CVS 2009 Annual Report Download - page 65
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 65 of the 2009 CVS annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
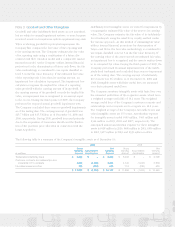
PENSION PLANS
The Company sponsors ten non-contributory defined benefit
pension plans that cover certain full-time employees, which
were frozen in prior periods. These plans are funded based on
actuarial calculations and applicable federal regulations. As of
December 31, 2009, the Company’s qualified defined benefit
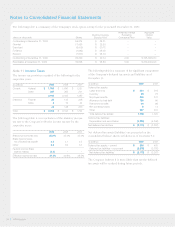
plans have a projected benefit obligation of $612 million and
plan assets of $372 million. As of December 31, 2008, the
Company’s qualified defined benefit plans had a projected
benefit obligation of $546 million and plan assets of $286 million.
Net periodic pension costs related to these qualified benefit
plans were $16 million, $9 million and $14 million in 2009,
2008 and 2007, respectively.
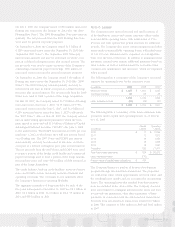
The discount rate is determined by examining the current
yields observed on the measurement date of fixed-interest,
high quality investments expected to be available during the
period to maturity of the related benefits on a plan by plan
basis. The discount rate for the plans was 6.0% in 2009
and 6.25% in 2008. The expected long-term rate of return is
determined by using the target allocation and historical returns
for each asset class on a plan by plan basis. The expected
long-term rate of return for all plans was 8.5% in 2009, 2008
and 2007.
The Company uses an investment strategy, which emphasizes
equities in order to produce higher expected returns, and in
the long run, lower expected expense and cash contribution
requirements. The pension plan assets allocation targets were
60% equity and 40% fixed income. As the result of a detailed
asset liability study performed during the fourth quarter of
2009, the pension plan asset allocation shall target 50% equity
and 50% fixed income during the upcoming year.
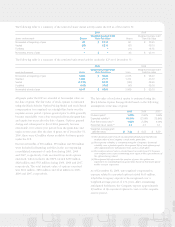
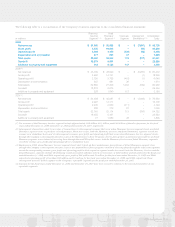
As of December 31, 2009, the Company’s qualified defined
benefit pension plan assets consisted of 64% equity, 35% fixed
income, and 1% money market securities of which 67% were
classified as Level 1 and 33% as Level 2 in the fair value
hierarchy. The Company’s qualified defined benefit pension
plan assets as of December 31, 2008 consisted of 62% equity,
37% fixed income, and 1% money market securities of which
69% were classified as Level 1 and 31% as Level 2 in the fair
value hierarchy.
The Company utilized a measurement date of December 31,
2009 to determine pension and other postretirement benefit
measurements. The Company contributed $50 million, $8 million
and $10 million to the pension plans during 2009, 2008 and
2007, respectively. The Company plans to make approximately
$55 million in contributions to the pension plans during 2010.
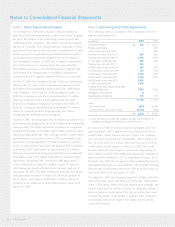
Note 9 Pension Plans and Other
Postretirement Benefits
During the fourth quarter of 2009, the Company adopted the
new disclosure requirements of ASC 715 Subtopic 20 – Defined
Benefit Plans (formerly FASB Staff Position (“FSP”) No. FAS
132(R)-1, “Employers’ Disclosures about Postretirement Benefit
Plan Assets”), which enhances the required disclosures about
plan assets in an employer’s defined benefit pension or other
postretirement plan, including investment allocations decisions,
inputs and valuations techniques used to measure the fair
value of plan assets and significant concentrations of risks
within plan assets.
DEFINED CONTRIBUTION PLANS
The Company sponsors voluntary 401(k) Savings Plans that
cover substantially all employees who meet plan eligibility
requirements. The Company makes matching contributions
consistent with the provisions of the plans. At the participant’s
option, account balances, including the Company’s matching
contribution, can be moved without restriction among various
investment options, including the Company’s common stock.
The Company also maintains a nonqualified, unfunded Deferred
Compensation Plan for certain key employees. This plan
provides participants the opportunity to defer portions of their
compensation and receive matching contributions that they
would have otherwise received under the 401(k) Savings
Plan if not for certain restrictions and limitations under the
Internal Revenue Code. The Company’s contribution under the
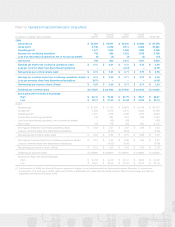
above defined contribution plans totaled $173 million in 2009,
$117 million in 2008 and $81 million in 2007. The Company
also sponsored an Employee Stock Ownership Plan. See
Note 8 for additional information about this plan.
OTHER POSTRETIREMENT BENEFITS
The Company provides postretirement health care and life
insurance benefits to certain retirees who meet eligibility
requirements. The Company’s funding policy is generally to
pay covered expenses as they are incurred. For retiree medical
plan accounting, the Company reviews external data and its
own historical trends for health care costs to determine the
health care cost trend rates. As of December 31, 2009 and
2008, the Company’s postretirement medical plans have an
accumulated postretirement benefit obligation of $17 million.
Net periodic benefit costs related to these postretirement
medical plans were approximately $1 million for 2009, 2008
and 2007.
2009 Annual Report 61