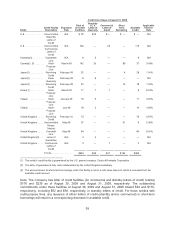
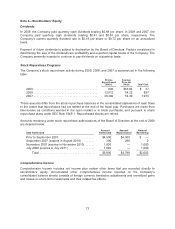
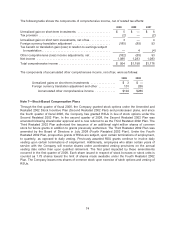
Costco 2009 Annual Report Download - page 68
Download and view the complete annual report
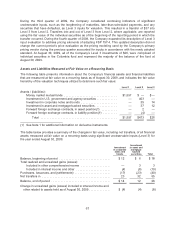
Please find page 68 of the 2009 Costco annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.SFAS 157 defines fair value as the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a
liability (an exit price) in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date.
SFAS 157 also establishes a fair value hierarchy, which requires an entity to maximize the use of
observable inputs when measuring fair value. The standard describes three levels of inputs:
Level 1: Quoted market prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities.
Level 2: Observable market-based inputs or unobservable inputs that are corroborated by market data.
Level 3: Significant unobservable inputs that are not corroborated by market data.
The following valuation techniques are used to measure fair value:
Level 1 primarily consists of financial instruments, such as money market mutual funds, whose value is
based on quoted market prices, such as quoted net asset values published by the fund as supported in
an active market, exchange-traded instruments and listed equities.
Level 2 includes assets and liabilities where quoted market prices are unobservable but observable
inputs other than Level 1 prices, such as quoted prices for similar assets or liabilities, or other inputs
that are observable or can be corroborated by observable market data for substantially the full term of
the assets or liabilities, could be obtained from data providers or pricing vendors. The Company’s
Level 2 assets and liabilities primarily include U.S. government and agency securities, investments in
corporate notes and bonds, asset and mortgage-backed securities, and forward foreign exchange
contracts. Valuation methodologies are based on “consensus pricing,” using market prices from a
variety of industry-standard independent data providers or pricing that considers various assumptions,
including time value, yield curve, volatility factors, credit spreads, default rates, loss severity, current
market and contractual prices for the underlying instruments or debt, broker and dealer quotes, as well
as other relevant economic measures. All are observable in the market or can be derived principally
from or corroborated by observable market data, for which the Company typically receives independent
external valuation information.
Level 3 is comprised of significant unobservable inputs for valuations from the Company’s independent
data and a primary pricing vendor that are also supported by little, infrequent, or no market activity.
Limited amounts of the Company’s investments, which comprise the majority of securities in the
Columbia fund that have not yet been sold or liquidated, are invested in asset and mortgage-backed
securities and corporate notes and bonds that are classified as Level 3 based upon management’s
assessment of the available inputs. Management considers indicators of significant unobservable
inputs such as the lengthening of maturities, later-than-scheduled payments, and any remaining
individual securities that have otherwise matured, as indicators of Level 3. Assets and liabilities are
considered Level 3 when their fair value inputs are unobservable, unavailable or management
concludes that even though there may be some observable inputs, an item should be classified as a
Level 3 based on other indicators of significant unobservable inputs, such as situations involving
limited market activity, where determination of fair value requires significant judgment or estimation.
The Company utilizes the services of a primary pricing vendor, which does not provide access to their
proprietary valuation models, inputs and assumptions. While the Company is not provided access to
proprietary models of the vendor, the Company reviewed and contrasts pricing received with other
pricing sources to ensure accuracy of each asset class for which prices are provided. The Company’s
review also included an examination of the underlying inputs and assumptions for a sample of
individual securities across asset classes, credit rating levels and various durations, a process that is
continually performed for each reporting period. In addition, the pricing vendor has an established
challenge process in place for all security valuations, which facilitates identification and resolution of
potentially erroneous prices. The Company believes that the prices received from the primary pricing
vendor are representative of exit prices in accordance with SFAS 157, as amended, and are classified
appropriately in the SFAS 157 hierarchy.
66