Acer 2009 Annual Report Download - page 57
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 57 of the 2009 Acer annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
(v) Long-term debt
Long-term debt is obtained at oating interest rates which are calculated based on the prevailing market
rate adjusted by the Company’s credit spread. The carrying value of long-term debt approximates the
market value.
(vi) Derivative nancial instruments
The fair values of derivative financial instruments are estimated using a valuation technique, with
estimates and assumptions consistent with those made by market participants and are readily available to
the Consolidated Companies.
(c) For the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2009, valuation gain on nancial assets and liabilities using
a valuation technique amounted to NT$989,905 and NT$1,293,844, respectively.
(d) Disclosure of nancial risks
(i) Market risk
Open-end mutual funds and publicly traded stocks held by the Consolidated Companies classified as
“available-for-sale financial assets” are valued by fair value. Therefore, the Consolidated Companies
were exposed to the risk of price uctuation in the securities market.
The Consolidated Companies engaged in purchase and sale transactions which are denominated in
US dollars and Euros, respectively. Hence, the Consolidated Companies entered into foreign currency
forward contracts, foreign currency options, foreign exchange swap and cross currency swap for hedging
purposes. The lengths and amounts of aforementioned derivative transactions were in line with the
settlement date of the Consolidated Companies’ recorded foreign currency assets and liabilities and future
cash ows. Gains or losses from these hedging derivatives are expected to substantially offset those from
the hedged assets or liabilities. Therefore, management believes that market risk related to the changes in
exchange rates was not signicant.
(ii) Credit risk
The Consolidated Companies’ credit risk is mainly from potential breach of contract by the counter-
party associated with cash, equity investment, and derivative transactions. In order to control its
exposure to the credit risk of each nancial institution, the Consolidated Companies maintain cash with
various nancial institutions and hold equity investments in the form of mutual funds and stocks issued
by companies with high credit quality. As a result, the concentration of credit risks related to cash and
equity investments is not signicant. Furthermore, the banks undertaking the derivative transactions are
reputable nancial institutions; therefore, the exposure related to the potential default by those counter-
parties is not considered signicant.
The Consolidated Companies primarily sell and market the multi-branded IT products to a large
number of customers in different geographic areas. As a result, the Consolidated Companies have no
signicant concentrations of credit risk, and in order to lower the credit risk, the Consolidated Companies
continuously evaluate the credit quality of their customers.
(iii) Liquidity risk
The Consolidated Companies’ capital and operating funds are sufcient to fulll their contract payment
obligations. Therefore, management believes that there is no signicant liquidity risk.
The available-for-sale nancial assets held by the Consolidated Companies are equity securities and mutual
funds, which are publicly traded and can be liquidated quickly at a price close to the fair market value.
In contrast, the financial assets carried at cost are not publicly traded and are exposed to liquidity risk.
The Consolidated Companies’ derivative nancial instruments are intended to hedge the exchange rate
risk resulting from assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currency and cash ows resulting from
anticipated transactions in foreign currency. The lengths of the contracts are in line with the payment date
of the Consolidated Companies’ assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currency and the anticipated
cash ows. At the maturity date of the derivative contract, the Consolidated Companies will settle these
contracts using the foreign currencies arising from the hedged assets and liabilities denominated in
foreign currency, and therefore, the liquidity risk is not signicant.
(iv) Cash ow risk related to the uctuation of interest rates
The Consolidated Companies’ short-term borrowings and long-term debt carried oating interest rates.
As a result, the effective rate changes along with the uctuation of the market interest rates and thereby
inuences the Consolidated Companies’ future cash ow. If the market interest rate increases by 1%, cash
outows in respect of these interest payments would increase by approximately NT$129,199 per annum.
5. Transactions with Related Parties
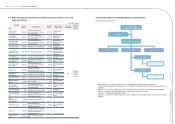
(1) Names and relationships of related parties with the Consolidated Companies
Name Relationship with the Company
Wistron Corporation (“Wistron”) Investee of the Company accounted for by equity method
Cowin Worldwide Corporation (“COWIN”) Subsidiary of Wistron
Bluechip Infotech Pty Ltd. (“SAL”) Investee of the Consolidated Companies accounted for by
equity method
e-Life Mall Corp. (“eLIFE”) Investee of the Company accounted for by equity method
iD Softcapital Inc. Its chairman is one of the Company’s supervisors
Directors, supervisors, chief executive ofcers and vice presidents The Consolidated Companies’ executive ofcers
(2) Signicant transactions with related parties as of and for the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2009 were as
follows:
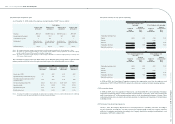
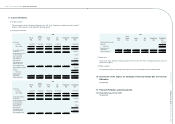
(a) Net sales and related notes and accounts receivable
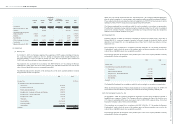
(i) Net sales to:
2008 2009
NT$ NT$ US$
SAL 758,797 768,379 23,989
eLIFE 885,662 690,738 21,566
COWIN 462,430 - -
Other (individually less than 5%) 114,486 77,605 2,423
2,221,375 1,536,722 47,978
The sales prices and payment terms to related parties were not significantly different from those of sales
to non-related parties.
Acer Incorporated 2009 Annual Report
108.
Acer Incorporated 2009 Annual Report
109. Financial Standing