Food Lion 2012 Annual Report Download - page 144
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 144 of the 2012 Food Lion annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
142 // DELHAIZE GROUP FINANCIAL STATEMENTS’12
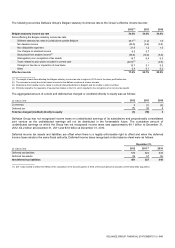
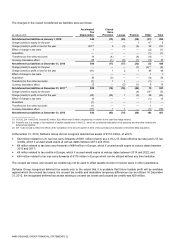
22. Income Taxes
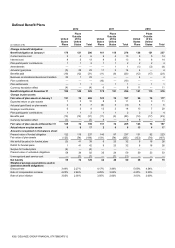
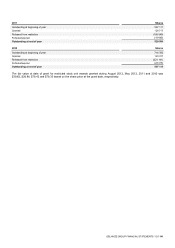
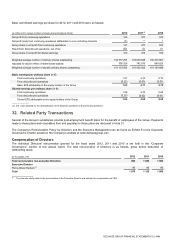
The major components of income tax expense for 2012, 2011 and 2010 were:
(in millions of €)
2012
2011
2010
Continuing operations
Current tax
110
103
17(1)
Taxes related to prior years recorded in the current year
(57)(2)
5
(2)
Utilization of previously unrecognized tax losses and tax credits
—
(1)
—
Other (current tax related)
2
—
—
Deferred tax
(62)
52
226(1)
Deferred taxes related to prior years recorded in the current year
6
(5)
3
Recognition of deferred tax on previously unrecognized tax losses and tax credits
(6)
(2)
—
Derecognition of previously recorded deferred tax assets
18
3
2
Deferred tax expense relating to changes in tax rates or the imposition of new taxes(3)
13
1
(1)
Total income tax expense from continuing operations
24
156
245
Total income tax expense from discontinued operations
(2)
—
—
Total income tax expense from continuing and discontinued operations
22
156
245
_______________
(1) In 2010, current tax decreased and deferred tax increased primarily due to a change in tax treatment of capital expenditures in the U.S., which are considered
deductible for tax purposes and therefore increase the deferred tax liabilities.
(2) Primarily related to the resolution of several tax matters in the U.S. which resulted in the recognition of an income tax benefit.
(3) In December 2012, the Serbian government enacted an increase in tax rate from 10 to 15%, effective as from January 1, 2013.
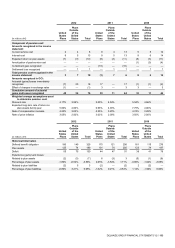
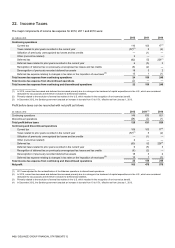
Profit before taxes can be reconciled with net profit as follows:
(in millions of €)
2012
2011(1)
2010
Continuing operations
149
633
821
Discontinued operations
(24)
(2)
(1)
Total profit before taxes
125
631
820
Continuing and discontinued operations
Current tax
109
103
17(2)
Taxes related to prior years recorded in the current year
(57)(3)
5
(2)
Utilization of previously unrecognized tax losses and tax credits
—
(1)
—
Other (current tax related)
2
—
—
Deferred tax
(63)
52
226(2)
Deferred taxes related to prior years recorded in the current year
6
(5)
3
Recognition of deferred tax on previously unrecognized tax losses and tax credits
(6)
(2)
—
Derecognition of previously recorded deferred tax assets
18
3
2
Deferred tax expense relating to changes in tax rates or the imposition of new taxes(4)
13
1
(1)
Total income tax expense from continuing and discontinued operations
22
156
245
Net profit
103
475
575
______________
(1) 2011 was adjusted for the reclassification of the Albanian operations to discontinued operations.
(2) In 2010, current tax decreased and deferred tax increased primarily due to a change in tax treatment of capital expenditures in the U.S., which are considered
deductible for tax purposes and therefore increase the deferred tax liabilities.
(3) Primarily related to the resolution of several tax matters in the U.S. which resulted in the recognition of an income tax benefit.
(4) In December 2012, the Serbian government enacted an increase in tax rate from 10 to 15%, effective as from January 1, 2013.