Square Enix 2004 Annual Report Download - page 57
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 57 of the 2004 Square Enix annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
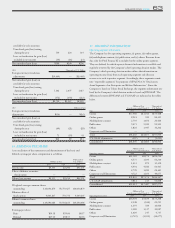
SQUARE ENIX 2004 55
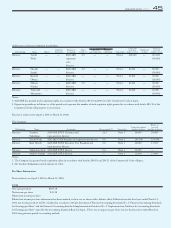
mates fair value because of their short maturity. Investments in marketable
securities are stated at their fair value based on quoted market prices.
Investments in non-marketable securities for which there are no quoted
market price are stated at cost because reasonable estimates of their fair
value could not be made without incurring excessive costs and it was not
practicable to estimate their fair value of common stock representing cer-
tain closely held companies. The carrying amount of the Company’s lines
of credit approximates fair value because the interest rates of the lines of
credit are based on floating rates identified by reference to market rates
Fair value estimates are made at a specific point in time, based on rele-
vant market information and information about the financial instruments.
These estimates are subjective in nature and involve uncertainties and mat-
ters of significant judgment and therefore cannot be determined with pre-
cision. Change in assumption could significantly affect the estimates
Inventories
Inventories are stated at the lower of cost or market. The Company peri-
odically evaluates the carrying value of its inventories and makes adjust-
ments as necessary. Cost is determined by the monthly average method for
finished goods, merchandise and work in progress, by the last purchase
price method for other supplies.
Software Development Costs
The Company applies Statement of Financial Accounting Standards
("SFAS") No.86, "Accounting for the Cost of Computer Software to be
Sold, Leased, or Otherwise Marketed", pursuant to which, the Company
capitalizes internal software development cost, as well as content cost, sub-
sequent to establishment of technological feasibility of a certain video game
software. Capitalized software development costs on the accompanying
consolidated balance sheets includes the payment to the outside indepen-
dent contactor as well as costs associated with internal development of the
video game product. Software development costs are amortized as a com-
ponent of "Cost of sales" over the expected life of each video game prod-
uct, starting from its initial delivery to the market. The Company continu-
ally evaluates the recoverability of capitalized software costs and will charge
to earnings any amounts that are deemed unrecoverable or for projects that
it will abandon.
Property and Equipment
Depreciation of property and equipment is computed on the declining-bal-
ance method for the Company and domestic subsidiaries, and the straight-
line method for foreign subsidiaries over the estimated useful lives of the
assets, ranging from 3 to 50 years for buildings and 3 to 20 years for
machinery and equipment. The cost of additions and betterments are capi-
talized, and repairs and maintenance costs are charged to earnings in the
periods incurred. When depreciable assets are retired or sold, the cost and
related allowances for depreciation are removed from the accounts and the
gain or loss is recognized.
Intangible Assets
Intangible assets consist of identifiable intangibles and the remaining excess
purchase price paid over identified intangible and tangible net assets of
acquired companies (goodwill). The Company applies the provisions of
SFAS No.141, "Business Combinations" in its entirety and SFAS No.141
requires all business combinations be accounted for using the purchase
method of accounting and that certain intangible assets acquired in a busi-
ness combination shall be recognized as assets apart from goodwill. SFAS
No.142, "Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets" addresses the recognition
and measurement of goodwill and other intangible assets subsequent to
their acquisition. SFAS No.142 provides that intangible assets with finite
useful lives be amortized and that intangible assets with indefinite lives and
goodwill not be amortized but tested for impairment annually.
SFAS No.142 requires an annual test for impairment of goodwill, and
between annual tests if events occur or circumstances change that would
more likely than not reduce the fair value of a reporting unit below its car-
rying amount. In assessing potential impairment of goodwill, the Company
determines the implied fair value of each reporting unit using discounted
cash flow analysis and compares such values to the respective reporting
unit’s carrying amount. The Company performs its annual test for indica-
tion of goodwill impairment in the fourth quarter of each fiscal year.
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets
The Company evaluates its long-lived assets for impairment as events or
changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of such assets
may not be fully recoverable. The Company evaluates the recoverability of
long-lived assets by measuring the carrying amount of the assets against the
estimated undiscounted future cash flows associated with them. At the time
such evaluations indicate that the future undiscounted cash flows of certain
long-lived assets are not sufficient to recover the carrying value of such
assets, the assets are adjusted to their fair values
Investment Securities
The Company invests in equity securities and bonds, and has classified its
investment securities as available-for-sale and held-to-maturity, in accor-
dance with SFAS No.115 "Accounting for Certain Investments in Debt
and Equity Securities." Investment securities designated as available-for-
sale, whose fair values are readily determinable, are carried at fair value
with unrealized gains or losses included as a component of accumulated
other comprehensive income, net of applicable taxes. Investment securities
that are expected to be held-to-maturity are carried at amortized cost.
Individual securities classified as either available-for-sale or held-to-matu-
rity are reduced to net realizable value by a charge to income for other than
temporary declines in fair value. Realized gains and losses are determined
on the moving average cost method and are reflected in income.
Income Taxes
The Company recognizes deferred taxes using the asset and liability
method. Under the asset and liability method, deferred income taxes are