Symantec 2003 Annual Report Download - page 51
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 51 of the 2003 Symantec annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Symantec 2003 49
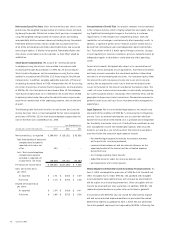
investments, previously serving as collateral for our synthetic lease
arrangements, no longer existed as of March 31, 2003, because we exer-
cised our option to purchase the related four facilities during the March
2003 quarter.
Trade Accounts Receivable Trade accounts receivable are recorded
at the invoiced amount and are not interest bearing. We maintain an
allowance for doubtful accounts to reserve for potentially uncollectible
trade receivables. We also review our trade receivables by aging cate-
gory to identify specific customers with known disputes or collectibility
issues. We exercise judgment when determining the adequacy of these
reserves as we evaluate historical bad debt trends, general economic
conditions in the U.S. and internationally, and changes in customer
financial conditions.
Equity Investments We have equity investments in privately held
companies for business and strategic purposes. These investments are
included in other long-term assets and are accounted for under the cost
method as we do not have significant influence over the investee. Under
the cost method, the investment is recorded at its initial cost and is peri-
odically reviewed for impairment. We regularly review our investment’s
actual and forecasted operating results, financial position and liquidity,
and business and industry factors in assessing whether a decline in
value of an equity investment has occurred that is other than temporary.
When such a decline in value is identified, the fair value of the equity
investment is estimated based on the preceding factors and an impair-
ment loss is recognized in other expense, net.
Derivative Financial Instruments We utilize some natural hedging to
mitigate our foreign currency exposures and we manage certain residual
exposures through the use of one-month forward foreign exchange
contracts. We enter into forward foreign exchange contracts with high-
quality financial institutions primarily to minimize currency exchange
risks associated with certain balance sheet positions. Gains and losses
on the contracts are included in other expense, net in the period that
gains and losses on the underlying transactions are recognized, and
generally offset. The fair value of forward foreign exchange contracts
approximates cost due to the short maturity periods.
Inventories Inventories are valued at the lower of cost or market. Cost
is principally determined using currently adjusted standards, which
approximate actual cost on a first-in, first-out basis. Inventory consists
of raw materials and finished goods.
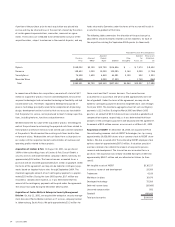
Property, Equipment and Leasehold Improvements Property, equip-
ment and leasehold improvements are stated at cost, net of accumu-
lated depreciation and amortization. Depreciation and amortization is
provided on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful lives of the
respective assets as follows:
•computer hardware and software – three to five years;
•office furniture and equipment – three to five years;
•leasehold improvements – the shorter of the lease term or
seven years; and
•buildings – twenty five to thirty years.
Acquired Product Rights Acquired product rights are comprised of
purchased product rights, technologies, databases and revenue related
order backlog and contracts from acquired companies. Acquired product
rights are stated at cost less accumulated amortization. Amortization of
acquired product rights is provided on a straight-line basis over the esti-
mated useful lives of the respective assets, generally one to five years,
and is included in cost of revenues or income, net of expense, from
sale of technologies and product lines. On April 1, 2002, we adopted
Statement of Financial Standards, or SFAS, No. 142, Goodwill and Other
Intangibles. As a result, the net balance of workforce-in-place, that was
previously included in acquired product rights, was reclassified to good-
will and was no longer amortized, but subjected to an annual impair-
ment test.
Goodwill Goodwill is recorded through acquisitions. For acquisitions
completed prior to July 1, 2001, goodwill was stated at cost less accu-
mulated amortization through March 31, 2002. Amortization in each
case was provided on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful life
of the respective goodwill, generally four to five years, and was included
in operating expenses. On April 1, 2002, we ceased the amortization
of goodwill, in accordance with SFAS No. 142, and will test goodwill
annually for impairment or more frequently if events and circumstances
warrant.
Long-Lived and Intangible Assets On April 1, 2002, we adopted SFAS
No. 144, Accounting for Impairment or Disposal of Long-Lived Assets.
SFAS No. 144 requires that long-lived and intangible assets, including
property, equipment, leasehold improvements and acquired product
rights, be evaluated for impairment whenever events or changes in cir-
cumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not be
recoverable. An impairment loss would be recognized when the sum of
the undiscounted future net cash flows expected to result from the use
of the asset and its eventual disposition is less than its carrying amount.
Such impairment loss would be measured as the difference between the
carrying amount of the asset and its fair value. Assets to be disposed
of would be separately presented in the balance sheet and reported at
the lower of the carrying amount or fair value less costs to sell, and no
longer depreciated. The assets and liabilities of a disposal group classi-
fied as held for sale would be presented separately in the appropriate
asset and liability sections of the balance sheet. The adoption of this
standard did not have an effect on our financial position or our operat-
ing results.
Income Taxes The provision for income taxes is computed using the lia-
bility method, under which deferred tax assets and liabilities are recog-
nized for the expected future tax consequences of temporary differences
between the financial reporting and tax bases of assets and liabilities.
Deferred tax assets are reduced by a valuation allowance when it is more
likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets will not
be realized.