Toyota 2005 Annual Report Download - page 67
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 67 of the 2005 Toyota annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.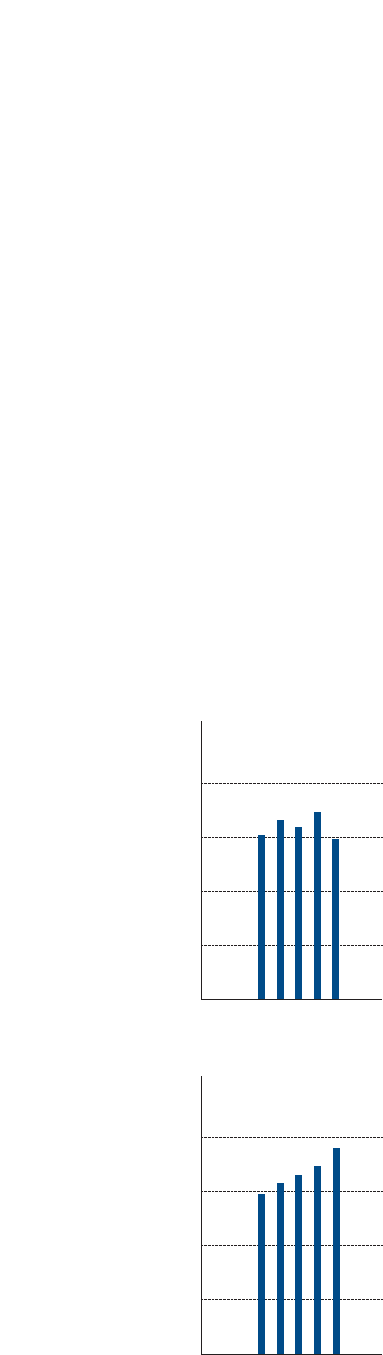
Based on currently available information, Toyota does not
expect environmental matters to have a material impact
on its financial position, results of operations, liquidity or
cash flows during fiscal 2006. However, there exists a sub-
stantial amount of uncertainty with respect to Toyota’s
obligations under current and future environment regula-
tions as described in “Information on the Company—
Business Overview—Governmental Regulations, Environment
and Safety Standards” in Toyota’s annual report on Form 20-F.
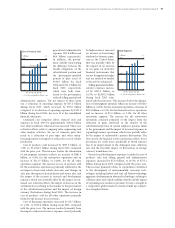
Cash and cash equivalents were ¥1,483.7 billion at
March 31, 2005. Most of Toyota’s cash and cash equi-
valents are held in Japanese yen and the U.S. dollars. In
addition, time deposits were ¥63.6 billion and marketable
securities were ¥543.1 billion at March 31, 2005.
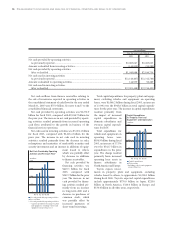
Liquid assets, which Toyota defines as cash and cash
equivalents, time deposits, marketable debt securities and
its investment in monetary
trust funds, increased dur-
ing fiscal 2005 by ¥353.8
billion, or 10.2%, to ¥3,810.0
billion.
Trade accounts and notes
receivable, net increased dur-
ing fiscal 2005 by ¥84.7
billion, or 5.5%, to ¥1,616.3
billion, reflecting the impact
of increased revenues and
the impact of the change in
foreign currency translation
rates.
Inventories increased during
fiscal 2005 by ¥223.4 billion,
or 20.6%, to ¥1,306.7 billion,
reflecting the impact of
increased volumes and the
impact of the change in
foreign currency translation
rates.
Total finance receivables,
net increased during fiscal
2005 by ¥1,135.1 billion, or
19.4%, to ¥6,987.0 billion.
The change resulted from
the increase in retail financ-
ings due to the increase in
vehicle unit sales, the
increase in wholesale and
other dealer loans, including
real estate loans and work-
ing capital financings pro-
vided to dealers and a decrease
in securitizations of finance receivables in finance subsi-
diaries in North America. These increases were partially
offset by the decrease in finance leases. As of March 31,
2005, finance receivables were geographically distributed
as follows: in North America 64.0%, in Japan 15.7%, in
Europe 10.3% and in all other markets 10.0%. Toyota
maintains programs to sell finance receivables through
special purpose entities and obtained proceeds from
securitization transactions, net of purchased and retained
interests totaling ¥48.9 billion during fiscal 2005.
Marketable securities and other securities investments,
including those included in current assets, increased during
fiscal 2005 by ¥556.8 billion, or 20.7%, to ¥3,247.2 billion,
primarily reflecting the increase of U.S. treasury notes held
by a manufacturing subsidiary in North America and
Japanese government bonds held by the parent company.
Property, plant and equipment increased during fiscal
2005 by ¥440.9 billion, or 8.2%, reflecting an increase in
capital expenditures and the impact of changes in foreign
currency translation rates, which was partially offset by the
depreciation charges during the year.
Accounts payable increased during fiscal 2005 by ¥147.4
billion, or 8.6%, reflecting the increased product volumes
and the impact of changes in foreign currency translation rates.
Accrued expenses increased during fiscal 2005 by ¥156.1
billion, or 13.8%, reflecting the increase in expenses due to
the expansion of the business.
Income taxes payable increased during fiscal 2005 by
¥40.3 billion, or 15.9%, principally as a result of the
increase in taxable income especially in subsidiaries in
North America and Asia.
Toyota’s total borrowings increased during fiscal 2005 by
¥986.1 billion, or 13.0%. Toyota’s short-term borrowings
consist of loans with a weighted-average fixed interest rate of
1.58% and commercial paper with a weighted-average fixed
interest rate of 2.81%. Short-term borrowings increased
during fiscal 2005 by ¥192.8 billion, or 8.8%, to ¥2,381.8
billion. Toyota’s long-term debt consists of unsecured and
secured loans, medium-term notes, unsecured notes and
long-term capital lease obligations ranging from 0.01% to
27.00%, with maturity dates ranging from 2005 to 2035.
Toyota’s long-term debt also consists of notes payable
related to securitized finance receivables structured as
collateralized borrowings. The current portion of long-term
debt increased during fiscal 2005 by ¥25.7 billion, or 2.3%,
to ¥1,150.9 billion and the non-current portion increased by
¥767.6 billion, or 18.1%, to ¥5,014.9 billion. The increase in
total borrowings reflects the expansion of the financial
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS >65
1,000
500
1,500
2,000
’01 ’02 ’03 ’04 ’05
0
Cash and Cash Equivalents
at End of Year
(¥ Billion)
FY
2,000
3,000
1,000
4,000
’01 ’02 ’03 ’04 ’05
0
Liquid Assets*
(¥ Billion)
FY
* Cash and cash equivalents, time
deposits, marketable debt
securities and its investment
in monetary trust funds