Red Lobster 2012 Annual Report Download - page 53
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 53 of the 2012 Red Lobster annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Darden
Darden Restaurants, Inc. 2012 Annual Report 49
` NOTE 10
DERIVATIVE INSTRUMENTS
AND HEDGING ACTIVITIES
We use financial and commodities derivatives to manage interest rate, equity-
based compensation and commodities pricing and foreign currency exchange
rate risks inherent in our business operations. By using these instruments, we
expose ourselves, from time to time, to credit risk and market risk. Credit risk is
the failure of the counterparty to perform under the terms of the derivative
contract. When the fair value of a derivative contract is positive, the counterparty
owes us, which creates credit risk for us. We minimize this credit risk by entering
into transactions with high-quality counterparties. We currently do not have any
provisions in our agreements with counterparties that would require either party
to hold or post collateral in the event that the market value of the related derivative
instrument exceeds a certain limit. As such, the maximum amount of loss due to
counterparty credit risk we would incur at May 27, 2012, if counterparties to the
derivative instruments failed completely to perform, would approximate the values
of derivative instruments currently recognized as assets in our consolidated balance
sheet. Market risk is the adverse effect on the value of a financial instrument that
results from a change in interest rates, commodity prices, or the market price of
our common stock. We minimize this market risk by establishing and monitoring
parameters that limit the types and degree of market risk that may be undertaken.
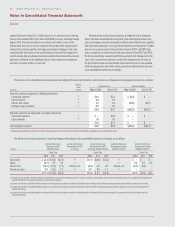
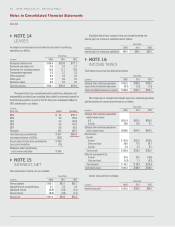
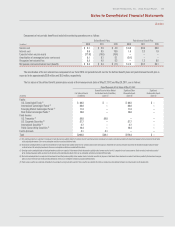
The notional values of our derivative contracts designated as hedging
instruments and derivative contracts not designated as hedging instruments
are as follows:
(in millions)
May 27, 2012 May 29, 2011
Derivative contracts designated as
hedging instruments:
Natural gas $ 1.1 $ 3.8
Other commodities 7.6 —
Foreign currency 19.4 20.7
Interest rate locks — 150.0
Interest rate swaps 550.0 350.0
Equity forwards 21.7 18.0
Derivative contracts not designated as
hedging instruments:
Natural gas $ — $ 7.7
Other commodities — 12.7
Equity forwards 50.0 24.0
We periodically enter into natural gas futures, swaps and option contracts
(collectively “natural gas contracts”) to reduce the risk of variability in cash flows
associated with fluctuations in the price of natural gas during the fiscal year. For
a certain portion of our natural gas purchases, changes in the price we pay for
natural gas is highly correlated with changes in the market price of natural gas.
For these natural gas purchases, we designate natural gas contracts as cash flow
hedging instruments. For the remaining portion of our natural gas purchases,
changes in the price we pay for natural gas are not highly correlated with changes
in the market price of natural gas, generally due to the timing of when changes
in the market prices are reflected in the price we pay. For these natural gas
purchases, we utilize natural gas contracts as economic hedges. Our natural gas
contracts currently extend through September 2012.
We periodically enter into other commodity futures and swaps (typically for
soybean oil, milk, diesel fuel, gasoline and butter) to reduce the risk of fluctuations
in the price we pay for these commodities, which are either used directly in our
restaurants (i.e., class III milk contracts for cheese and soybean oil for salad
dressing) or are components of the cost we pay for items used in our restaurants
(i.e., diesel fuel contracts to mitigate risk related to diesel fuel surcharges charged
by our distributors). Our other commodity futures and swap contracts currently
extend through May 2013.
We periodically enter into foreign currency forward contracts to reduce the
risk of fluctuations in exchange rates specifically related to forecasted transactions
or payments made in a foreign currency either for commodities and items used
directly in our restaurants or for forecasted payments of services. Our foreign
currency forward contracts currently extend through May 2013.
We entered into treasury-lock derivative instruments with $300.0 million of
notional value to hedge a portion of the risk of changes in the benchmark interest
rate prior to the issuance of the New Senior Notes in the second quarter of fiscal
2012, as changes in the benchmark interest rate would cause variability in our
forecasted interest payments. These derivative instruments were designated as
cash flow hedges. These instruments were settled at the issuance of the New
Senior Notes for a cumulative loss of $53.7 million. Of the cumulative loss,
$52.6 million was recorded in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss)
and will be reclassified into earnings as an adjustment to interest expense on the
New Senior Notes or similar debt as incurred.
We entered into forward-starting interest rate swap agreements with
$300.0 million of notional value to hedge a portion of the risk of changes in the
benchmark interest rate associated with the expected issuance of long-term debt
to refinance our $350.0 million 5.625 percent senior notes due October 2012, as
changes in the benchmark interest rate will cause variability in our forecasted
interest payments. These derivative instruments are designated as cash flow hedges.
We entered into interest rate swap agreements with $250.0 million of notional
value to limit the risk of changes in fair value of a portion of the $350.0 million
5.625 percent senior notes due October 2012 and a portion of the $400.0 million
4.500 percent senior notes due October 2021 attributable to changes in the
benchmark interest rate, between inception of the interest rate swap agreements
and maturity of the related debt. The swap agreements effectively swap the fixed
rate obligations for floating rate obligations, thereby mitigating changes in fair
value of the related debt prior to maturity. The swap agreements were designated
as fair value hedges of the related debt and met the requirements to be accounted
for under the short-cut method, resulting in no ineffectiveness in the hedging
relationship. During fiscal 2012, 2011 and 2010, $3.3 million, $3.6 million and
$3.4 million, respectively, was recorded as a reduction to interest expense
related to the net swap settlements.
We enter into equity forward contracts to hedge the risk of changes in
future cash flows associated with the unvested, unrecognized Darden stock
units. The equity forward contracts will be settled at the end of the vesting peri-
ods of their underlying Darden stock units, which range between four and five
years. The contracts were initially designated as cash flow hedges to the extent
the Darden stock units are unvested and, therefore, unrecognized as a liability in
our financial statements. As of May 27, 2012, we were party to equity forward