Entergy 2008 Annual Report Download - page 102
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 102 of the 2008 Entergy annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
100100
ENTERGY CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES 2008
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements continued
100
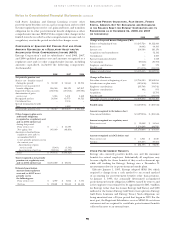
Other
In the second quarter 2008, Entergy sold its remaining interest in
Warren Power and realized a gain of $11.2 million ($6.9 million
net-of-tax) on the sale.
In the second quarter 2006, Entergy sold its remaining interest in
a power development project and realized a gain of $14.1 million
($8.6 million net-of-tax) on the sale.
In April 2006, Entergy sold the retail electric portion of the
Competitive Retail Services business operating in the ERCOT
region of Texas, realized an $11.1 million gain (net-of-tax) on the
sale, and now reports this portion of the business as a discontinued
operation.
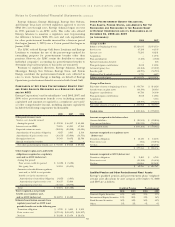
NOTE 16. RISK MANAGEMENT AND FAIR VALUES
MA R K E T A N D CO M M O D I T Y RI S K S
In the normal course of business, Entergy is exposed to a number
of market and commodity risks. Market risk is the potential loss
that Entergy may incur as a result of changes in the market or fair
value of a particular instrument or commodity. All financial and
commodity-related instruments, including derivatives, are subject
to market risk. Entergy is subject to a number of commodity and
market risks, including:
Type of Risk Affected Businesses
Power price risk Utility, Non-Utility Nuclear,
Non-Nuclear Wholesale Assets
Fuel price risk Utility, Non-Utility Nuclear,
Non-Nuclear Wholesale Assets
Foreign currency exchange rate risk Utility, Non-Utility Nuclear,
Non-Nuclear Wholesale Assets
Equity price and interest rate risk -
investments Utility, Non-Utility Nuclear
Entergy manages these risks through both contractual
arrangements and derivatives. Contractual risk management tools
include long-term power purchase and sales agreements and fuel
purchase agreements, capacity contracts, and tolling agreements.
Commodity and financial derivative risk management tools can
include natural gas and electricity futures, forwards, swaps, and
options; foreign currency forwards; and interest rate swaps. Entergy
enters into derivatives only to manage natural risks inherent in its
physical or financial assets or liabilities.
Entergy manages fuel price risk for its Louisiana jurisdictions
(Entergy Gulf States Louisiana, Entergy Louisiana, and Entergy
New Orleans) and Entergy Mississippi primarily through the
purchase of short-term swaps. These swaps are marked-to-market
with offsetting regulatory assets or liabilities. The notional volumes
of these swaps are based on a portion of projected annual purchases
of gas for electric generation and projected winter purchases for
gas distribution at Entergy Gulf States Louisiana and Entergy
New Orleans.
Entergy’s exposure to market risk is determined by a number of
factors, including the size, term, composition, and diversification
of positions held, as well as market volatility and liquidity. For
instruments such as options, the time period during which the
option may be exercised and the relationship between the current
market price of the underlying instrument and the option’s
contractual strike or exercise price also affects the level of market
risk. A significant factor influencing the overall level of market
risk to which Entergy is exposed is its use of hedging techniques
to mitigate such risk. Entergy manages market risk by actively
monitoring compliance with stated risk management policies as well
as monitoring the effectiveness of its hedging policies and strategies.
Entergy’s risk management policies limit the amount of total net
exposure and rolling net exposure during the stated periods. These
policies, including related risk limits, are regularly assessed to ensure
their appropriateness given Entergy’s objectives.
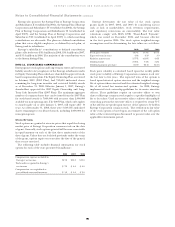
Hedging Derivatives
Entergy classifies substantially all of the following types of
derivative instruments held by its consolidated businesses as cash
flow hedges:
Instrument Business
Natural gas and electricity futures, Utility, Non-Utility Nuclear,
forwards, and options Non-Nuclear Wholesale Assets
Foreign currency forwards Utility, Non-Utility Nuclear
Based on market prices as of December 31, 2008, cash flow hedges
with net unrealized gains of approximately $79 million net-of-tax at
December 31, 2008 are expected to be reclassified from accumulated
other comprehensive income to operating revenues in 2009. The
actual amount reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive
income, however, could vary due to future changes in market prices.
Net losses totaling approximately $63 million were realized during
2008 on the maturity of cash flow hedges. Unrealized gains or losses
result from hedging power output at the Non-Utility Nuclear power
stations and foreign currency hedges related to Euro-denominated
nuclear fuel acquisitions. The related gains or losses from hedging
power are included in revenues when realized. The realized gains or
losses from foreign currency transactions are included in the cost of
capitalized fuel. The maximum length of time over which Entergy is
currently hedging the variability in future cash flows for forecasted
transactions at December 31, 2008 is approximately four years. The
ineffective portion of the change in the value of Entergy’s cash flow
hedges during 2008, 2007, and 2006 was insignificant.
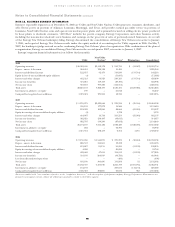
Fair Values
Effective January 1, 2008, Entergy and the Registrant Subsidiaries
adopted Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 157,
“Fair Value Measurements” (SFAS 157), which defines fair value,
establishes a framework for measuring fair value in GAAP, and
expands disclosures about fair value measurements. SFAS 157
generally does not require any new fair value measurements.
However, in some cases, the application of SFAS 157 in the future
may change Entergy’s and the Registrant Subsidiaries’ practice
for measuring and disclosing fair values under other accounting
pronouncements that require or permit fair value measurements.
SFAS 157 defines fair value as an exit price, or the price that would
be received to sell an asset or the amount that would be paid to
transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between knowledgeable
market participants at date of measurement. Entergy and the
Registrant Subsidiaries use assumptions or market input data that
market participants would use in pricing assets or liabilities at
fair value. The inputs can be readily observable, corroborated by
market data, or generally unobservable. Entergy and the Registrant
Subsidiaries endeavor to use the best available information to
determine fair value.