Seagate 2010 Annual Report Download - page 82
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 82 of the 2010 Seagate annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Table of Contents
SEAGATE TECHNOLOGY PLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
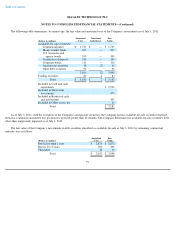
financial statement purposes, as well as tax liabilities associated with uncertain tax positions. The calculation of tax liabilities involves
uncertainties in the application of complex tax rules and the potential for future adjustment of the Company's uncertain tax positions by the
Internal Revenue Service or other tax jurisdictions. If estimates of these tax liabilities are greater or less than actual results, an additional tax
benefit or provision will result. The deferred tax assets the Company records each period depend primarily on the Company's ability to generate
future taxable income in the United States and certain non-U.S. jurisdictions. Each period, the Company evaluates the need for a valuation
allowance for its deferred tax assets and, if necessary, adjusts the valuation allowance so that net deferred tax assets are recorded only to the
extent the Company concludes it is more likely than not that these deferred tax assets will be realized. If the Company's outlook for future
taxable income changes significantly, the Company's assessment of the need for a valuation allowance may also change.
Foreign Currency Remeasurement and Translation. The U.S. dollar is the functional currency for substantially all of the Company's
foreign operations. Monetary assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies are remeasured into U.S. dollars at the balance sheet date.
The gains and losses from the remeasurement of foreign currency denominated balances into U.S. dollars are included in net income (loss) for
those operations.
Concentrations
Concentration of Credit Risk. The Company's customer base for disk drive products is concentrated with a small number of OEMs and
distributors. The Company does not generally require collateral or other security to support accounts receivable. To reduce credit risk, the
Company performs ongoing credit evaluations on its customers' financial condition. The Company establishes an allowance for doubtful
accounts based upon factors surrounding the credit risk of customers, historical trends and other information. Hewlett-Packard Company and
Dell Inc. each accounted for more than 10 percent of the Company's accounts receivable as of July 1, 2011.
Financial instruments that potentially subject the Company to concentrations of credit risk consist primarily of cash equivalents, short-term
investments and foreign currency forward exchange contracts. The Company further mitigates concentrations of credit risk in its investments
through diversification, by limiting its investments in the debt securities of a single issuer, and investing in highly rated securities.
In entering into foreign currency forward exchange contracts, the Company assumes the risk that might arise from the possible inability of
counterparties to meet the terms of their contracts. The counterparties to these contracts are major multinational commercial banks, and the
Company has not incurred and does not expect any losses as a result of counterparty defaults.
Supplier Concentration. Certain of the raw materials, components and equipment used by the Company in the manufacture of its
products are available from a sole supplier or a limited number of suppliers. Shortages could occur in these essential materials and components
due to an interruption of supply or increased demand in the industry. If the Company were unable to procure certain materials, components or
equipment at acceptable prices, it would be required to reduce its manufacturing operations, which could have a material adverse effect on its
results of operations. In addition, the Company has made prepayments to certain suppliers. Should these suppliers be unable to deliver on their
obligations or experience financial difficulty, the Company may not be able to recover these prepayments.
76