Acer 2009 Annual Report Download - page 39
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 39 of the 2009 Acer annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
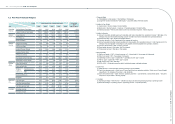
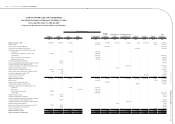
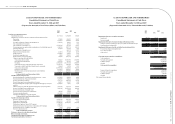
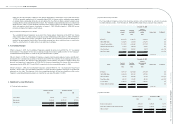
(4) Classication of current and non-current assets and liabilities
Cash or cash equivalents, and assets that will be held primarily for the purpose of being traded or are expected
to be realized within 12 months after the balance sheet date are classied as current assets; all other assets are
classied as non-current.
Liabilities that will be held primarily for the purpose of being traded or are expected to be settled within 12
months after the balance sheet date are classied as current liabilities; all other liabilities are classied as non-
current.
(5) Cash and cash equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents consist of cash on hand, cash in banks, miscellaneous petty cash, and other highly
liquid investments which do not have a significant level of market or credit risk from potential interest rate
changes.
(6) Allowance for doubtful accounts
Allowance for doubtful accounts is provided based on the collectibility, aging and quality analysis of notes and
accounts receivable.
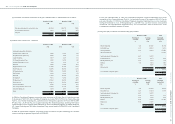
(7) Inventories
Effective January 1, 2009, the Consolidated Companies adopted the newly revised Republic of China Statement
of Financial Accounting Standards (SFAS) No. 10 “Accounting for Inventories”. Under this revised accounting
principle, the cost of inventories comprises all costs of purchase and other costs incurred in bringing the
inventories to their present location and condition. Inventories are measured individually at the lower of cost and
net realizable value. Net realizable value is determined based on the estimated selling price in the ordinary course
of business, less all estimated costs of completion and selling expenses. Costs of inventory are determined using
the weighted-average method.
Prior to January 1, 2009, inventories for the Acer brand information technology business group were stated at the
lower of weighted-average cost or market value. Market value represents net realizable value. Any write-down
was made based on the aggregate amount of inventories.
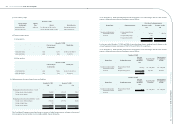
(8) Financial instruments
The Consolidated Companies adopted transaction-date accounting for nancial instrument transactions. At initial
recognition, financial instruments are evaluated at fair value plus, in the case of a financial instrument not at
fair value through prot or loss, transaction costs that are directly attributable to the acquisition or issue of the
financial instrument. Subsequent to initial recognition, financial instruments are classified into the following
categories in accordance with the purpose of holding or issuing of such nancial instruments:
(a) Financial assets/liabilities at fair value through prot or loss
An instrument is classied as at fair value through prot or loss if it is held for trading or is designated as
such upon initial recognition. Derivatives that do not meet the criteria for hedge accounting are classied as
nancial assets or liabilities at fair value through prot or loss. Financial instruments at fair value through
prot or loss are measured at fair value, and changes therein are recognized in prot or loss.
(b) Hedging derivative nancial assets / liabilities
Hedging derivative financial assets / liabilities represent derivatives that are intended to hedge the risk of
changes in exchange rates resulting from operating activities denominated in foreign currency and meet the
criteria for hedge accounting.
(c) Available-for-sale nancial assets
Available-for-sale nancial assets are measured at fair value and changes therein, other than impairment losses
and foreign exchange gains and losses on available-for-sale monetary items, are recognized in a separate
line item in stockholders’ equity. When an investment is derecognized, the cumulative unrealized gain or
loss recognized in equity is transferred to prot or loss. If there is objective evidence which indicates that a
nancial asset is impaired, a loss is recognized in prot or loss. If, in a subsequent period, events or changes
in circumstances indicate that the amount of impairment loss decreases, reversal of a previously recognized
impairment loss for equity securities is charged to equity; while for debt securities, the reversal is allowed
through prot or loss provided that the decrease is clearly attributable to an event which occurred after the
impairment loss was recognized.
(d) Financial assets carried at cost
Equity investments whose fair value cannot be reliably measured are carried at original cost. If there is
objective evidence which indicates that an equity investment is impaired, a loss is recognized. A subsequent
reversal of such impairment loss is prohibited.
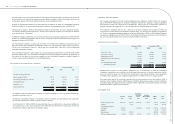
(9) Derivative nancial instruments and hedging activities
Hedge accounting recognizes the offsetting effects on prot or loss of changes in the fair values of the hedging
instrument and the hedged item. The designated hedging instruments that conform to the criteria for hedge
accounting are accounted for as follows:
(a) Fair value hedges
Changes in the fair value of a hedging instrument designated as a fair value hedge are recognized in prot
or loss. The hedged item is also stated at fair value in respect of the risk being hedged, with any gain or loss
being recognized in prot or loss.
(b) Cash ow hedges
Changes in the fair value of a hedging instrument designated as a cash ow hedge are recognized directly in
equity. If a hedge of a forecasted transaction subsequently results in the recognition of an asset or a liability,
then the amount recognized in equity is reclassied into prot or loss in the same period or periods during
which the asset acquired or liability assumed affects prot or loss.
(10) Noncurrent assets held for sale and discontinued operation
Noncurrent assets and groups of assets and liabilities which comprise disposal groups are classified as held
for sale when the assets are available for immediate sale in their present condition subject only to terms that
are usual and customary for sales of such assets (or disposal groups), and their sale within one year is highly
probable.Noncurrent assets or disposal groups classified as held for sale are measured at the lower of their
book value or fair value less costs to sell, and ceased to be depreciated or amortized. Noncurrent assets or
disposal groups classied as held for sale are shown separately and excluded from the individual line items of
the consolidated balance sheets. Interest and other expenses attributable to the liabilities of a disposal group
classied as held for sale are continued to be recognized.
An impairment loss is recognized for any initial or subsequent write-down of the assets (or disposal groups) to
fair value less costs to sell in the consolidated statements of income. A gain from any subsequent increase in
fair value less costs to sell of an asset (or a disposal group) is recognized, but not in excess of the cumulative
impairment loss that has been recognized.
A discontinued operation is a component of an entity that either has been disposed of or is classied as held
for sale. A component of an entity comprises operations and cash ows that can be distinguished clearly, both
Acer Incorporated 2009 Annual Report
72.
Acer Incorporated 2009 Annual Report
73. Financial Standing