Boeing 2014 Annual Report Download - page 82
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 82 of the 2014 Boeing annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
70
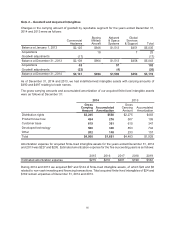
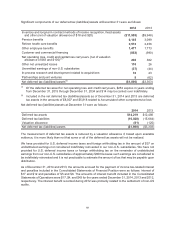
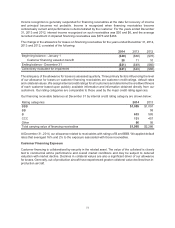
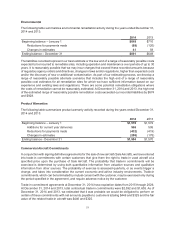
A reconciliation of the beginning and ending amount of unrecognized tax benefits is as follows:
2014 2013 2012
Unrecognized tax benefits – January 1 $1,141 $1,055 $939
Gross increases – tax positions in prior periods 403 10 55
Gross decreases – tax positions in prior periods (251) (125) (20)
Gross increases – current-period tax positions 217 202 83
Gross decreases – current-period tax positions (1) (1)
Settlements (197) (1)
Lapse of statute of limitations (1)
Unrecognized tax benefits – December 31 $1,312 $1,141 $1,055
As of December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, the total amount of unrecognized tax benefits was $1,312,
$1,141 and $1,055, respectively, of which $1,180, $1,018 and $945 would affect the effective tax rate, if
recognized. As of December 31, 2014, these amounts are primarily associated with U.S. federal tax issues
such as the amount of research tax credits claimed, the domestic production activities deductions claimed,
tax basis adjustments and U.S. taxation of foreign earnings. Also included in these amounts are accruals
for domestic state tax issues such as the allocation of income among various state tax jurisdictions and
the amount of state tax credits claimed.
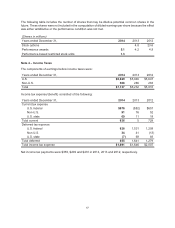
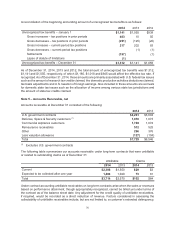
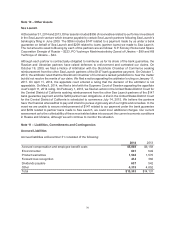
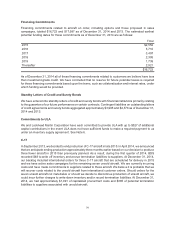
Note 5 – Accounts Receivable, net
Accounts receivable at December 31 consisted of the following:
2014 2013
U.S. government contracts $4,281 $3,604
Defense, Space & Security customers (1) 1,018 1,073
Commercial Airplanes customers 1,749 1,072
Reinsurance receivables 512 525
Other 296 376
Less valuation allowance (127) (104)
Total $7,729 $6,546
(1) Excludes U.S. government contracts
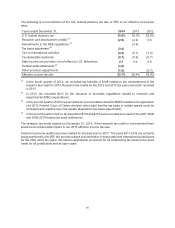
The following table summarizes our accounts receivable under long-term contracts that were unbillable
or related to outstanding claims as of December 31:
Unbillable Claims
2014 2013 2014 2013
Current $2,306 $1,550 $29 $3
Expected to be collected after one year 1,408 1,020 73 61
Total $3,714 $2,570 $102 $64
Under contract accounting unbillable receivables on long-term contracts arise when the sales or revenues
based on performance attainment, though appropriately recognized, cannot be billed yet under terms of
the contract as of the balance sheet date. Any adjustment for the credit quality of unbillable receivables,
if required, would be recorded as a direct reduction of revenue. Factors considered in assessing the
collectability of unbillable receivables include, but are not limited to, a customer’s extended delinquency,