CarMax 2012 Annual Report Download - page 61
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 61 of the 2012 CarMax annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.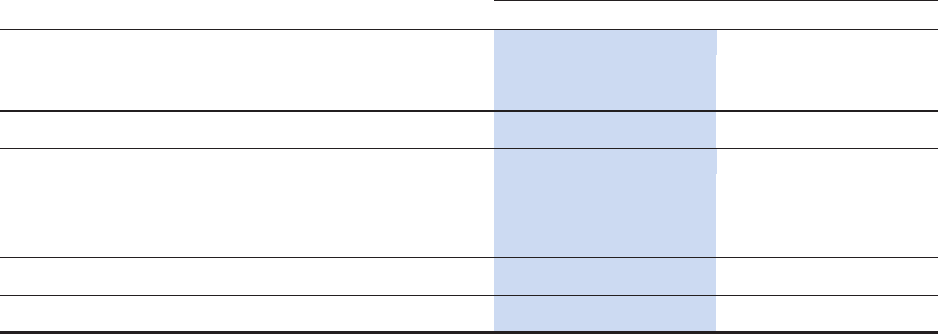
55
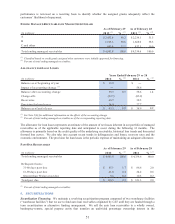
Credit risk is the exposure to nonperformance of another party to an agreement. We mitigate credit risk by dealing
with highly rated bank counterparties.
Cash Flow Hedges of Interest Rate Risk. Our objectives in using interest rate derivatives are to add stability to
interest expense, to manage our exposure to interest rate movements and to better match funding costs to the interest
received on the fixed-rate receivables being securitized. To accomplish these objectives, we primarily use interest
rate swaps. Interest rate swaps designated as cash flow hedges involve the receipt of variable amounts from a
counterparty in exchange for our making fixed-rate payments over the life of the agreements without exchange of
the underlying notional amount. These interest rate swaps are designated as cash flow hedges of forecasted interest
payments in anticipation of permanent funding in the term securitization market.
For derivatives that are designated and qualify as cash flow hedges, the effective portion of changes in the fair value
is initially recorded in accumulated other comprehensive loss (“AOCL”) and is subsequently reclassified into CAF
income in the period that the hedged forecasted transaction affects earnings. The ineffective portion of the change in
fair value of the derivatives is recognized directly in CAF income. Amounts reported in AOCL related to
derivatives will be reclassified to CAF income as interest expense is incurred on our future issuances of fixed-rate
debt. During the next 12 months, we estimate that an additional $12.5 million will be reclassified as a decrease to
CAF income.
As of February 29, 2012, we had interest rate swaps outstanding with a combined notional amount of $603.0 million
that were designated as cash flow hedges of interest rate risk.
Non-designated Hedges. Derivative instruments not designated as accounting hedges, including interest rate swaps
and interest rate caps, are not speculative. These instruments are used to limit risk for investors in the warehouse
facilities, to minimize the funding costs related to certain term securitization vehicles and to mitigate interest rate
risk associated with related financial instruments. Changes in the fair value of derivatives not designated as
accounting hedges are recorded directly in CAF income. Prior to March 1, 2010, substantially all of the changes in
the fair value of derivatives were offset by the changes in fair value of our retained interest in the related securitized
receivables, which were also recorded in CAF income. See Note 5 for additional information on retained interest.
As of February 29, 2012, we had interest rate swaps outstanding with a combined notional amount of $60.2 million
and interest rate caps outstanding with offsetting (asset and liability) notional amounts of $853.7 million that were
not designated as accounting hedges.
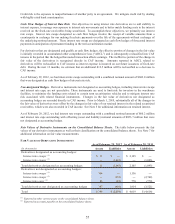
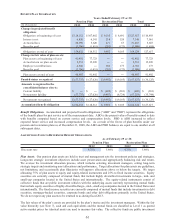
Fair Values of Derivative Instruments on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. The table below presents the fair
values of our derivative instruments as well as their classification on the consolidated balance sheets. See Note 7 for
additional information on fair value measurements.
FAIR VALUES OF DERIVATIVE INSTRUMENTS
(In thousands)
Derivatives designated as accounting hedges:
Interes t rate swaps (1) 11$ ʊ$ 2,105$ ʊ$
Interes t rate swaps (2) ʊ (1,643) ʊ (1,093)
Total derivatives designated as accounting hedges 11 (1,643) 2,105 (1,093)
Derivatives not designated as accounting hedges:
Interes t rate swaps (1) 304 ʊ 1,136 ʊ
Interes t rate swaps (2) ʊ (335) ʊ (2,742)
Interes t rate caps (1) 83 (81) 778 (779)
Total derivatives not designated as accounting hedges 387 (416) 1,914 (3,521)
Total 398$ (2,059)$ 4,019$ (4,614)$
Assets Liabilities
As of February 28, 2011
Assets Liabilities
As of February 29, 2012
(1) Reported in other current assets on the consolidated balance sheets.
(2) Reported in accounts payable on the consolidated balance sheets.