Kia 2003 Annual Report Download - page 55
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 55 of the 2003 Kia annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
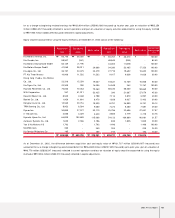
2003 Annual Report 55
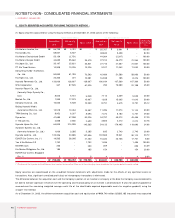
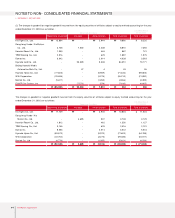
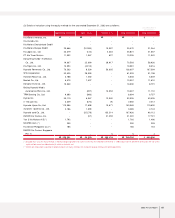
NOTES TO NON-CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
▶DECEMBER 31, 2003 AND 2002
1. THE COM PANY :
Kia Motors Corporation (the “Company”), incorporated in December 1944 under the laws of the Republic of Korea, is one of the leading motor
vehicle manufacturers in Korea producing and offering for sale a range of passenger cars, recreational vehicles and commercial vehicles both in
the domestic and the export markets. The Company owns and operates three principal automobile production bases: the Sohari factory, the
Hwasung factory and the Kwangju factory. The shares of the Company have been listed on the Korea Stock Exchange since 1973.
Overseas subsidiaries for export sales include Kia Motors America, Inc. (KMA) in America, Kia Canada, Inc. (KCI) in Canada, Kia Motors
Deutschland GmbH (KMD) and Kia Motors Europe GmbH (KME) in Germany.
As of December 31, 2003, the largest shareholder is Hyundai Motor Company, which holds 37.3 percent of the Company’s stock.
In common with other Asian countries, the economic environment in the Republic of Korea continues to be volatile. In addition, the Korean
government and the private sector continue to implement structural reforms to historical business practices including corporate governance.
The Company may be either directly or indirectly affected by these economic conditions and the reform program described above. The
accompanying financial statements reflect management’s assessment of the impact to date of the economic environment on the financial
position and results of operations of the Company. Actual results may differ materially from management’s current assessment.
2. SUM M ARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES :
Basis of Financial Statement Presentation
The Company maintains its official accounting records in Korean won and prepares statutory non-consolidated financial statements in the
Korean language (Hangul) in conformity with the accounting principles generally accepted in the Republic of Korea. Certain accounting
principles applied by the Company that conform with financial accounting standards and accounting principles in the Republic of Korea may not
conform with generally accepted accounting principles in other countries. Accordingly, these financial statements are intended for use by those
who are informed about Korean accounting principles and practices. The accompanying financial statements have been condensed, restructured
and translated into English (with certain expanded descriptions) from the Korean language financial statements. Certain information included in
the Korean language financial statements, but not required for a fair presentation of the Company's financial position, results of operations or
cash flows, is not presented in the accompanying financial statements.
The U.S. dollar amounts presented in these financial statements were computed by translating the Korean won into U.S. dollars based on the
Bank of Korea Basic Rate of ₩1,197.80 to US$1.00 at December 31, 2003, solely for the convenience of the reader. This convenience
translation into U.S. dollars should not be construed as a representation that the Korean won amounts have been, could have been, or could in
the future be, converted at this or any other rate of exchange.
Implementation of Statements of Korea Accounting Standards
The Korea Accounting Standards Board (KASB), a standard setting body of the Korea Accounting Institute (KAI), has issued Statements of Korea
Accounting Standards (“SKAS”) No. 1 to No. 13, to enhance the usefulness of accounting information and global convergence of the existing
Korea Financial Accounting Standards.
The Company prepared its non-consolidated financial statements as of December 31, 2003 in accordance with the existing Korea Financial
Accounting Standards and the SKAS No. 1-”Accounting Changes and Corrections of Errors”, SKAS No. 2-”Interim Financial Reporting”, No.
3-”Intangible Assets”, No. 4-”Revenue Recognition”, No. 5-”Tangible Assets”, No. 6-”Events Occurring after the Balance Sheet Date”, No.
7-”Capitalization of Financing Costs’, No. 8-”Investments in Securities” and No. 9-”Convertible Securities”. The Company has applied SKAS
No. 1, No. 6 and No. 7 since the year ended December 31, 2002 and did not adopt SKAS No. 10 through No. 13, which are effective for fiscal
year subsequent to December 31, 2003 ; however, early adoption is allowed.