TCF Bank 2011 Annual Report Download - page 108
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 108 of the 2011 TCF Bank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
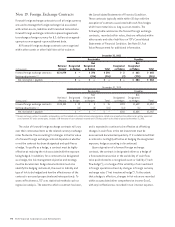
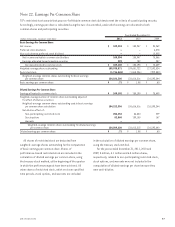
Note 19. Foreign Exchange Contracts
Forward foreign exchange contracts to sell a foreign currency
are used to manage the foreign exchange risk associated
with certain assets, liabilities and forecasted transactions.
Forward foreign exchange contracts represent agreements
to exchange a foreign currency for U.S. dollars at an agreed-
upon price on an agreed-upon settlement date.
All forward foreign exchange contracts are recognized
within other assets or other liabilities at fair value on
the Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition.
These contracts typically settle within 30 days with the
exception of contracts associated with cash flow hedges
which have maturities as long as seven months. The
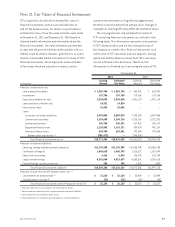
following table summarizes the forward foreign exchange
contracts, recorded at fair value, that are reflected within
other assets and other liabilities on TCF’s Consolidated
Statements of Financial Condition. See Note 20, Fair
Value Measurement for additional information.
December 31, 2011
Receivables Payables
(In thousands)
Notional
Amount
Designated
as Hedges
Not
Designated
as Hedges Total
Designated
as Hedges
Not
Designated
as Hedges Total
Forward foreign exchange contracts $176,979 $ – $ 396 $ 396 $ 3 $ 662 $ 665
Netting adjustments (1) – (396) (396) (3) (378) (381)
Net receivable / payable $ – $ – $ – $ – $ 284 $ 284
December 31, 2010
Receivables Payables
(In thousands)
Notional
Amount
Designated
as Hedges
Not
Designated
as Hedges Total
Designated
as Hedges
Not
Designated
as Hedges Total
Forward foreign exchange contracts $185,540 $ 12 $ 3 $ 15 $198 $1,659 $1,857
Netting adjustments (1) (12) (3) (15) (12) (3) (15)
Net receivable / payable $ – $ – $ – $186 $1,656 $1,842
(1) Foreign exchange contract receivables and payables, and the related cash collateral received and paid are netted when a legally enforceable master netting agreement
exists between TCF and a counterparty. Includes $150 thousand of cash collateral received and $135 thousand of cash collateral posted at December 31, 2011.
The value of forward foreign exchange contracts will vary
over their contractual term as the related currency exchange
rates fluctuate. The accounting for changes in the fair value
of a forward foreign exchange contract depends on whether
or not the contract has been designated and qualifies as
a hedge. To qualify as a hedge, a contract must be highly
effective at reducing the risk associated with the exposure
being hedged. In addition, for a contract to be designated
as a hedge, the risk management objective and strategy
must be documented. Hedge documentation must also
identify the hedging instrument, the asset or liability and
type of risk to be hedged and how the effectiveness of the
contract is assessed prospectively and retrospectively. To
assess effectiveness, TCF uses statistical methods such as
regression analysis. The extent to which a contract has been,
and is expected to continue to be effective at offsetting
changes in cash flows or the net investment must be
assessed and documented quarterly. If it is determined that
a contract is not highly effective at hedging the designated
exposure, hedge accounting is discontinued.
Upon origination of a forward foreign exchange
contract, the contract is designated either as a hedge of
a forecasted transaction or the variability of cash flows
to be paid related to a recognized asset or liability (“cash
flow hedge”); or a hedge of the volatility of an investment
in foreign operations driven by changes in foreign currency
exchange rates (“net investment hedge”). To the extent
that a hedge is effective, changes in fair value are recorded
within accumulated other comprehensive income (loss),
with any ineffectiveness recorded in non-interest expense.
90 TCF Financial Corporation and Subsidiaries