Kia 2003 Annual Report Download - page 59
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 59 of the 2003 Kia annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
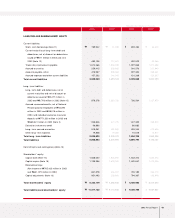
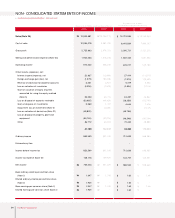
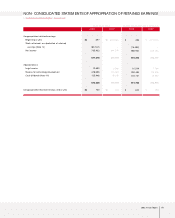
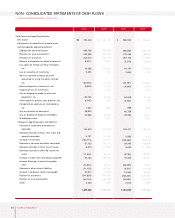
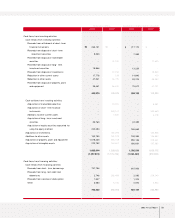
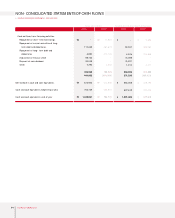
2003 Annual Report 59
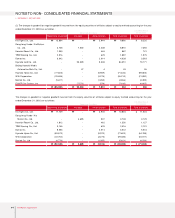
Derivative Instruments
All derivative instruments are accounted for at fair value with the valuation gain or loss recorded as an asset or liability. If the derivative
instrument is not part of a transaction qualifying as a hedge, the adjustment to fair value is reflected in current operations. The accounting for
derivative transactions that are part of a qualified hedge based both on the purpose of the transaction and on meeting the specified criteria for
hedge accounting differs depending on whether the transaction is a fair value hedge or a cash flow hedge. Fair value hedge accounting is
applied to a derivative instrument designated as hedging the exposure to changes in the fair value of an asset or a liability or a firm commitment
(hedged item) that is attributable to a particular risk. The gain or loss both on the hedging derivative instruments and on the hedged item
attributable to the hedged risk is reflected in current operations. Cash flow hedge accounting is applied to a derivative instrument designated as
hedging the exposure to variability in expected future cash flows of an asset or a liability or a forecasted transaction that is attributable to a
particular risk. The effective portion of gain or loss on a derivative instrument designated as a cash flow hedge is recorded as a capital
adjustment and the ineffective portion is recorded in current operations.
The effective portion of gain or loss recorded as a capital adjustment is reclassified to current earnings in the same period during which the
hedged forecasted transaction affects earnings. If the hedged transaction results in the acquisition of an asset or the incurrence of a liability, the
gain or loss in capital adjustment is added to or deducted from the asset or the liability.
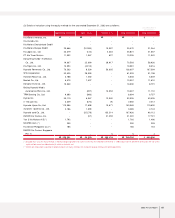
Accounting for Foreign Currency Transactions and Translation
The Company maintains its accounts in Korea won. Transactions in foreign currencies are recorded in Korean won based on the prevailing rates
of exchange on the transaction date. Monetary accounts with balances denominated in foreign currencies are recorded and reported in the
accompanying non-consolidated financial statements at the exchange rates prevailing at the balance sheet dates. The balances have been
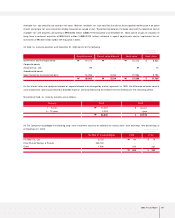
translated using the Bank of Korea Basic Rate, which was ₩1,197.80 and ₩1,200.40 to US$1.00 at December 31, 2003 and 2002, respectively,
and the translation loss and gain is reflected in current operations.
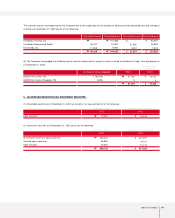
Income Tax Expense
The Company recognizes deferred income taxes. Accordingly, income tax expense is determined by adding or deducting the total income tax
and surtaxes to be paid for the current period and the changes in deferred income tax debits (credits). The difference between the income tax
expense and the amount of income tax shown in the current period’s tax return will be offset against the deferred income tax credits (debits),
which will occur in subsequent periods.
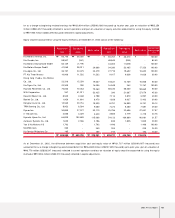
Earnings Per Share
Ordinary income per common share and earnings per common share are computed by dividing ordinary income (after deduction for tax effect)
and net income, respectively, by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding during period. The numbers of shares used in
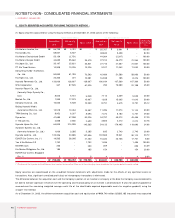
computing earnings per common share are 362,335,493 and 367,993,115 for the years ended December 31, 2003 and 2002, respectively.
Diluted ordinary income per share and diluted earnings per share are computed by dividing ordinary income and net income, after addition for
the effect of expenses related to diluted securities on net income, by the number of the weighted average number of common shares plus the
number of dilutive potential common shares. Stock options, which have dilutive effect, are regarded as being exercised at the beginning of the
period, and the number of dilutive potential common shares computed using treasury stock method (352,306 shares in 2003) is added to the
diluted number of common shares. Stock options granted to employees and directors as of December 31, 2002 have no dilutive effect on
ordinary income per share and earnings per share.