Pentax 2007 Annual Report Download - page 27
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 27 of the 2007 Pentax annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.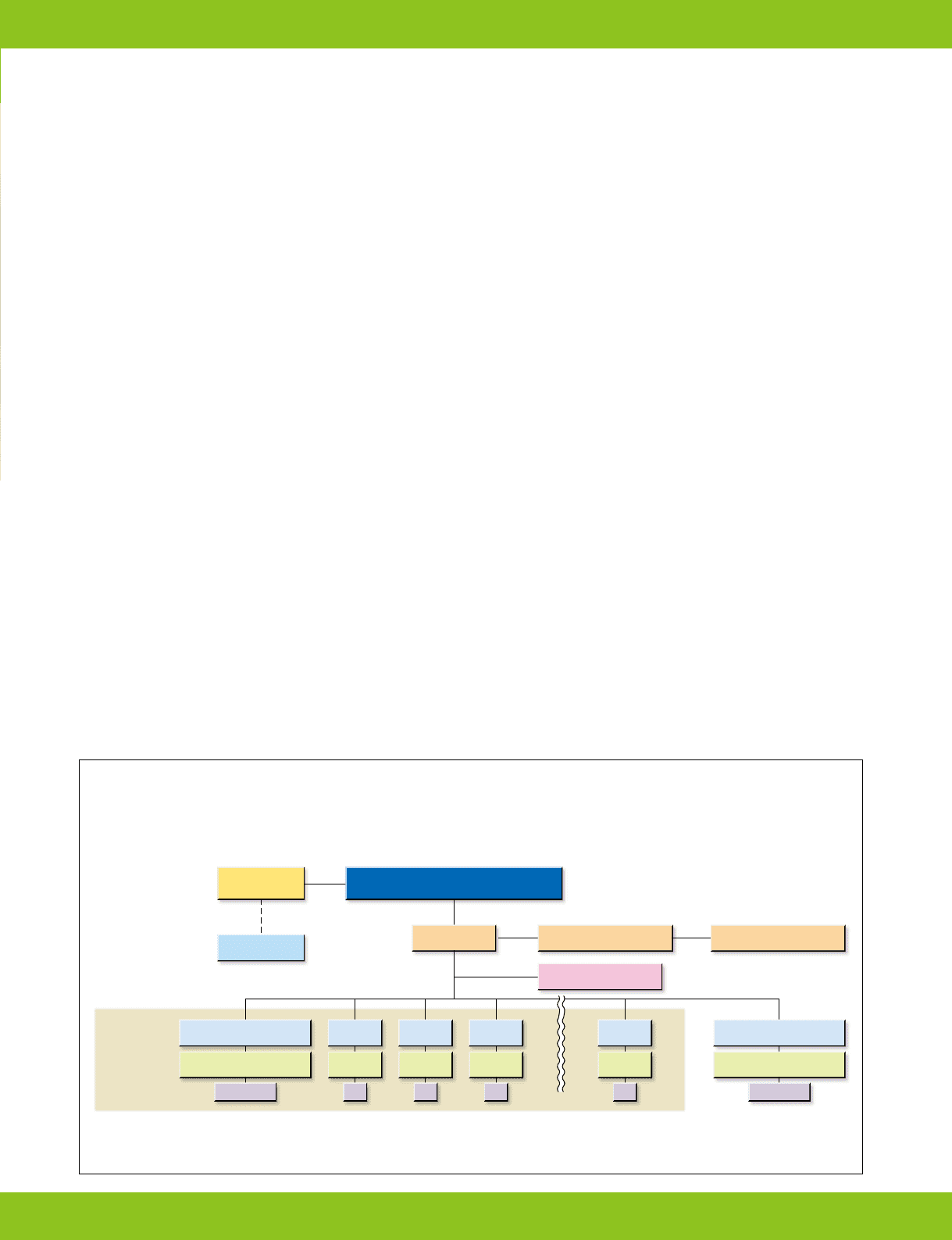
25
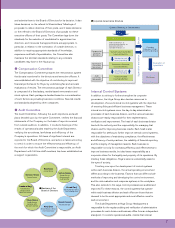
Aiming for the concrete realization of the Environmental Philosophy and Fundamental Environmental Principles, an Environmental Headquarters
headed by the CEO establishes and manages environmental protection systems and structures as the most senior body responsible for the
environment, and it oversees all of the Hoya Group’s environmental protection activities
●The Hoya Group’s Environmental Management Organization
General Manager of Hoya Group
Environmental Headquarters: CEO
Environmental
Headquarters
Audit Department
Environmental Protection
Officers
Environmental Protection
Committees
Audit Committee
Environmental Headquarters
Secretariat
Committee on Specific
Environmental Issues
Environmental Headquarters
Secretariat Council
Secretariat
Subsidiary Environmental
Protection Officers
Subsidiary Environmental
Protection Committees
Secretariat
3. Introduction of Environmental Management Systems (ISO 14001 Certification)
In October 1996, Hoya announced its intention to make its environmental management systems compliant with ISO 14001 certification
standards, and in December 1997 Hoya Lens Deutschland GmbH became the first in the Hoya Group to gain such certification. Since then,
Hoya has proceeded with efforts to gain certification for its plants, including overseas production bases, and a total of 35 Hoya group sites
(11 in Japan, 24 abroad) had been certified by the end of March 2007. The certification process is continuing.
●
● Efforts to reduce water consumption
Steps have been taken to limit the amount of water used. These
include promoting the re-use of factory waste water and the
introduction of automated water faucet control in washroom
hand basins.
● Steps taken to reduce waste disposal volumes
Resources have been devoted towards achieving reductions in
the volume of waste disposal. Steps taken have included
chemical recycling of polishing sludge as raw material for
concrete, and thermal recycling of discarded plastics
and chemicals.
● Efforts to reduce the volume of packaging materials used
Hoya has taken steps to reduce the volume of packaging
materials used, through such means as promoting the reuse of
cardboard packing boxes used to deliver products to clients,
and by broadening the scope of a changeover to
returnable containers.
● Steps taken to reduce chemical usage
Steps have been taken to reduce the amount of chemicals used
in production processes. These include a collaboration between
Japanese and overseas plants to switch from the use of
HCFC141b (1,1-dichloro-1-fluoroethane) to water for cleaning
processes, and a reduction in the amount of monomers
consumed through a change in the shape of gaskets used in the
production of eyeglass lenses.
Other steps taken have included controls for the amount of
substances used or emitted in production processes, and the
introduction of chemical substitutions, in response to various laws
and regulations, such as Japan’s Law Concerning Reporting, etc.
of Releases to the Environment of Specific Chemical Substances
and Promoting Improvements in Their Management.
● Improvements to waste water disposal
In February 2006, Hoya introduced a means of boosting the
removal of fluorine from factory waste water. The new method of
removal by crystal growth achieved a 50% reduction in fluorine
levels. This new system is notable in that the crystals to which
the fluorine has adhered (fluorine apatite) are valuable, saleable
items, and it also plays a part in reducing waste volumes.
● Emergency response measures
Hoya has produced procedural manuals setting out responses to
be instituted in an emergency at each of its plants. Should worst
come to worst, efforts would be made to limit to the smallest
extent possible any environmental effects outside the plant.
Steps have been taken to develop reliable countermeasures at
the facilities level also. These include, for example, the
introduction of oil/water separation equipment and oil leak
monitoring equipment to prevent any oil leak from
entering waterways.
Business
Divisions/
Factories
The top managers of each business division and each factory, in their roles as Senior Environmental Protection Officers, have overall responsibility for the management of
environmental protection activities in each division or factory under their management. A Secretariat assists the Environmental Protection Committee, which is presided over
by the Senior Environmental Protection Officer.