQUACY
The Bank and the Savings Bank are subject to capital adequacy
guidelines adopted by the Federal Reserve Board (the "Federal
Reserve") and the Office of Thrift Supervision (the "OTS") (collec-
tively, the "regulators"), respectively. The capital adequacy
guidelines and the regulatory framework for prompt corrective
action require the Bank and the Savings Bank to maintain specific
capital levels based upon quantitative measures of their assets, lia-
bilities and off-balance sheet items.
The most recent notifications received from the regulators cat-
egorized the Bank and the Savings Bank as "well-capitalized." As of
December 31, 2000, there are no conditions or events since the
notifications discussed above that management believes have
changed either the Bank’s or the Savings Bank's capital category.
In August 2000, the Bank received regulatory approval and
established a subsidiary bank in the United Kingdom. In connection
with the approval of its former branch office in the United Kingdom,
the Company committed to the Federal Reserve that, for so long as
the Bank maintains a branch or subsidiary bank in the United King-
dom, the Company will maintain a minimum Tier 1 Leverage ratio of
3.0%. As of December 31, 2000 and 1999, the Company's Tier 1
Leverage ratio was 11.14% and 12.79%, respectively.
Additional information regarding capital adequacy can be
found in Note J to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
Additional information regarding funding can be found in Note
E to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
LIQUIDITY
Liquidity refers to the Company's ability to meet its cash needs. The
Company meets its cash requirements by securitizing assets, gath-
ering deposits and issuing debt. As discussed in "Managed
Consumer Loan Portfolio," a significant source of liquidity for the
Company has been the securitization of consumer loans. Maturity
terms of the existing securitizations vary from 2001 to 2008 and
typically have accumulation periods during which principal pay-
ments are aggregated to make payments to investors. As payments
on the loans are accumulated and are no longer reinvested in new
loans, the Company's funding requirements for such new loans
increase accordingly. The occurrence of certain events may cause
the securitization transactions to amortize earlier than scheduled,
which would accelerate the need for funding.
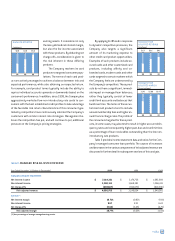
Table 11 shows the amounts of investor principal from off-
balance sheet securitized consumer loans that are expected to
amortize, or be otherwise paid over the periods indicated, based on
outstanding securitized consumer loans as of January 1, 2001. As
of December 31, 2000 and 1999, 49% and 51%, respectively, of the
Company's total managed loans were securitized.
As such amounts amortize or are otherwise paid, the Company
believes it can securitize consumer loans, purchase federal funds
and establish other funding sources to fund the amortization or
other payment of the securitizations in the future, although no
assurance can be given to that effect. Additionally, the Company
maintains a portfolio of high-quality securities such as U.S. Trea-
suries and other U.S. government obligations, commercial paper,
interest-bearing deposits with other banks, federal funds and other
cash equivalents in order to provide adequate liquidity and to meet
its ongoing cash needs. As of December 31, 2000, the Company
held $1.9 billion of such securities.
Liability liquidity is measured by the Company's ability to
obtain borrowed funds in the financial markets in adequate
amounts and at favorable rates. As of December 31, 2000, the Com-
pany, the Bank and the Savings Bank collectively had over $1.9
billion in unused commitments, under its credit facilities, available
for liquidity needs.
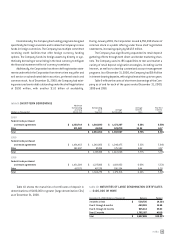
table 11: SECURITIZATIONS — AMORTIZATION TABLE
(Dollars in Thousands) 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005–2008
Balance at beginning of year $ 14,397,050 $ 10,757,198 $ 8,782,005 $ 6,035,622 $ 4,041,017
Less repayment amounts (3,639,852) (1,975,193) (2,746,383) (1,994,605) (4,041,017)
Balance at end of year $ 10,757,198 $ 8,782,005 $ 6,035,622 $ 4,041,017 $ —