Kia 2003 Annual Report Download - page 57
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 57 of the 2003 Kia annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
2003 Annual Report 57
Available-for-sale securities are those not classified either as held-to-maturity or trading securities. Trading securities are classified as short
term investment securities, whereas available-for-sale securities and held-to-maturity securities are classified as long-term investment
securities, except for those whose maturity dates or whose likelihood of being disposed of are within one year from the balance sheet date,
which are classified as short-term investment securities.
▶Valuation of Securities
Investments in securities are initially measured at cost, which consists of the market price of the consideration given to acquire them and
incidental expenses. If the market price of the consideration given is not available, the market prices of the securities purchased are used as the
basis for measurement. If neither the market price of the consideration given nor those of the acquired securities are available, the acquisition
cost is measured at the best estimates of its fair value.
After initial recognition, held-to-maturity securities are valued at amortized cost. The difference between their acquisition costs and face values
is amortized over the remaining term of the securities by applying the effective interest method and added to or subtracted from the acquisition
costs and interest income of the remaining period. Trading securities are valued at fair value, with unrealized gains or losses included in current
operations. Available-for-sales securities are also valued at fair value, with unrealized holding gains or losses recognized in capital adjustments,
until the securities are sold or if the securities are determined to be impaired and the lump-sum cumulative amount of capital adjustments are
reflected in current operations. However, available-for-sales securities that are not traded in an active market and whose fair value cannot be
reliably measured are valued at cost.
If the estimated recoverable amount of securities is less than the acquisition cost of equity securities or amortized cost of debt securities and any
objective evidence for such impairment loss exists, impairment loss is recognized in current operations in the period when it arises.
Equity Securities Accounted for Using the Equity M ethod
Equity securities held for investment in companies in which the Company is able to exercise significant influence over the operating and financial
policies of the investees are accounted for using the equity method. The Company’s share in the net income or net loss of investees is reflected
in current operations. Changes in the retained earnings, capital surplus or other capital accounts of investees are accounted for as an adjustment
to retained earnings or to capital adjustments.
Property, Plant and Equipment and Related Depreciation
Property, plant and equipment are stated at cost, except for assets revalued upward in accordance with the Asset Revaluation Law of Korea.
Routine maintenance and repairs are expensed as incurred. Expenditures that result in the enhancement of the value or extension of the useful
lives of the facilities involved are treated as additions to property, plant and equipment.
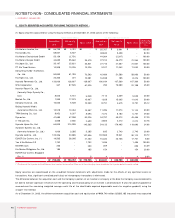
Depreciation is computed using the straight-line method based on the estimated useful lives of the assets as follows :
The Company charges all financing cost to current operations in accordance with SKAS No. 7 -“Capitalization of Financing Costs”. In addition,
the Company assesses possible recognition of impairment loss when there is an indication that expected future economic benefits of an asset is
considerably less than its carrying amount, as a result of technological obsolescence or rapid declines in market value. When it is determined that
an asset may have been impaired and that its estimated total future cash flows from continued use or disposal is less than its carrying amount,
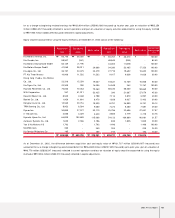
Useful lives (years)
Buildings and structures
Machinery and equipment
Tools, dies and moulds
Vehicles
Office equipment
20 ~ 40
15
5
5
5